Woven Geotextile
Long-fiber woven fabric, also known as woven fabric, is made by interweaving mutually perpendicular yarns. It uses high-strength industrial synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, polyester and nylon as raw materials.
It has remarkable properties such as high strength, low elongation, durability and corrosion resistance.
The woven fabric has a stable structure, a high compliance rate of engineering parameters, and can effectively control the structural pores to achieve a certain degree of water permeability.
It is lightweight, environmentally friendly, can be packaged as required, and is extremely convenient in terms of transportation, storage and construction.
Excellent mechanical properties
1. High strength and anti-destruction ability
Long-fiber Woven Geotextile are made from synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, polyester or nylon. After being processed through a regular interwoven structure, their tensile strength can reach more than twice that of short-fiber geotextiles.
2. Ductility and stress dispersion
The material has excellent elongation performance, which can quickly disperse and transfer stress, making the load distribution uniform. It is particularly suitable for foundation reinforcement and slope protection scenarios.
Specification
Item | Index | |||||||||||||
Nominal Strength (kN/m)Nominal Strength (kN/m) | ||||||||||||||
35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | ||||
1 Longitudinal Tensile Strength/(kN/m) ≥ | 35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | |||
2 Transverse Tensile Strength/(kN/m) ≥ | 0.7 × Longitudinal Tensile Strength×0.7 | |||||||||||||
3 | Maximum Load Elongation/% | Longitudinal ≤ | 35 | |||||||||||
Transverse | 30 | |||||||||||||
4 | Puncture Strength/kN ≥ | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 10.5 | 13.0 | 15.5 | 18.0 | 20.5 | 23.0 | 28.0 | ||
5 | Equivalent Aperture DiameterOg(O₉s)/mm | 0.05~0.50 | ||||||||||||
6 | Vertical Permeability Coefficient/(cm/s) | K×(10⁵~102)in: K=1.0~9.9 | ||||||||||||
7 | Width Deviation Rate/% ≥ | -1.0 | ||||||||||||
8 | Longitudinal Tear Strength/kN 2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.7 | ||
9 | Unit Area Mass Deviation Rate/% ≥ | -5 | ||||||||||||
10 | Length and Width Deviation Rate/% | ±2 | ||||||||||||
11 | Seam/Joint Strengtha/(kN/m) ≥ | Nominal Strength×0.5 | ||||||||||||
12 | Oxidation Resistance (Longitudinal Strength Retention Rate) a / % ≥ | Polypropylene: 90; Other Fibers: 80 | ||||||||||||
13 | Anti-UV Performance (Gas Chromatography Method)b | Longitudinal Strength Retention Rate/%≥ | 90 | |||||||||||
Anti-UV Performance (UV Lamp Method) | Longitudinal Strength Retention Rate/%≥ | 90 | ||||||||||||
Durability and Environmental Adaptability
1. Corrosion resistance and weather resistance
The characteristics of synthetic fibers make them resistant to acids, alkalis, insect infestation and mold erosion, and they remain stable in complex geological or chemical environments.
2. Anti-aging and long lifespan
It is not easily decomposed by ultraviolet rays or natural weathering, and can still maintain more than 80% of its original strength after long-term use.
Engineering Functional Advantages
1. Water permeability and drainage control
By precisely controlling the pore structure of the fabric, it can not only effectively filter water to prevent soil erosion, but also quickly discharge the water pressure in the gaps. It is particularly suitable for drainage systems or tunnel anti-seepage projects.
2. Coefficient of Friction and Construction stability
A high coefficient of friction (typically ≥0.4) ensures that the project is less likely to slip during construction, enhancing the reliability of the project in scenarios such as reinforcing retaining walls or isolating roadbeds.
Economy and Construction Convenience
1. Lightweight and convenient for storage and transportation
The material weighs only 1/3 to 1/2 of traditional materials, supports roll transportation and rapid laying, and reduces logistics and labor costs.
2. Multi-functional integrated application
It has multiple functions such as reverse filtration, isolation, reinforcement and protection, and can replace the traditional multi-layer construction process, shortening the construction period by more than 30%.
Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development
By using recyclable polyester raw materials (such as PET), the energy consumption during the production process is reduced by 20% compared with traditional materials, which meets the requirements of green building standards. Some of the products have passed the ISO14001 environmental management system certification.
In summary, long-fiber woven fabrics have demonstrated irreplaceable technical advantages in fields such as civil engineering and environmental protection through the combination of material innovation and structural design. Its high strength, durability and functional integration make it one of the core materials for modern infrastructure.
Application fields of filament woven fabric:
Filament woven fabrics have demonstrated extensive application value in multiple fields due to their high strength, durability and multi-functionality. The following is a systematic review of its core application fields:
I. Civil Engineering Field
1. Foundation reinforcement and slope protection
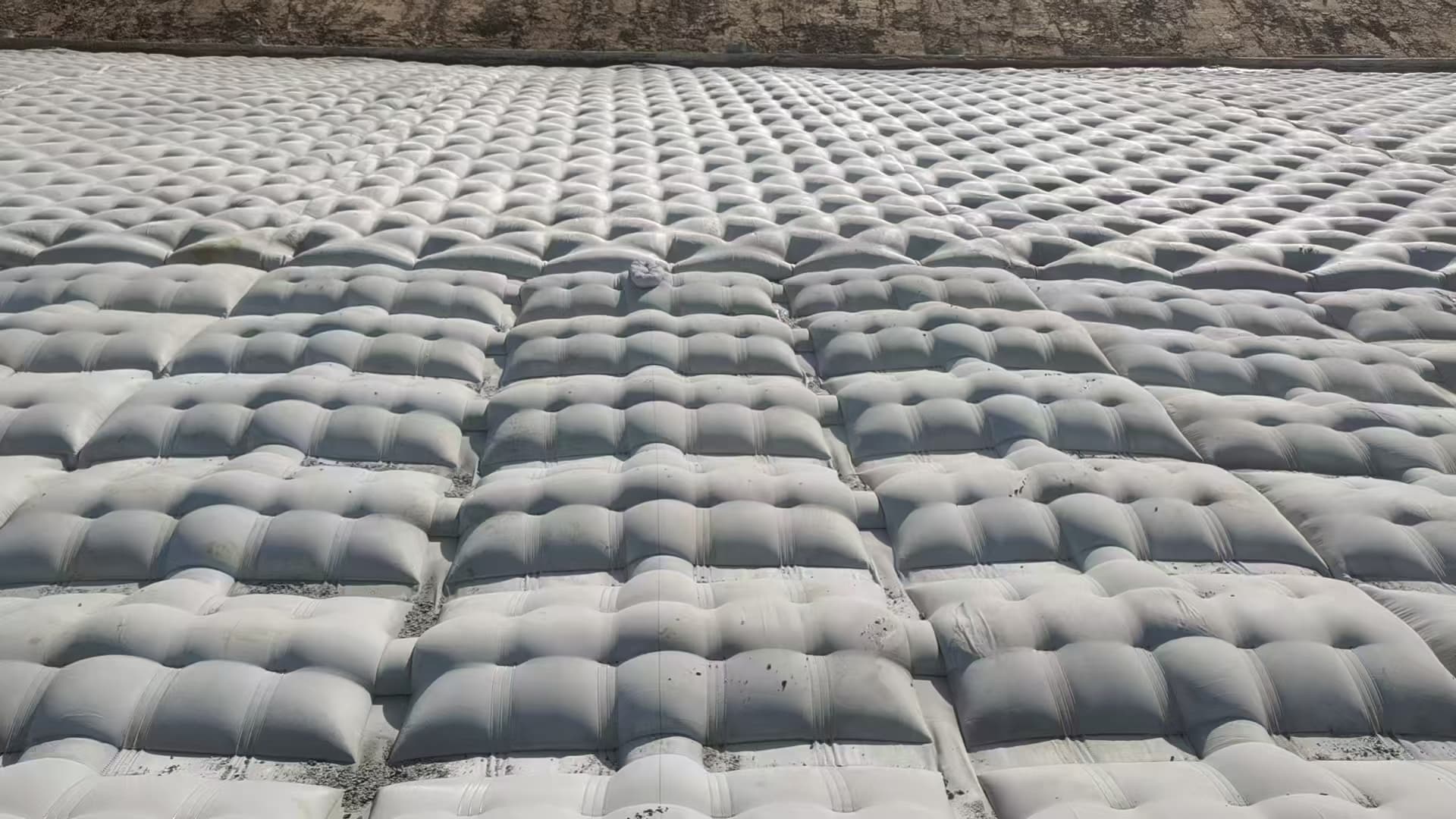
It is widely used in the backfilling reinforcement of retaining walls, the construction of wrapped retaining walls and the reinforcement of abutments. It effectively enhances the structural stability through high tensile strength (the puncture resistance can reach over 2200 Newtons). In crushed stone slope and reinforced soil projects, it can prevent soil erosion and low-temperature frost damage, and enhance the bearing capacity of the foundation.
2. Isolation and reverse filtration system
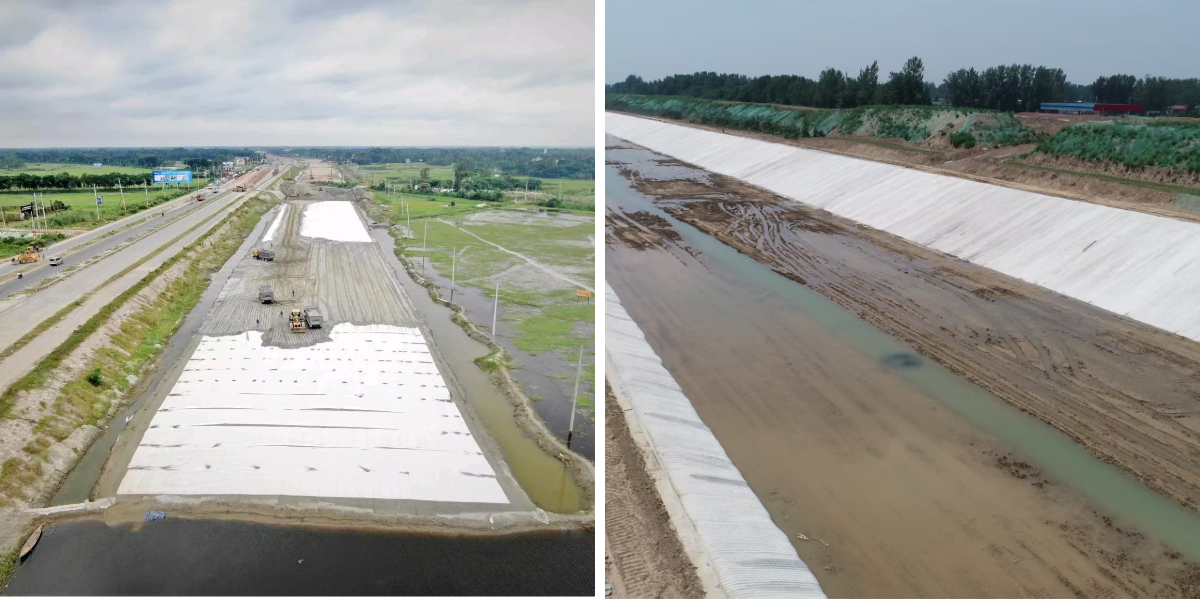
As an isolation layer between the roadbed and the soft foundation, and between the road ballast and the foundation, it prevents the mixture of different materials and maintains the unobstructed drainage channels. In ash storage DAMS and tailings DAMS, it is used as the initial filter layer on the dam face to prevent the loss of fine particles.
Ii. Construction of Transportation Infrastructure
1. Road engineering
It is used for reinforcing flexible pavements, repairing cracks and preventing reflective cracks, and extends the service life of roads through stress dispersion characteristics. In projects such as highways and airport runways, it serves as an isolation layer between the foundation and the filling material to enhance the bearing capacity of weak foundations.
2. Railway engineering
It is applied to the isolation between railway ballast and roadbed to prevent track settlement, and at the same time, it is used as a filter layer in the drainage system to reduce the damage to the roadbed caused by freeze-thaw cycles.
Iii. Water Conservancy and Environmental Protection Projects
1. Drainage and seepage control system
It plays a crucial role in scenarios such as vertical/horizontal drainage within earth DAMS and water seepage drainage in tunnels, capable of dissipating void water pressure and reducing the external water pressure of concrete linings. It is used as the base material for the anti-seepage layer of artificial lakes, water pools and landfill sites, combined with geomembranes to form a composite anti-seepage structure.
2. Ecological restoration
In soil and water conservation projects, it is used as a slope protection material to prevent soil erosion, and is also applied in urban greening projects and wetland restoration projects.
Iv. Industrial and Civil Buildings
1. Construction engineering drainage
Drainage systems should be set up in basements, sports field foundations and other scenarios to prevent water accumulation from eroding the building structure.
2. Protection of industrial facilities
It is used as an isolation layer in chemical plants, ash storage yards and other places to resist chemical corrosion and extend the service life of facilities.
V. Extended Applications in Traditional Textile Fields
1. Functional textiles
Nylon and polyester filament woven fabrics, with their wear-resistant and anti-wrinkle properties, are applied in high-end outdoor clothing, automotive interiors and military equipment.
2. Home textiles and industrial fabrics
As materials for home textile products such as curtains and sofa covers, as well as industrial textiles such as agricultural covering fabrics and industrial filter fabrics.
Development trend
With the upgrading of environmental protection demands, filament woven fabrics are developing towards recyclable polyester (PET) materials and low-energy consumption production processes. It has huge application potential in emerging fields such as Marine engineering and new energy facilities (such as photovoltaic field foundation reinforcement) in the future.