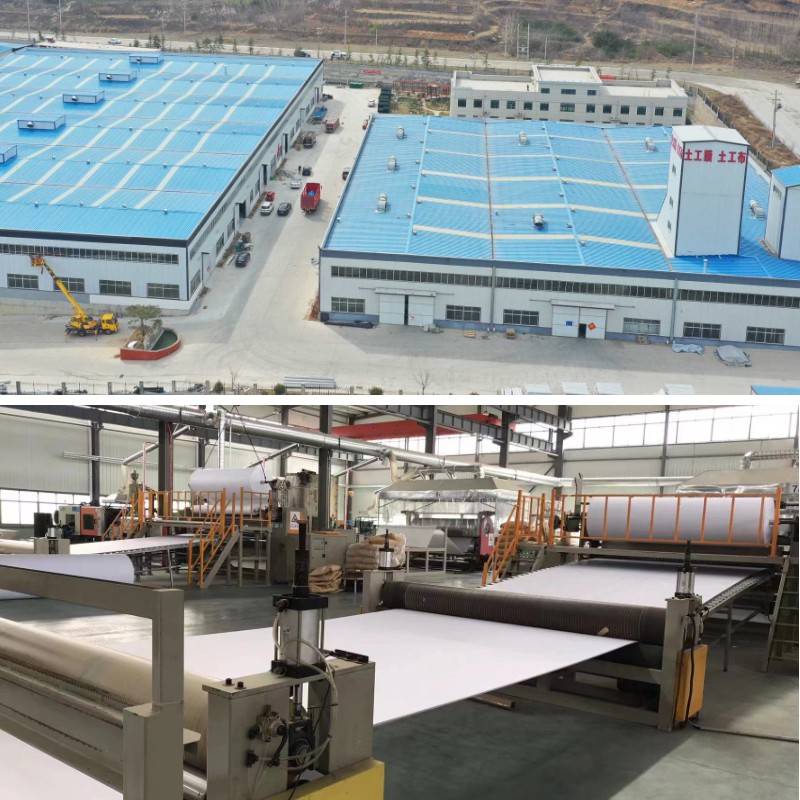
Geotextile Polypropylene Fabric
1.Durable and damage resistant: Resistant to UV rays, acid and alkali, and microorganisms, not easily aged outdoors or in harsh environments, with a long service life;
2.Efficient filtration: Uniform pores, capable of intercepting soil particles, preventing loss, and ensuring smooth infiltration of water and air;
3.Mechanical stability: High tensile and tear strength, can disperse soil stress, enhance the stability of structures such as roadbeds and slopes;
4.Construction worry free: Lightweight and flexible, easy to cut, lay and splice, suitable for complex terrain, reducing construction difficulty.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Material foundation: Geotextile Polypropylene Fabric is a synthetic fiber fabric made from polypropylene (PP) resin through spinning, needle punching, hot bonding or weaving processes, with high purity of raw materials and no natural fiber impurities.
Physical characteristics: lighter density than water, easy to transport; The pore distribution is uniform and stable, with good flexibility and a certain degree of rigidity. It can be bent to adapt to terrain and resist local compression deformation.
Chemical characteristics: It has tolerance to common weak acids and bases in soil, is not easily decomposed by bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms, and can resist UV aging. Its chemical properties remain stable in outdoor environments.
2、 Core functions
Filtering protection: By accurately intercepting soil particles through pores, soil loss can be avoided, while ensuring smooth infiltration of rainwater, groundwater, etc., preventing pore blockage, and maintaining normal exchange between soil and water bodies.
Reinforced stability: With high tensile and tear strength, it is embedded in structural layers such as roadbeds and slopes, effectively dispersing soil stress, improving overall bearing capacity, and preventing problems such as settlement and collapse of the structure.
Isolation and Separation: It can separate sand, gravel, soil, or other building materials of different particle sizes, such as avoiding mixing of roadbed soil and cushion gravel, preventing material mixing from deteriorating engineering performance, and ensuring structural stability.
Drainage and infiltration: Using fiber gaps to form natural drainage channels, guiding excess water inside the soil to be discharged, reducing soil moisture content, and minimizing engineering diseases such as roadbed overturning and slope landslides.
3、 Main features
Outstanding durability: It has excellent anti-aging, weather resistance and chemical erosion resistance. It can be used for a long time in outdoor or complex soil environment, and its service life is far longer than that of traditional natural fiber geotechnical materials.
Convenient and efficient construction: lightweight texture, easy to cut, can be quickly assembled according to engineering needs, can adapt to complex terrains such as slopes and curves, greatly reducing labor and time costs during the construction process.
Excellent cost-effectiveness: Polypropylene raw materials have a wide range of sources, mature production processes, and relatively low product costs; And there is no need for frequent maintenance during the service life, and in the long run, the engineering economy is significant.
Environmentally friendly: No harmful substances will be released during use, and there is no pollution to the ecological environment such as soil and water. Some products can also be recycled and reused, which meets the requirements of green engineering.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1、 Road and Traffic Engineering
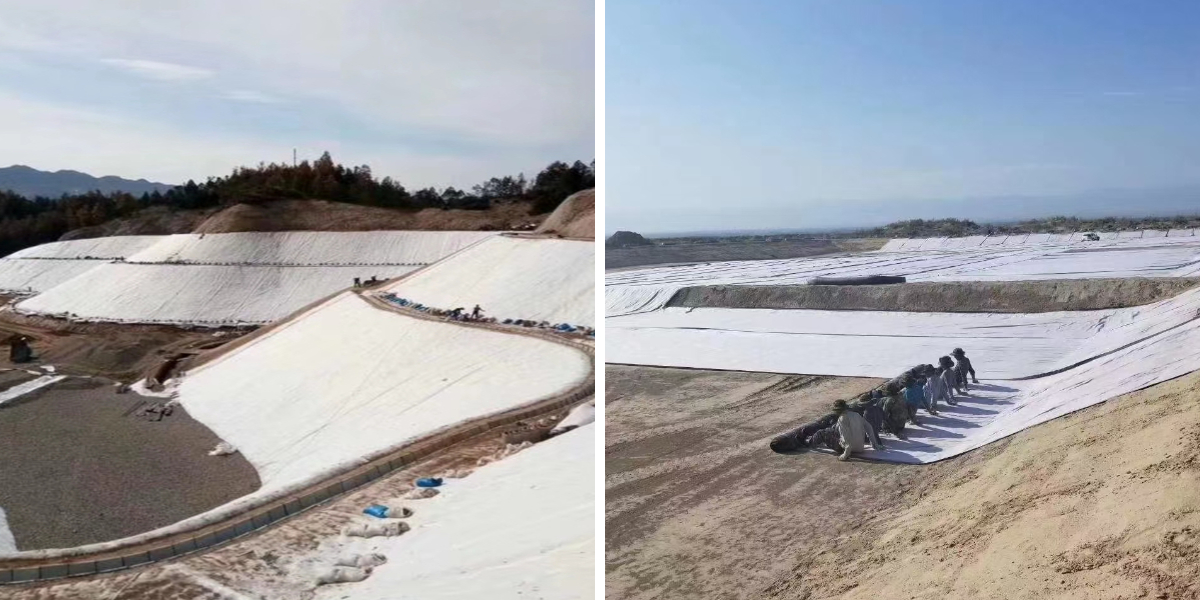
Roadbed reinforcement: laid between the roadbed soil and the cushion layer (sand and gravel layer), isolating different materials to avoid mixing, while dispersing the stress generated by vehicle loads, reducing roadbed settlement and cracking, improving the overall bearing capacity of the road, and adapting to various road constructions such as highways, municipal roads, and rural roads.
Road maintenance: When renovating an old road surface or adding a new surface layer, it is laid between the old and new road surfaces to isolate and prevent seepage, prevent the transmission of old road surface diseases (such as cracks and water accumulation) to the new surface layer, and extend the service life of the road surface.
Slope protection: used for slopes on both sides of roads to enhance soil stability through reinforcement, combined with vegetation planting to further prevent soil erosion and avoid slope collapse, especially suitable for mountainous roads and high fill sections.
2、 Water conservancy and waterway engineering
Dam anti-seepage and reinforcement: laid on the upstream slope of the dam or inside the dam body as an anti-seepage auxiliary layer to prevent water from penetrating the dam body; At the same time, through reinforcement and isolation functions, the overall integrity of the dam body soil is enhanced, reducing problems such as dam erosion and piping caused by water flow erosion, and adapting to reservoir embankments, river embankments, irrigation channels, etc.
Port and waterway construction: In the slope protection of port terminal foundation treatment and waterway dredging, it is used to isolate sand and gravel materials, filter water impurities, prevent foundation settlement or sediment loss of waterway slopes, and ensure the stability of port terminal structure and smooth navigation of waterways.
Artificial Lake and Water Landscape Engineering: Installed at the bottom of artificial lakes or water landscape slopes, it isolates soil and impermeable membranes to prevent soil particles from blocking the impermeable membranes. At the same time, it guides excess water to be discharged, maintains clear water bodies, and prevents lake bottom subsidence and slope collapse.
3、 Construction and Municipal Engineering
Building foundation: In the foundation treatment of high-rise buildings, factories, etc., it is laid between the foundation soil and gravel cushion layer to isolate different soil layers, filter impurities, reduce uneven settlement of the foundation, and improve the bearing capacity of the foundation, especially suitable for soft soil foundation areas.
Underground pipe gallery and tunnel: wrapped around the outer wall of the underground pipe gallery or the outside of the tunnel lining, it plays a filtering and drainage role, preventing soil particles from infiltrating into the interior of the pipe gallery or tunnel, while draining excess moisture from the surrounding soil, avoiding corrosion of the pipe gallery and water seepage in the tunnel.
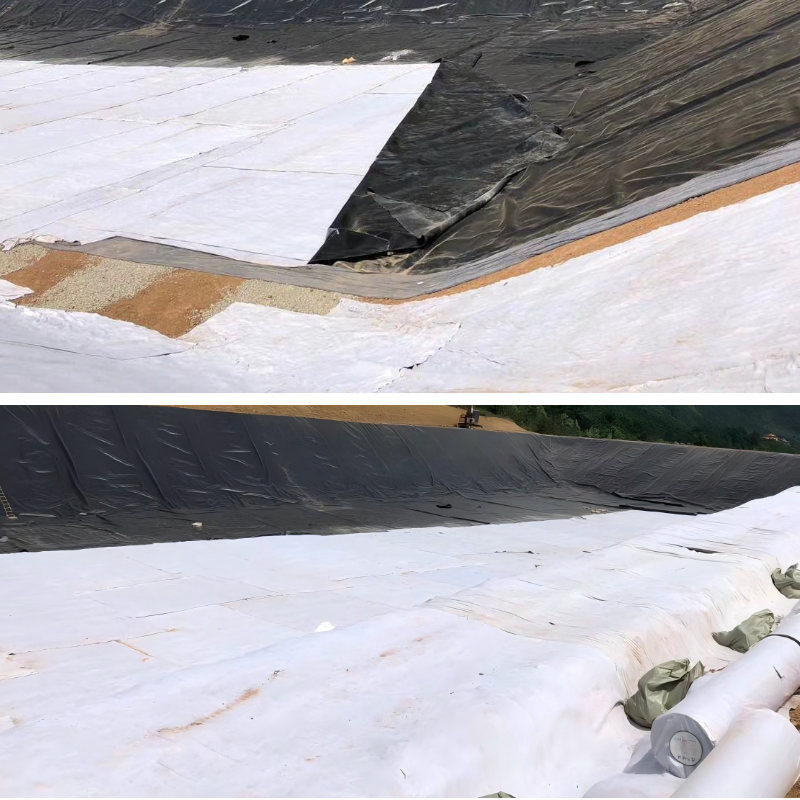
Landfill site: As an auxiliary layer of the anti-seepage system of the landfill site, it is laid on both sides of the anti-seepage membrane, with the upper layer separating garbage from the anti-seepage membrane to prevent sharp garbage from piercing the anti-seepage membrane; The lower layer isolates the soil and impermeable membrane, filters soil impurities, and guides the orderly collection of leachate to reduce environmental pollution.
4、 Ecological and Agricultural Engineering
Slope ecological restoration: In projects such as mine greening, landslide control, and riverbank ecological restoration, it is laid on the surface of the slope soil to fix the soil and prevent soil erosion. At the same time, it provides a stable base for vegetation seed germination (which can be used as a grass blanket carrier), promotes ecological vegetation restoration, and achieves the dual effect of "engineering protection+ecological greening".
Agricultural water conservancy facilities: used for the slopes and bottoms of farmland irrigation channels and drainage ditches, isolating soil and water bodies, preventing channel erosion and sedimentation, and improving irrigation efficiency; It can also be used for greenhouse foundations, playing a role in anti-seepage, drainage, and regulating soil moisture inside the greenhouse.
Construction of artificial wetlands: laying between the substrate layers (soil, sand and gravel layers) of artificial wetlands, isolating different substrates, filtering water impurities, and guiding the internal water circulation of wetlands to improve the efficiency of wetland water purification, suitable for urban wetland parks, rural sewage treatment wetlands, etc.
5、 Other special scenarios
Railway engineering: used for railway subgrade reinforcement, track bed isolation, reducing the impact of train vibration on the subgrade, preventing the mixing of roadbed sand and gravel with subgrade soil, and ensuring smooth and stable railway tracks.
Power engineering: used for foundation treatment in the construction of transmission line tower bases and wind power plant foundations, to enhance the stability of tower bases and foundations, prevent equipment tilting due to foundation settlement, and adapt to the construction of power facilities in complex geological areas such as mountainous areas and soft soil.
Polypropylene geotextile, with its core functions of filtration, reinforcement, isolation, and drainage, has become a key engineering material in various fields such as cross road transportation, water conservancy and transportation, construction and municipal engineering, ecological agriculture, and electric railways. Whether it is ensuring the structural stability of infrastructure, extending the service life of engineering, or assisting in ecological restoration and green agriculture development, it can play a precise role according to the needs of different scenarios, effectively solving practical problems such as soil loss, structural settlement, and water pollution in engineering. It combines practicality and economy, providing important support for high-quality construction and long-term operation and maintenance of various projects.