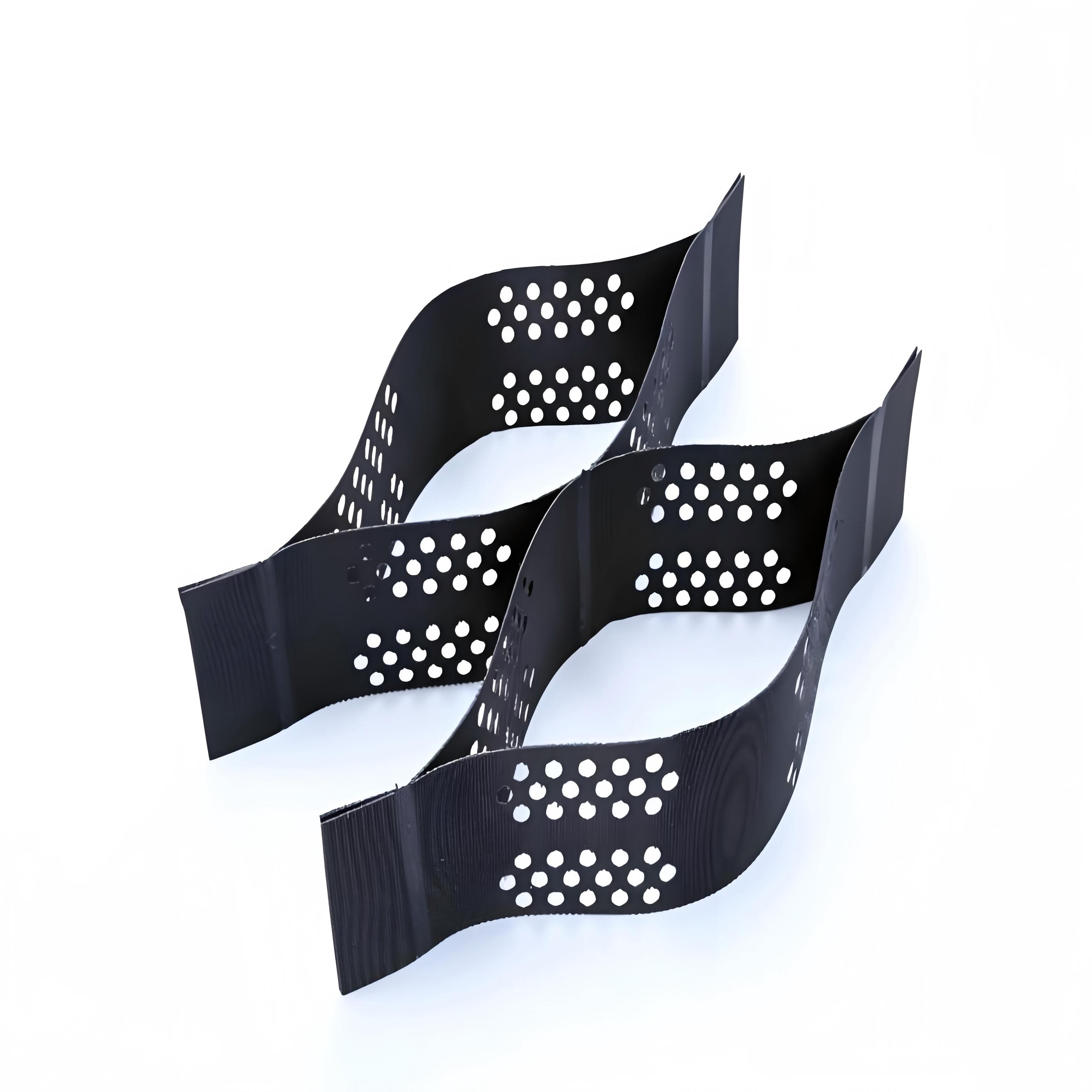
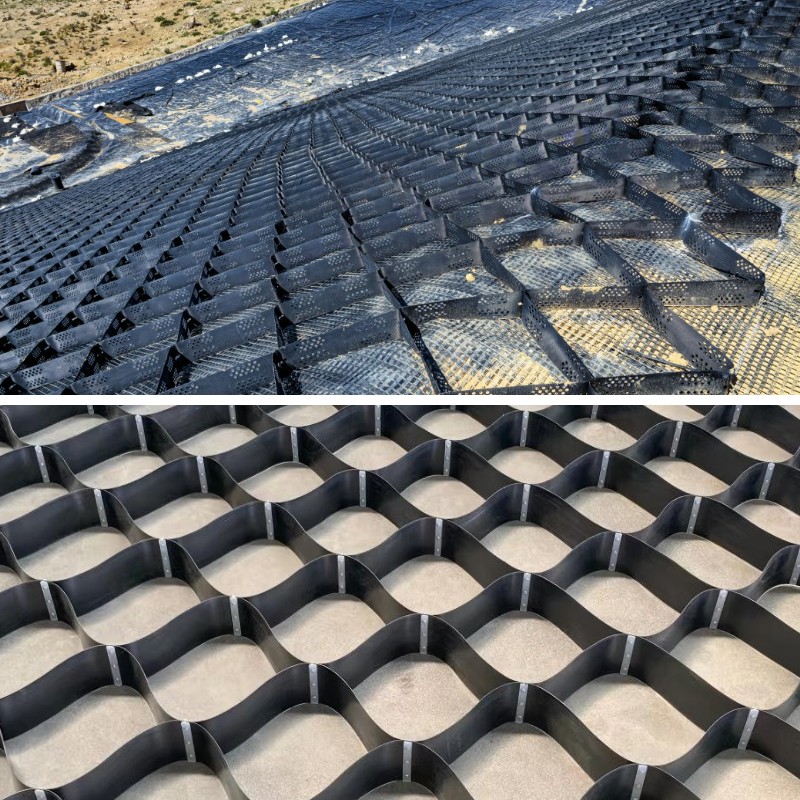
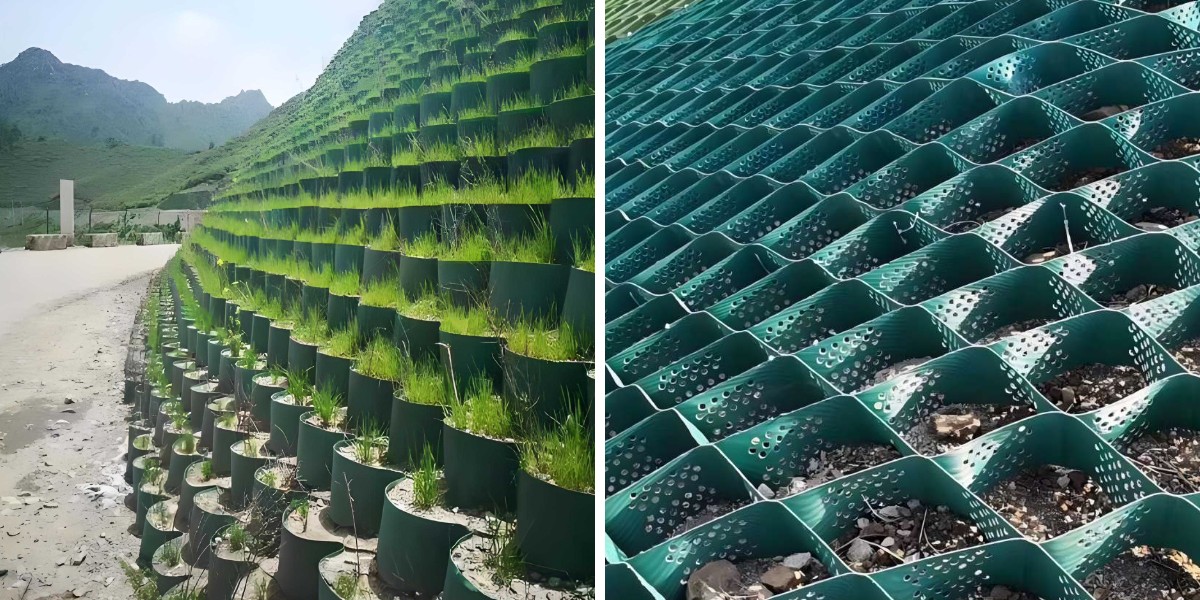
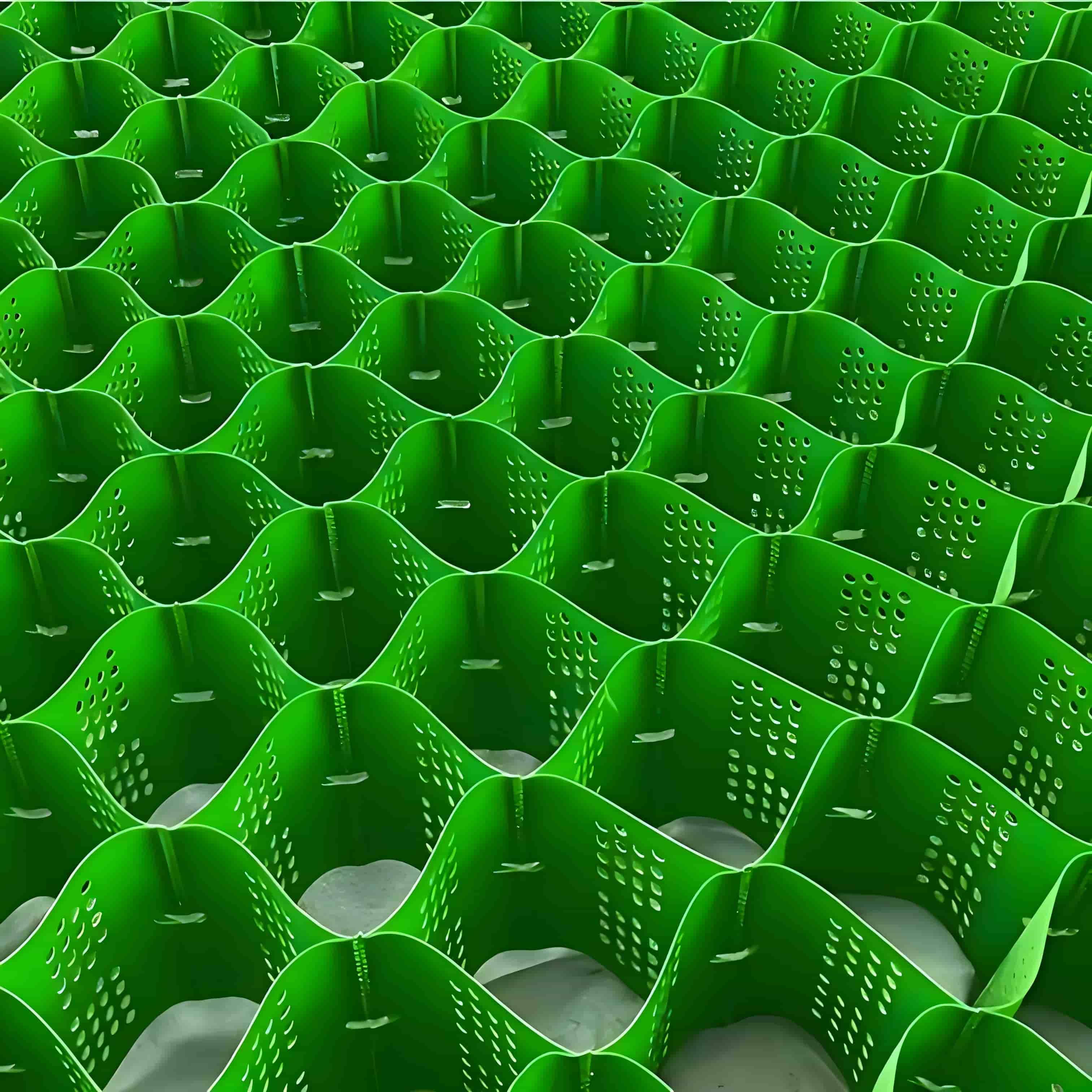
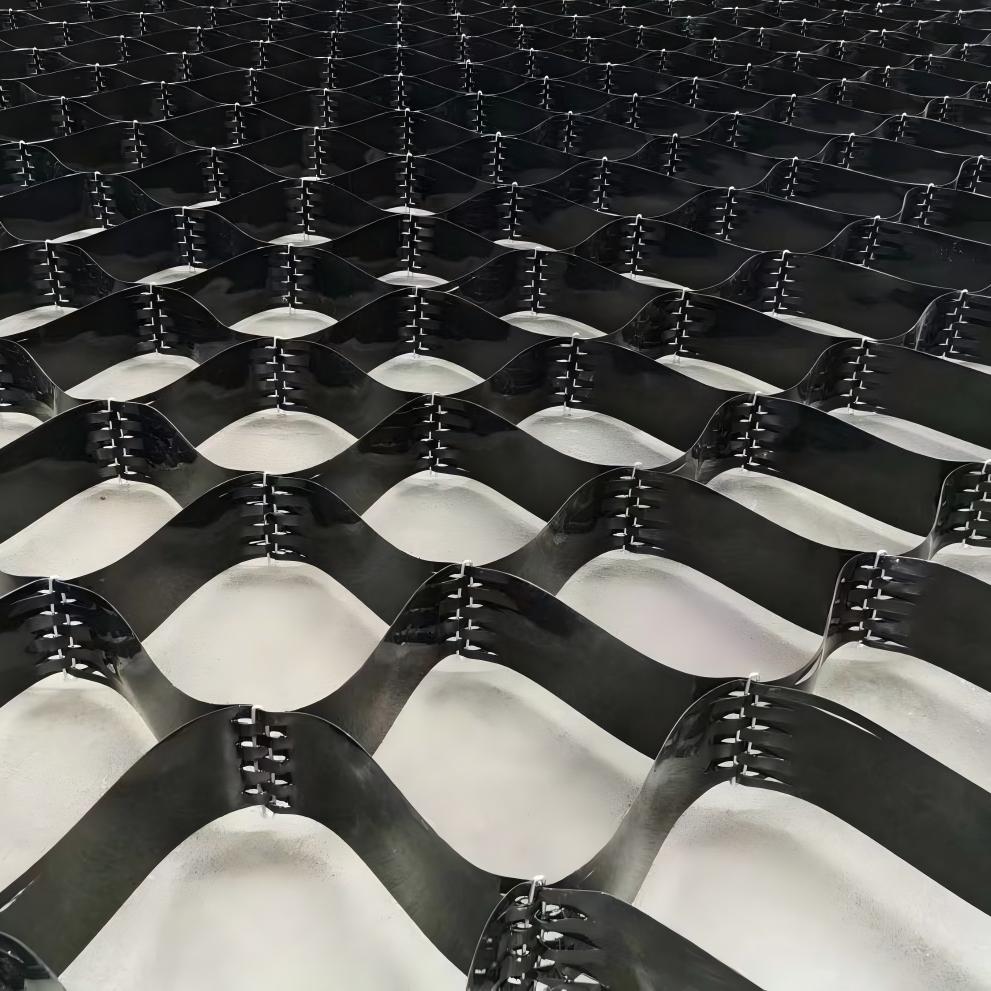
Road Construction Geocell
1. Enhance the bearing capacity of the foundation: disperse the load, reduce uneven settlement, suitable for soft soil subgrade treatment.
2. Preventing soil erosion: When used for slope protection, it can effectively fix the soil, reduce erosion and landslide risks.
3. Save material costs: Compared to traditional concrete or masonry structures, reduce the amount of filler used and lower project costs.
4. Environmental sustainability: recyclable and reduces damage to the natural environment, in line with the concept of green construction.
5. Strong adaptability: It can be used for various complex geological conditions such as steep slopes, deserts, wetlands, etc.
Product Introduction:
Road Construction Geocell is a three-dimensional mesh structure material made of high-strength polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) or other polymer materials processed by special processes. It is usually composed of multiple identical cells arranged in a honeycomb or grid pattern, which can form a three-dimensional structure with a certain height and stiffness when unfolded. When in use, it can be stretched to unfold and then filled with materials such as sand, gravel, soil, etc., thereby exerting reinforcement, protection, and other effects.
Characteristics
Three dimensional structure: This is the most prominent feature of geogrids. It is different from traditional planar geotechnical materials. The three-dimensional structure formed after unfolding can form lateral constraints on the materials filled in it, limit the lateral displacement of the materials, and improve the stability of the structure.
Scalability: During transportation and storage, the geogrid can be folded up, with a small volume, making it easy to transport and store; At the construction site, it can be stretched to the design size as needed, making it easy to operate.
High strength and durability: The polymer materials used have high mechanical properties such as tensile strength and tear strength, and can withstand large loads. At the same time, this material also has good corrosion resistance, aging resistance, and UV resistance, and can play a long-term role in various complex environments.
Permeability: Its grid structure allows for the circulation of water and air, which is beneficial for removing accumulated water inside the structure and reducing water erosion on the structure.
Product Parameters:
order number | raw and processed material | |||||||
test item | unit | polytene | sulan | polyester | ||||
Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | |||
1 | tensile strength | kN/m | ≥20 | ≥100 | ≥23 | ≥100 | ≥30 | ≥120 |
2 | Tensile yield strain | % | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | - |
3 | Tensile fracture strain | % | — | 8~ 20 | — | 6~ 15 | — | 8~ 20 |
4 | Carbon black content a | % | 2. 0~ 3. 0 | |||||
5 | Carbon black dispersion a | — | There should be no more than one level 3 data item in ten data items and no level 4 or 5 data items | |||||
6 | 200℃ oxidation induction time | min | ≥20 | ≥20 | — | |||
7 | Tensile load stress cracking | h | ≥300 | — | ||||
8 | B. Resistance to artificial climate aging retention rateb | % | ≥80 | |||||
9 | Chemical resistance performance retention rate c | % | — | ≥80 | ||||
Product Applications:
1. Transportation Engineering
Roadbed reinforcement: deal with semi filled and semi excavated roadbeds, roadbeds in windy and sandy areas, and solve the problem of uneven settlement. For example, when laying geogrids on steep slopes, the width of the steps can be reduced to 1 meter while ensuring stability.
Backfill soil: Reduce the settlement difference between the bridge pier and the roadbed, alleviate the phenomenon of "bridge head jumping", and extend the service life of the bridge deck.
2. Water conservancy and coastal engineering
River management: As a revetment structure, it enhances soil erosion resistance and protects riverbank vegetation. For example, in the treatment of the mudflat of the Yellow River, the stability of the bank slope was improved by 40% due to the geocell.
Coastal protection: resist wave erosion, prevent beach degradation, and maintain coastal ecosystems.
3. Prevention and control of geological disasters
Slope stability: Construct flexible retaining walls in landslide and debris flow prone areas, and prevent soil sliding through the frictional force between the grid and the filling material.
Earthquake protection: In earthquake active areas, geogrids can absorb some seismic energy and reduce structural damage.
4. Special geological treatment
Permafrost area: Ensure the minimum filling height to prevent roadbed collapse caused by thawing of the frozen layer.
Collapsible loess area: By limiting the collapsible deformation of loess through grid cells, the bearing capacity of the foundation is improved.
5. Agriculture and Environmental Protection
Greenhouse construction: As a foundation reinforcement material, it improves the wind resistance of the greenhouse.
Waste disposal: Limit the spread of pollutants and prevent soil and groundwater pollution.
Geogrids have become an indispensable reinforcement material in modern civil engineering due to their unique three-dimensional structure, excellent material properties, and wide applicability. From transportation roadbeds to coastal protection, from geological disaster management to ecological restoration, its economic and functional advantages continue to drive the progress of engineering technology. With the development of materials science, the application scenarios of geogrids will be further expanded, providing more efficient solutions for global infrastructure construction.