Geotextile Road Fabric: A Complete Guide to Road Construction Reinforcement
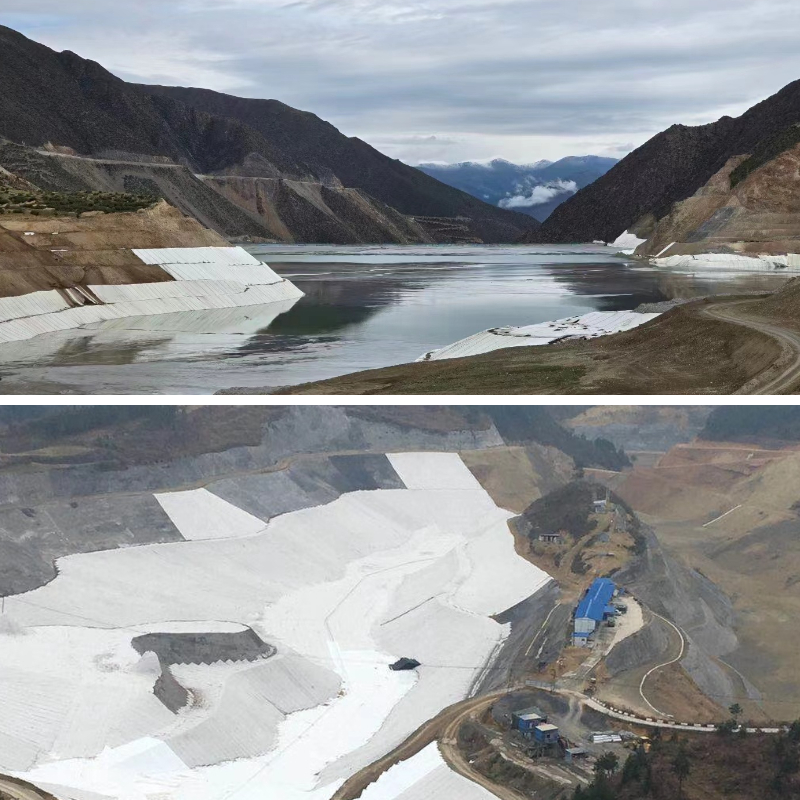
Geotextile street cloth has revolutionized street construction, presenting a inexpensive and long-lasting answer to improve soil, forestall erosion, and prolong street lifespan. Made from artificial polymers like polypropylene or polyester, this engineered cloth acts as a barrier, separator, and reinforcement layer—critical for stabilizing roadbeds in a number of conditions. In this guide, we’ll discover its core functions, types, set up high-quality practices, and versatile applications, which include its position past roads, such as with geotextile material for pavers.
1. Core Functions of Geotextile Road Fabric in Road Construction
Geotextile street cloth serves three principal roles in avenue building, every contributing to long-term steadiness and decreased maintenance:
Separation: Prevents mixing of subgrade soil and mixture layers. Without separation, satisfactory soil particles can migrate into aggregate, weakening the street structure. Geotextile avenue cloth acts as a filter, permitting water to drain whilst preserving layers distinct.
Reinforcement: Adds tensile power to the roadbed, distributing heavy hundreds (like trucks) throughout a wider area. This reduces soil compaction and rutting, in particular in gentle or clay-rich subgrades.
Drainage: Facilitates water drift away from the roadbed, stopping moisture buildup that can motive frost heave in cold climates or soil erosion in wet regions.
These features work collectively to lengthen avenue existence through 30–50% in contrast to normal building methods. Even in high-traffic areas, geotextile avenue material minimizes cracks and potholes, reducing long-term restore costs. It’s additionally like minded with geotextile material variations used in adjoining projects, like sidewalks or parking lots, making sure regular overall performance throughout building sites. For instance, geotextile material for pavers used in close by walkways can gain from comparable separation and drainage properties, developing a cohesive building system.
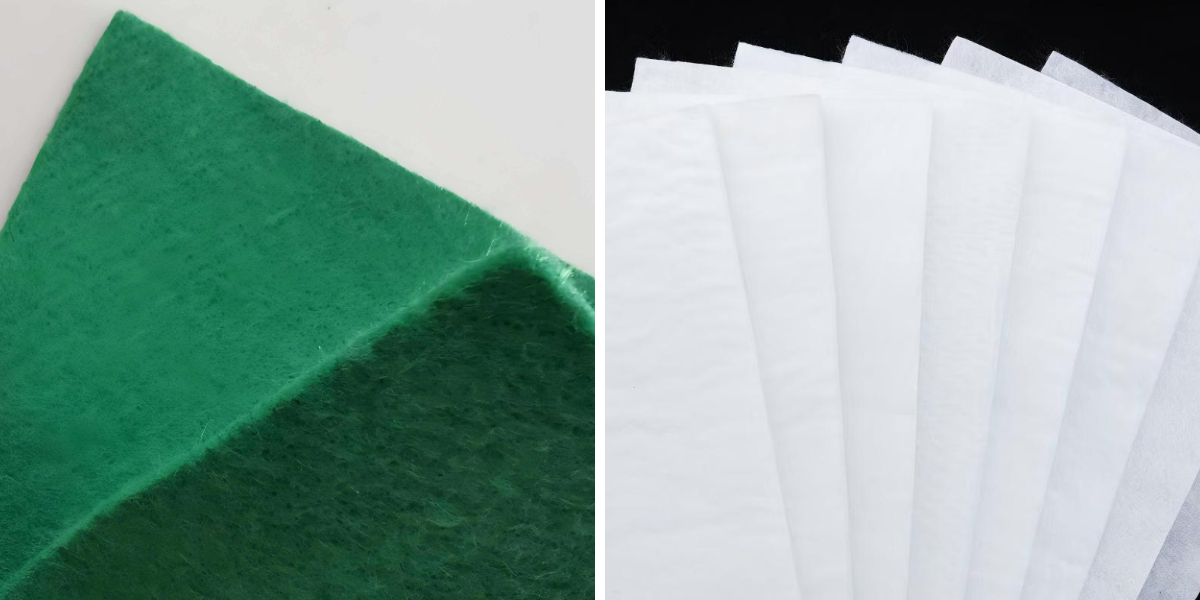
2. Types of Geotextile Road Fabric: Woven vs. Non-Woven
Choosing the proper kind of geotextile avenue cloth relies upon on challenge needs, soil type, and load requirements. The two foremost classes are woven and non-woven:
Woven Geotextile Road Fabric: Made through interlacing polypropylene or polyester threads, developing a strong, inflexible material. It excels at reinforcement and load distribution, making it perfect for heavy-traffic roads, highways, and industrial areas. Its excessive tensile electricity (200–1,000 lbs per inch) resists tearing underneath pressure, and it pairs properly with geotextile material in multi-layered reinforcement systems.
Non-Woven Geotextile Road Fabric: Produced by way of bonding fibers into a felt-like mat, supplying foremost filtration and drainage. It’s extra bendy than woven variants, adapting nicely to uneven terrain. Non-woven choices are frequently used in residential roads, driveways, or as a base layer for geotextile material for pavers, the place drainage and separation are prioritized over severe load-bearing.
Both kinds are durable, UV-resistant, and resistant to chemicals, however woven fabric are higher for high-stress applications, whilst non-woven types shine in drainage-focused projects. For combined needs, some contractors mix layers: a woven base for reinforcement (using geotextile street fabric) and a non-woven pinnacle layer (a kind of geotextile cloth) for more advantageous filtration.
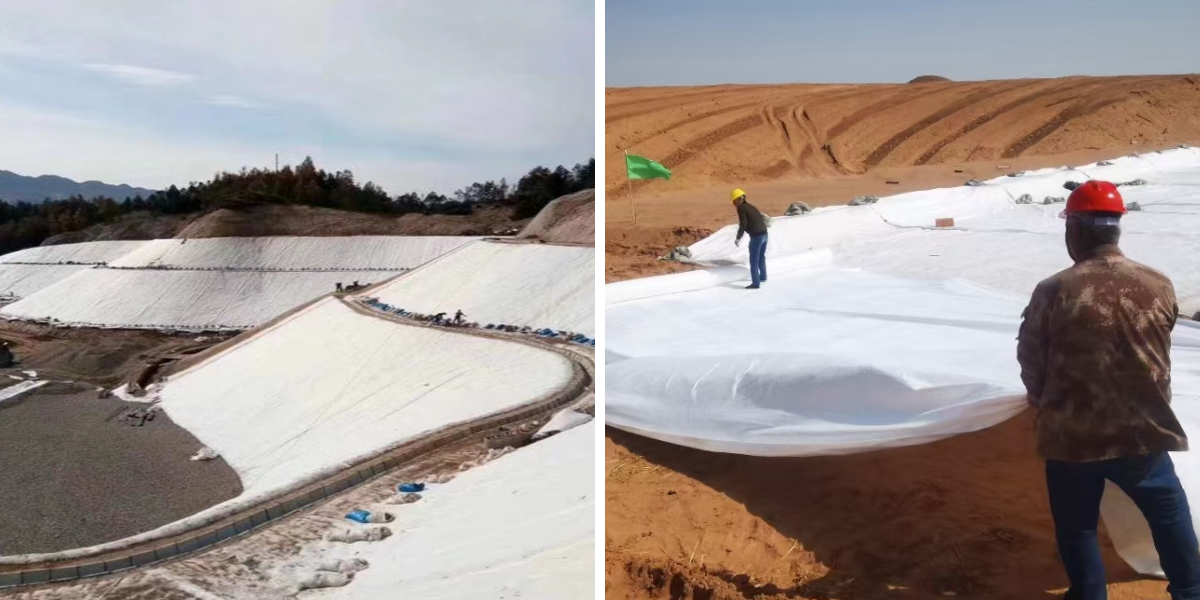
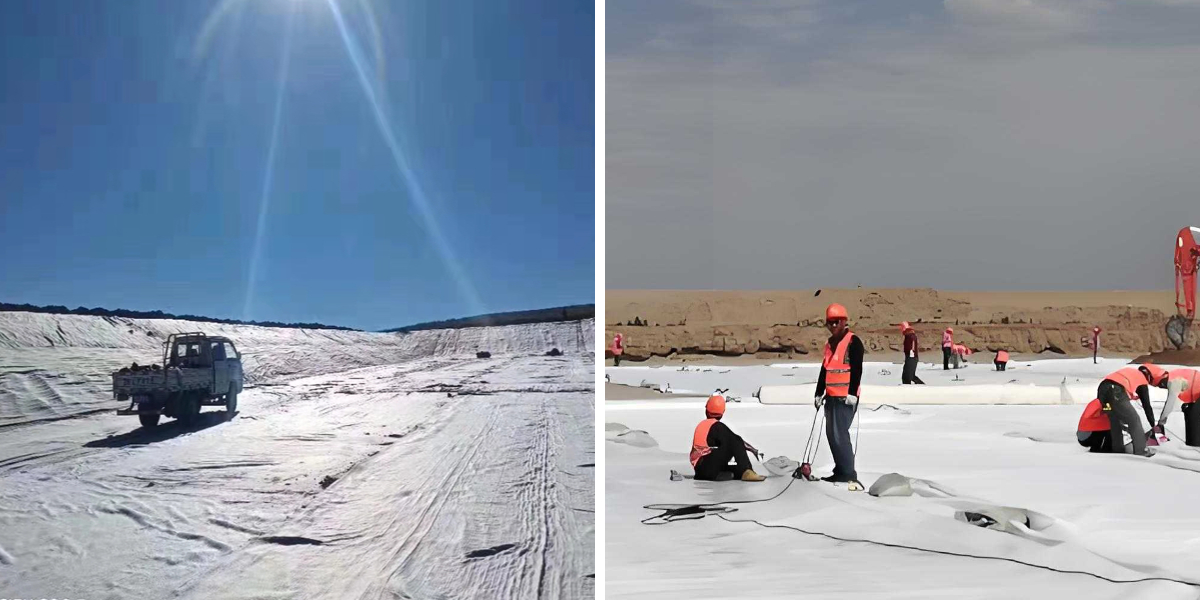
3. Installation Best Practices for Geotextile Road Fabric
Proper set up is key to maximizing the effectiveness of geotextile avenue fabric. Follow these steps for most useful results:
Prepare the Subgrade: Clear debris, rocks, and vegetation from the roadbed. Compact the soil to make sure a smooth, even surface—any unevenness can puncture the fabric. This step is equally vital for geotextile fabric used in different applications, like underneath geotextile material for pavers.
Lay the Fabric Correctly: Unroll geotextile street material from the pinnacle of the slope (if grading) to the bottom, overlapping edges via 6–12 inches to forestall gaps. Secure with stakes or sandbags to keep away from moving for the duration of mixture placement. The equal approach applies when laying geotextile material for paver projects, making sure a tight, invulnerable fit.
Avoid Damage: Use sharp equipment to reduce material (dull blades can tear it) and keep away from dragging heavy tools over unprotected fabric. For giant projects, set up equipment on pinnacle of a brief mixture layer to distribute weight, a precaution that additionally protects geotextile cloth for pavers in smaller-scale jobs.
Cover with Aggregate Promptly: Once laid, add the combination layer (gravel or beaten stone) inside 24 hours to protect the material from UV exposure, which can degrade it over time. This step preserves the integrity of each geotextile avenue material and geotextile cloth, making sure long-term performance.
4. Beyond Roads: Versatile Applications of Geotextile Cloth
While geotextile avenue material is designed for roads, its versatility extends to different development areas, with geotextile fabric and geotextile cloth for pavers being remarkable examples:
Geotextile Fabric for Pavers: Used below patios, walkways, or driveways to forestall paver shifting. It separates sand bedding from soil, decreasing weed boom and enhancing drainage—critical for keeping paver alignment. This utility depends on the identical separation and filtration houses as geotextile avenue fabric.
Retaining Walls: Reinforces backfill soil in the back of walls, stopping erosion and wall collapse. Woven geotextile material provides tensile energy to preserve soil in place, even on steep slopes, working in a similar way to geotextile avenue material in distributing pressure.
Railroad Beds: Stabilizes tracks through isolating ballast from subgrade, lowering preservation and extending music life. Here, geotextile avenue cloth offers the vital reinforcement and separation, whilst geotextile material can also be used in adjoining drainage systems.
Landscaping: Controls erosion in gardens or alongside slopes, frequently paired with mulch. Non-woven geotextile fabric is desired right here for its breathability and eco-friendliness, complementing geotextile cloth for pavers used in close by hardscaping.
Conclusion
Geotextile street material is a cornerstone of current avenue construction, imparting unmatched advantages in separation, reinforcement, and drainage. Its counterparts, geotextile fabric and geotextile cloth for pavers, lengthen these advantages to a vary of different building projects, from walkways to keeping walls. By selecting the proper kind (woven or non-woven) and following appropriate installation, contractors can drastically prolong infrastructure existence and limit costs. Whether constructing a highway, a driveway, or a patio, integrating these substances ensures durability, stability, and long-term performance.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province