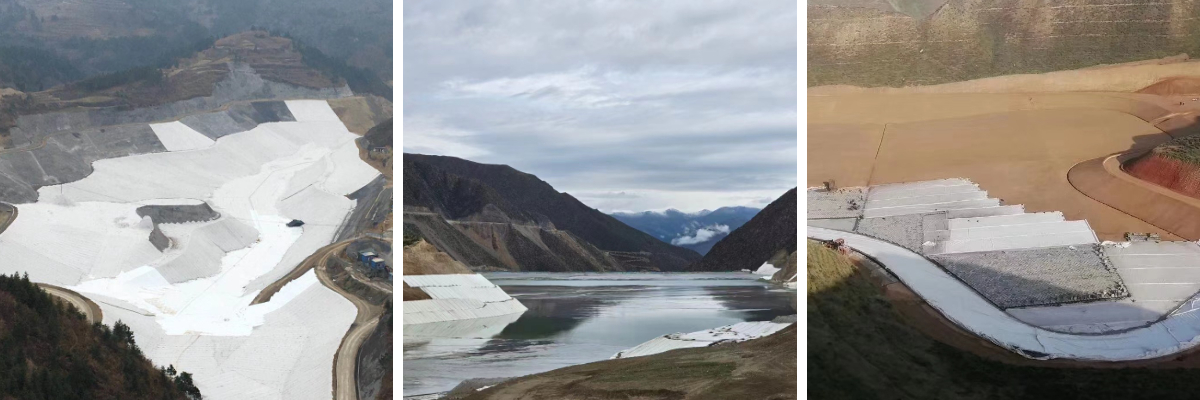
Geotextile 300g
1. Enhance foundation stability: disperse loads and reduce uneven settlement.
2. Isolate different soil layers: prevent mixing of different materials and maintain structural integrity.
3. Filtration and drainage: prevent soil erosion while allowing water infiltration.
4. Convenient construction: lightweight, easy to lay, saving labor and time costs.
5. Environmental Economy: Reduce the use of traditional materials (such as sand and gravel) and lower engineering costs.
Product Introduction:
Geotextile 300g is a permeable geosynthetic material made from high molecular weight polymers through processing. It can work synergistically with building materials such as soil, rock, and sand to improve the mechanical properties and durability of engineering structures.
characteristic
1. High strength and ductility
Plastic fiber material enables it to maintain sufficient strength and elongation in both dry and wet conditions, with a tensile strength of 2-3 times that of short fiber cloth (long fiber geotextile), suitable for high stress scenarios.
2. Corrosion resistance and aging resistance
Long term corrosion resistance in acidic and humid environments, as well as resistance to microorganisms and insect infestations, with a service life of several decades.
3. Permeability and Filtration
The pores between fibers allow water flow to pass through while blocking soil particles, fine sand, etc., forming natural drainage channels.
4. Lightweight and convenient construction
The unit area mass is only 100-1000g/m ², and the material is soft and easy to cut. It can be manually rolled or mechanically installed, reducing construction costs.
Comparison: Compared with the concrete drainage layer, the construction efficiency of geotextile is improved by more than 50%.
5. Environmental Protection and Economy
Non toxic and harmless, recyclable or degradable, and with a lower overall cost than traditional materials.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
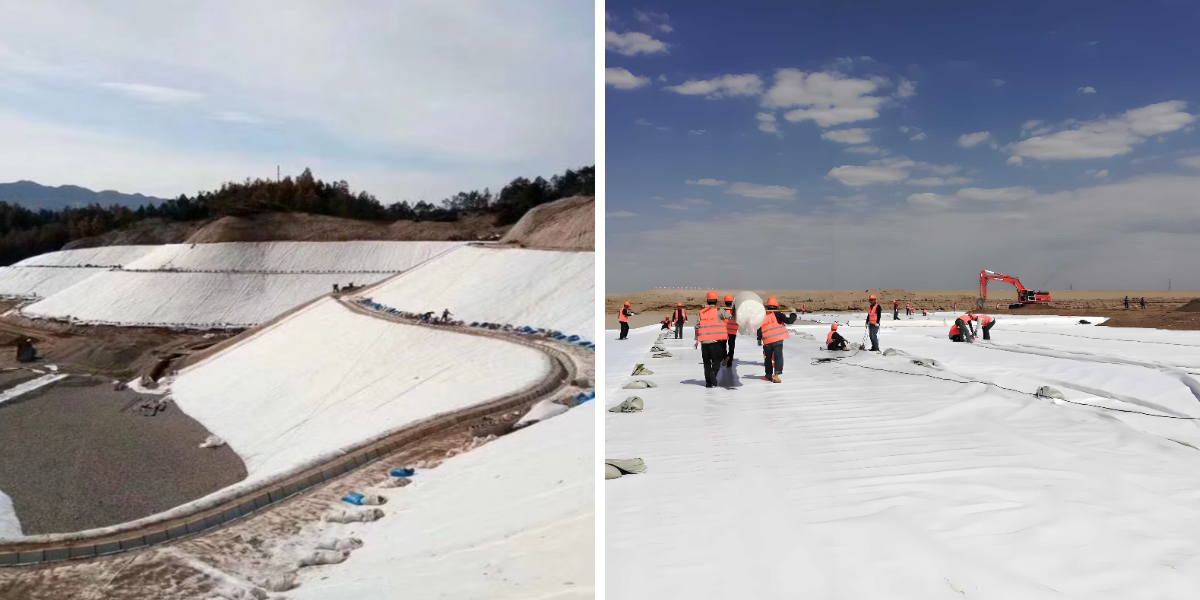
1. Transportation infrastructure
Roadbed reinforcement: Lay geotextile isolation layer in soft soil foundation to prevent material mixing from causing collapse (such as the Beijing Shanghai high-speed railway).
Slope protection: Short fiber needle punched geotextile covers the slope surface, combined with grass planting to achieve ecological slope stabilization and reduce soil erosion.
2. Water conservancy engineering
Dam anti filtration: Long fiber geotextile is used as a filtering medium to allow water flow but block sediment, protecting the dam structure.
Drainage system: Three dimensional geotextile is buried in soft soil areas to guide groundwater discharge and prevent roadbed collapse.
3. Environmental Protection Engineering
Landfill site: Composite geotextile (cloth+membrane) is used to construct an anti-seepage barrier to prevent pollutants from seeping into groundwater.
Remediation of polluted soil: Cover polluted soil with short fiber cloth, isolate harmful substances, and promote vegetation restoration.
4. Urban infrastructure
Underground engineering: Textile geotextile reinforcement is used in subway tunnels to resist soil pressure deformation.
Sponge City: Permeable geotextile is laid on the lower layer of permeable pavement to enhance rainwater infiltration and storage capacity.
5. Civil field
Garden vegetable field: Cover with geotextile to suppress weed growth while maintaining soil permeability.
Emergency leak prevention: Temporarily cover roof leakage points, guide rainwater drainage, and avoid indoor water accumulation.
Geotextile, as a multifunctional geotechnical material, plays an important role in modern engineering construction due to its excellent mechanical properties, permeability, and durability. It can improve engineering quality and reduce construction costs, and is one of the indispensable materials in civil engineering.