Non Woven Geotextile
1. Efficient filtration and drainage: Three dimensional pores intercept fine soil to prevent blockage, quickly divert water, and maintain soil stability
2. Strong adhesion: flexible, lightweight, easy to cut, suitable for irregular terrain, no blind spots for laying
3. Weather resistant and durable: resistant to UV rays and acid and alkali, stable for use at -30 ℃ to 70 ℃, with a lifespan of 5-10 years
4. Economic efficiency: low unit price, woven fabric 20% -40%, manual laying saves costs, construction is 2-3 times faster
Products Introduction:
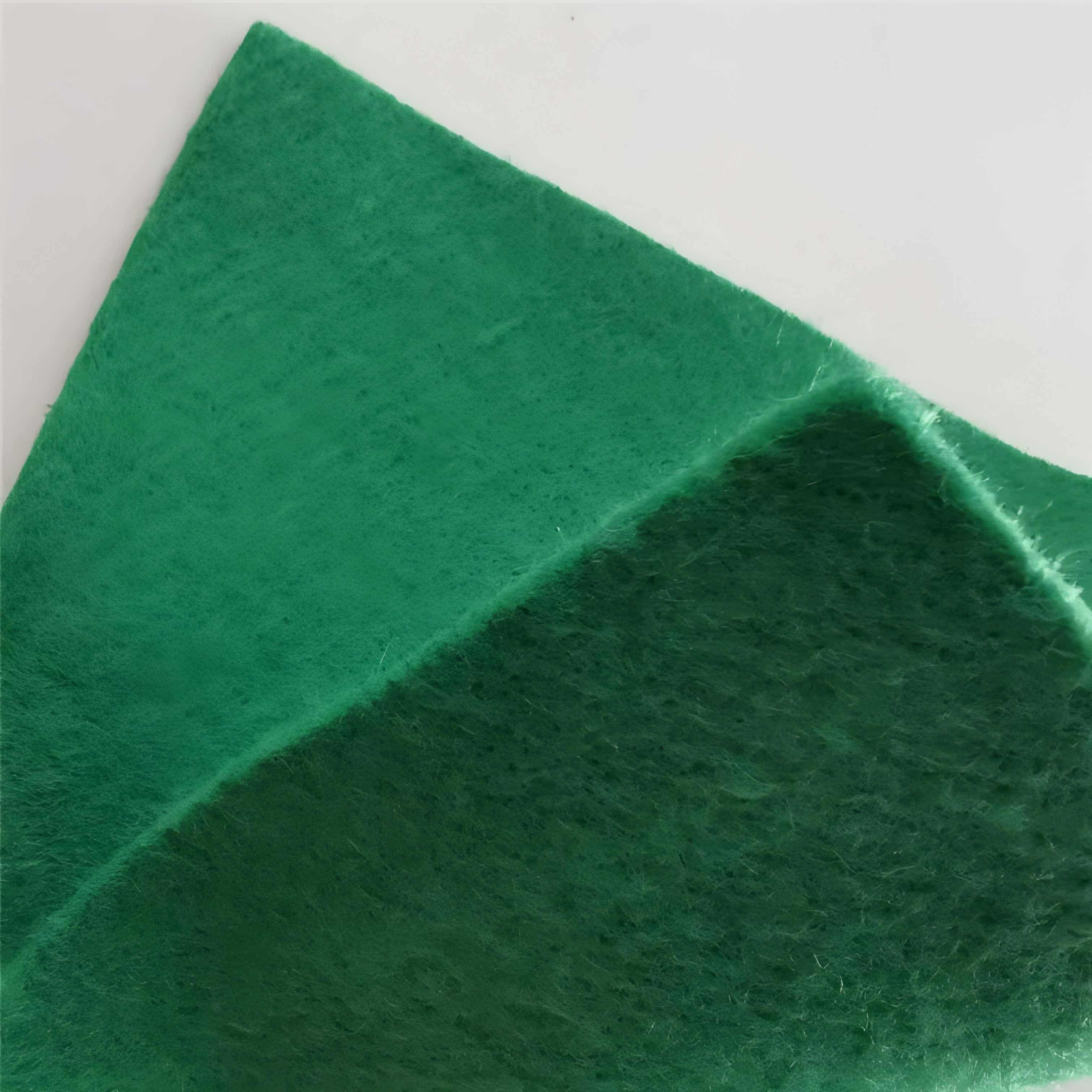
Non Woven Geotextile is a core category of geosynthetic materials, which uses polymer short fibers or long fibers such as polypropylene (PP) and polyester (PET) as raw materials, and randomly interweaves and solidifies the fibers through processes such as needle punching, thermal bonding, and spunbonding, without the traditional weaving of warp and weft yarns. Its core functions revolve around "filtration, drainage, isolation, and protection". With its three-dimensional porous structure and flexible properties, it plays a key role in "preventing soil erosion, draining water, and protecting structures" in civil engineering.
Different from the high-strength reinforcement properties of woven geotextiles, non-woven geotextiles focus more on "functionality and adaptability", especially in scenarios that require precise filtering and fitting of irregular terrain. They have significant advantages and are widely used in fields such as water conservancy, transportation, municipal engineering, agriculture, etc. They are the basic protective materials that balance cost and efficiency in various engineering projects.
Product Features:
1. Efficient filtration and drainage, anti blocking and stable
The fibers are randomly interwoven to form uniform three-dimensional pores (pore size 0.05-0.3mm), with a retention rate of over 95% for fine soil particles. This can effectively prevent the loss of fine soil particles with water flow in the base layer and avoid blockages in the drainage system; At the same time, with a permeability coefficient of ≥ 1 × 10 ⁻ cm/s, it can quickly divert rainwater, groundwater, or leachate, reduce soil pore water pressure, prevent structural instability caused by soil softening, and adapt to scenarios with high filtration requirements such as landfill reverse filtration and river bank slope protection.
2. Flexible and snug fit, suitable for complex terrains
Soft texture and good ductility (fracture elongation of 15% -50%), can naturally adhere to irregular base layers such as potholes, slopes, and curved ditches, without blind spots for laying; Lightweight (50-400g/m ²), easy to cut, and can be manually laid without the need for professional equipment. It can even be quickly constructed in narrow spaces or temporary sites, solving the pain points of traditional rigid protective materials that are difficult to fit and prone to cracking.
3. Weather resistant and corrosion-resistant, long-lasting and durable
The raw materials have been treated with UV and acid-base resistance, and can be stably used in extreme environments ranging from -30 ℃ to 70 ℃, resisting soil corrosion, microbial decomposition, and outdoor sun and rain exposure; In ordinary soil or water environments, the service life can reach 5-10 years, and it can also maintain stable performance for 3-5 years in complex environments such as landfills, reducing the frequency of later maintenance and replacement.
4. Ecological compatibility, environmental protection and safety
Using non-toxic and harmless polymer materials, the production process has no harmful emissions, and after laying, it can work synergistically with soil and vegetation - for example, providing attachment carriers for grass seeds and shrub roots, not hindering soil permeability and water exchange, suitable for environmentally friendly scenarios such as ecological slopes and roof greening; Some biodegradable models can naturally decompose into harmless substances at the end of their service life, reducing environmental burden.
5. Cost economy and efficient construction
The production process is simplified, the utilization rate of raw materials is high, and the unit price is only 60% -80% of that of woven geotextiles; No large machinery is required for laying, and manual overlap (overlap width ≥ 10cm) can be completed. The construction efficiency is 2-3 times higher than traditional protective materials (such as sand and gravel filter layers), especially suitable for large-scale projects (such as farmland irrigation and municipal roads), significantly reducing overall costs.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
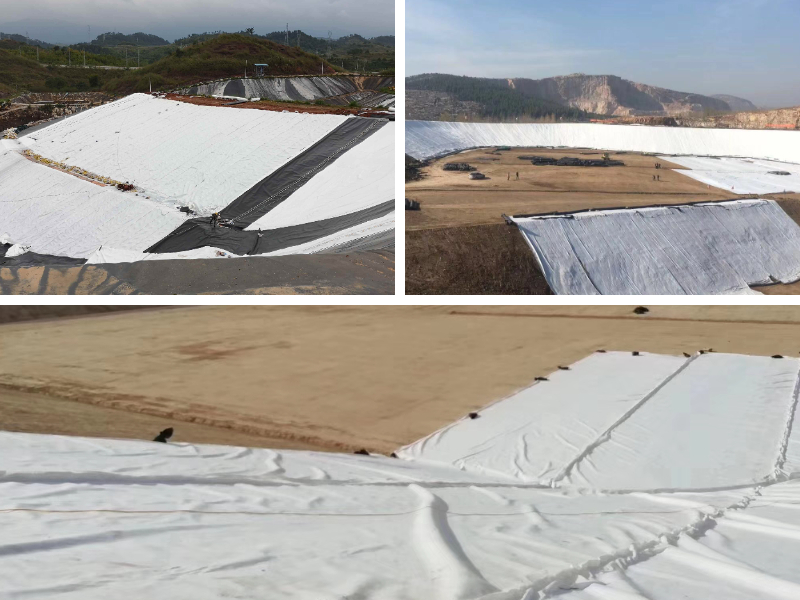
1. Water conservancy and ecological protection engineering
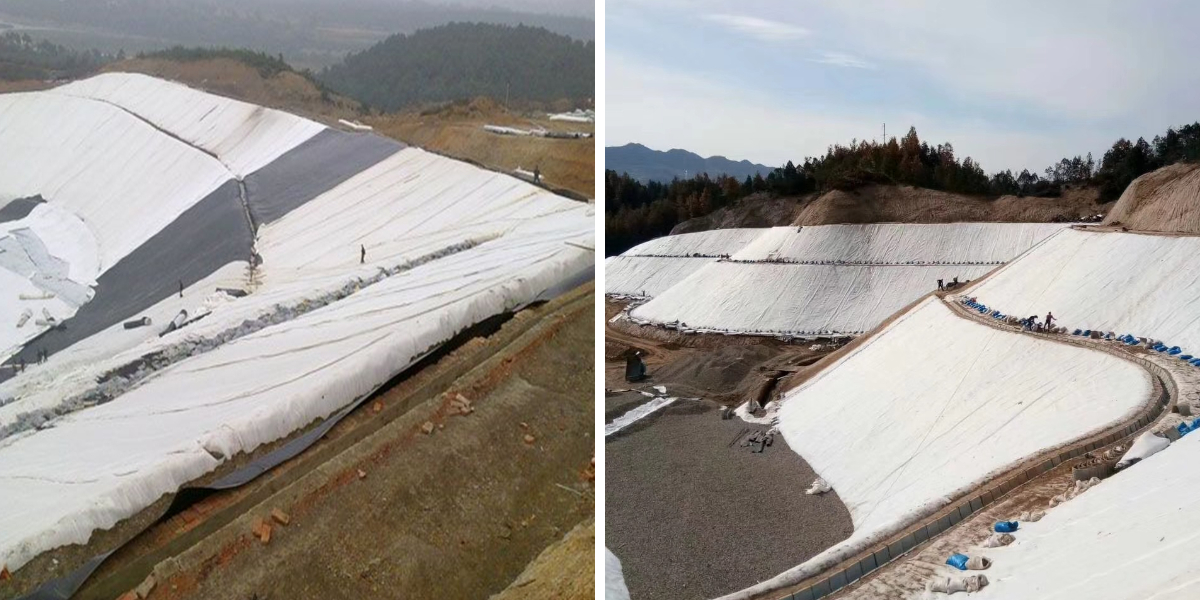
River bank slope protection: laid on the surface of the bank slope or below the ecological gabion, intercepting soil particles to prevent soil erosion caused by water flow, while diverting rainwater to maintain bank slope stability, and cooperating with vegetation planting to achieve a dual effect of "protection+ecology";
Anti filtration of reservoirs and dams: used around the back slope or seepage ditch of dams to filter the seepage of the dam body, prevent the loss of fine soil, and avoid hidden dangers such as piping and landslides in the dam body. It is suitable for reinforcement projects of small and medium-sized reservoirs and ponds.
2. Transportation and Municipal Engineering
Road base protection: laid between the subgrade and pavement base of highways and rural roads, isolating soil materials of different gradations (such as sand, gravel, and clay) to prevent pavement cracking caused by mixing; At the same time, it can alleviate the accumulated water on the roadbed, reduce the softening of the base layer, and extend the service life of the road;
Parking lot and square ground: laid on asphalt or cement ground base, filtering the fine particles of the base soil to prevent the ground from sinking due to soil erosion, suitable for light load scenarios such as residential parking lots and municipal squares.
3. Environmental Protection and Waste Management Engineering
Landfill filter layer: laid above the anti-seepage membrane of the landfill or around the leachate collection ditch to filter impurities in the leachate, prevent blockage of the collection pipeline, and isolate the garbage from the surrounding soil to reduce the risk of pollutant diffusion;
Oxidation pond of sewage treatment plant: used at the bottom or periphery of the oxidation pond to isolate the soil and sewage of the pond, prevent sewage from infiltrating and polluting groundwater, and filter sediment in the water to maintain stable water quality of the pond.
4. Agricultural and Horticultural Engineering
Irrigation system for farmland: wraps around the irrigation channels and inner walls of drainage ditches, filters sediment in the water flow, prevents channel blockage, and reduces irrigation losses; Simultaneously protecting the soil on the canal wall from erosion and extending the service life of drainage and irrigation facilities;
Horticulture and planting containers: After cutting, they are laid at the bottom of flower pots and planting boxes, replacing traditional mesh to filter out excess water and prevent root rot. At the same time, they trap soil particles in pots to avoid soil spillage during watering, making them suitable for home gardening and greenhouse seedling cultivation scenarios.
5. Temporary and emergency engineering
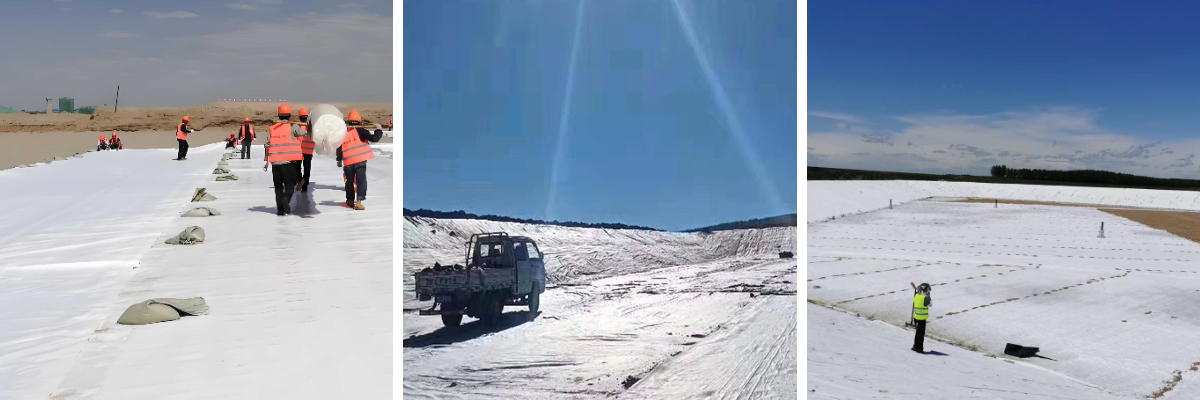
Temporary construction access road: laid on the base of the access road to enhance the bearing capacity of the temporary road surface, prevent mud and vehicle sinking caused by vehicle crushing, and can be recycled and reused after the project is completed;
Emergency flood prevention and rescue: After a flood disaster, quickly install damaged parts of riverbanks and roadbeds to temporarily prevent soil erosion, divert accumulated water, and buy time for subsequent repairs.
Non Woven Geotextile takes "efficient filtration and drainage, flexible adaptation, ecological protection, and economic efficiency" as its core advantages, accurately solving the multiple needs of "anti loss, drainage, cost reduction, and ecological protection" in civil engineering. Whether it is slope protection in water conservancy projects, grassroots reinforcement of municipal roads, or green construction of ecological projects, reliable protection solutions can be provided through flexible performance and convenient construction.
Compared to other geotechnical materials, non-woven geotextiles excel in balancing functionality and economy - meeting the core requirements of filtration and protection in engineering, reducing project investment through low cost and high efficiency, while also considering ecological and environmental protection needs. They are an ideal basic material for "multi scenario adaptation and full cycle reliability" in modern civil engineering. Its widespread application not only promotes the development of engineering construction towards a more efficient and green direction, but also provides strong support for people's livelihood fields such as water resource protection and ecological restoration.