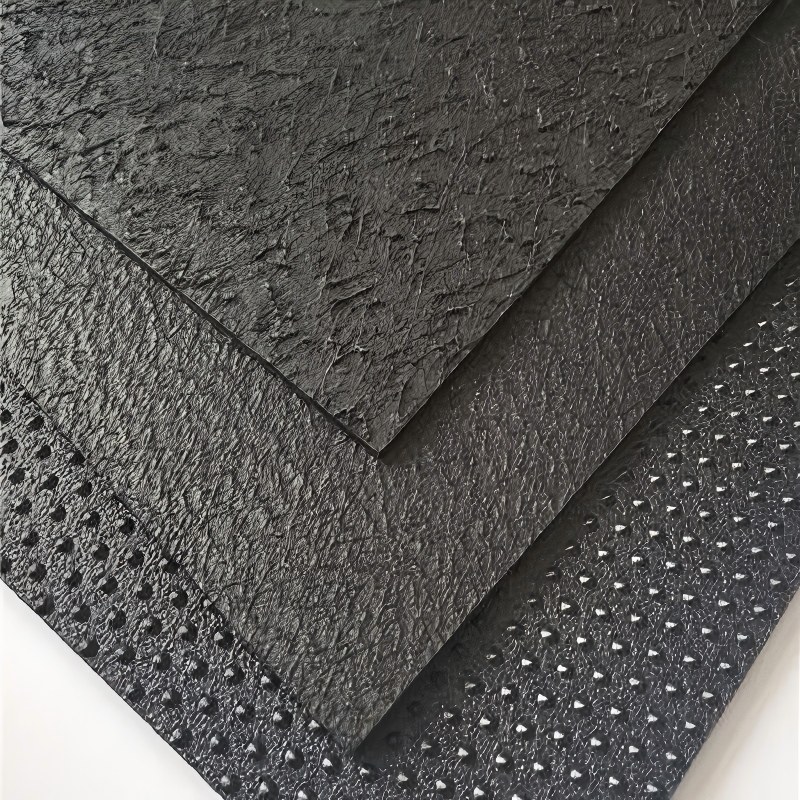
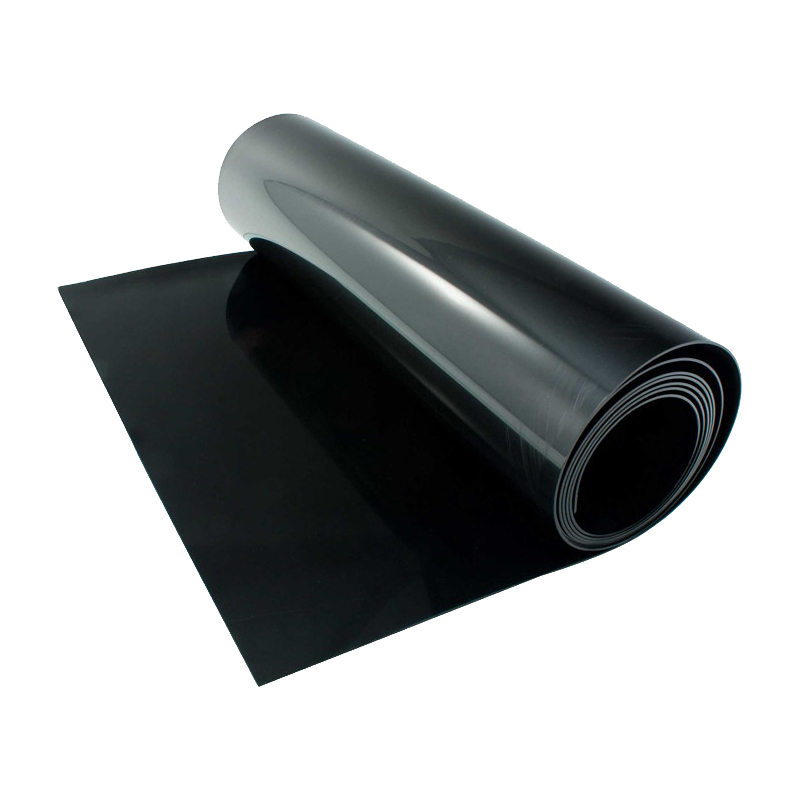
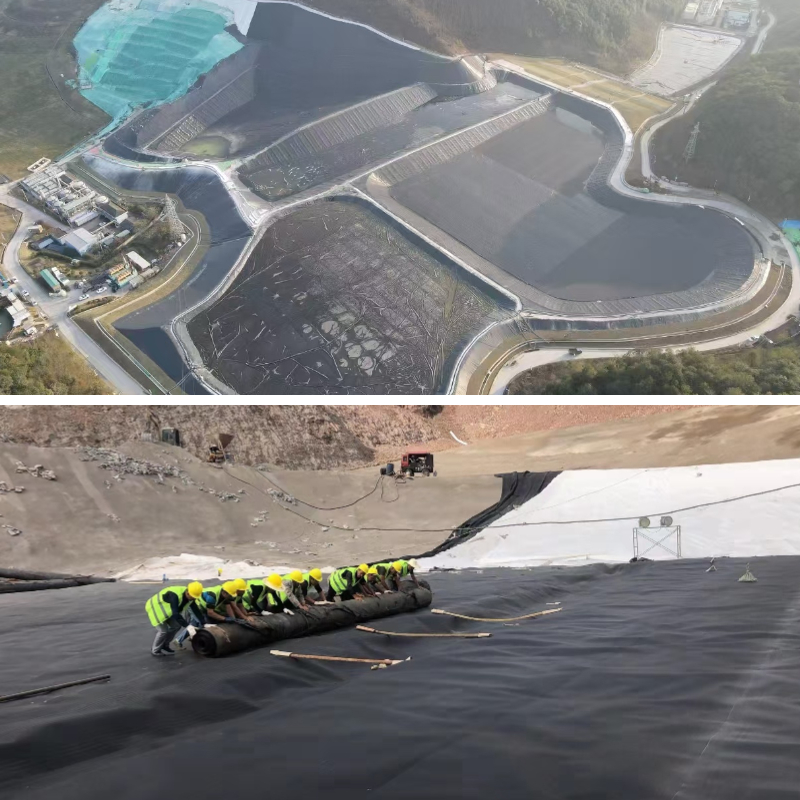
Geomembrana HDPE 30 mils
1.Excellent anti-seepage performance
Extremely low permeability coefficient (usually ≤ 10 ⁻¹³ cm/s), almost impermeable and non breathable, can effectively prevent the penetration of liquids and gases.
2. Excellent chemical corrosion resistance
HDPE, PVC and other materials can withstand acidic and alkaline environments with pH 2-13, and are suitable for corrosive environments such as chemical and mining industries.
3. High strength and durability
High tensile strength, puncture resistance, suitable for complex foundations. HDPE film with added anti UV agents has a long outdoor lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
4. Flexible construction
It can fit uneven base layers and is suitable for special terrains such as slopes and bends. The coil form is convenient for transportation and mechanized construction, greatly improving efficiency
Product Introduction:
Geomembrana HDPE 30 mils is a waterproof and barrier material made from polymer materials, widely used in civil engineering, water conservancy engineering, environmental engineering and other fields, mainly for anti-seepage, isolation, protection, etc.
Core performance characteristics
1. Anti leakage performance
The permeability coefficient of geomembrane is extremely low, which can effectively prevent the infiltration of liquids or gases and is the core material of anti-seepage engineering.
2. Chemical resistance
It has good tolerance to chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and salts, and is suitable for corrosive environments such as landfills and chemical tanks.
3. Aging resistance
After adding anti UV agents, it can be used outdoors for a long time to resist UV rays, oxidation, and temperature changes.
4. Mechanical strength
High strength geomembranes (such as HDPE) can withstand significant tensile, tearing, and puncture forces, and are suitable for foundation settlement or deformation.
5. Construction convenience
Lightweight, foldable, easy to transport and lay; A continuous anti-seepage layer can be formed by hot melt welding or adhesive connection.
Product Parameters:
Metric | ASTM | unit | Test value | Minimum test frequency | ||||||
test method | 0.75 mm | 1.00 mm | 1.25 mm | 1.50 mm | 2.00 mm | 2.50mm | 3.00 mm | |||
Minimum average thickness | D5199 | mm | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | Per volume |
Minimum value (any one of 10) | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | |||
minimum density | D 1505/D 792 | g/cm3 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 90,000 kg |
Minimum average tensile performance (1) | D638 Type IV | |||||||||
Breakage strength, | N/mm | 20 | 27 | 33 | 40 | 53 | 67 | 80 | 9,000 kg | |
yield strength | N/mm | 11 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 29 | 37 | 44 | ||
Strain extension, | % | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | ||
yield extension | % | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | ||
Minimum strength of right-angle tear | D 1004 | N | 93 | 125 | 156 | 187 | 249 | 311 | 374 | 20,000 kg |
Minimum puncture strength | D4833 | N | 240 | 320 | 400 | 480 | 640 | 800 | 960 | 20,000 kg |
Constant tensile load stress cracking (2) | D5397 | hour | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | Based on GRI GM-10 |
Carbon black content | D 1603(3) | % | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 9,000 kg |
Carbon black dispersion | D5596 | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | 20,000 kg | |
Oxygen induction time (OIT) (5) | 90,000 kg | |||||||||
(a) Standard OIT | D3895 | minute | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
(b) high-handed OIT | D5885 | minute | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | |
85℃ Oven aging (minimum average) (5)(6) | Per formula | |||||||||
(A) Standard OIT is retained after 90 days | D 5721 | % | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | |
(B) High voltage OIT is retained for 90 days | D 3895 D5885 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | |
Ultraviolet resistance (7) | Per formula | |||||||||
(a) standard OIT | D3895 | Note (8) 50 | ||||||||
(b) Retention of high pressure OIT after 1600 hours (9) | D5885 | % | ||||||||
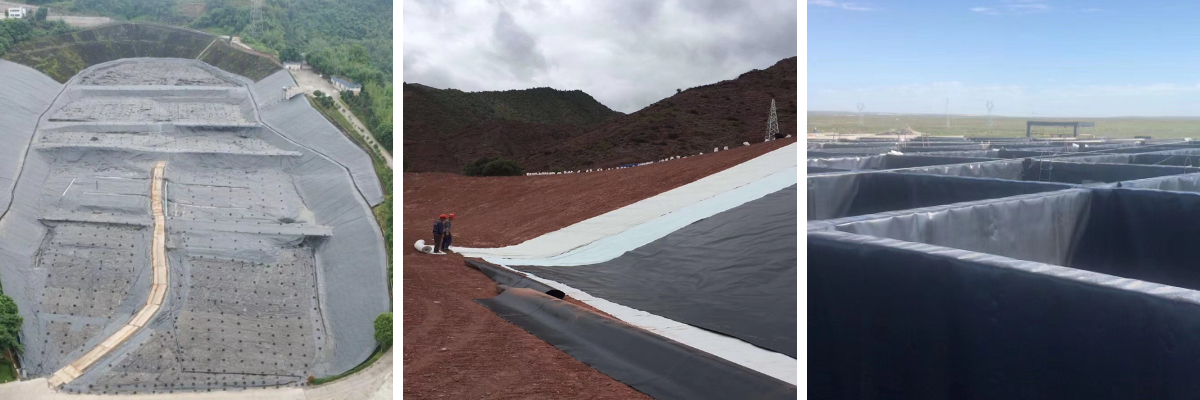
Product Applications:
1.Water conservancy engineering: used for anti-seepage treatment of reservoirs, dams, canals, pools, etc., to prevent water resource leakage and improve the efficiency and safety of water conservancy facilities.
2.Environmental protection engineering: anti-seepage liners for landfills can prevent soil and groundwater pollution caused by leachate from garbage; It is also widely used in sewage treatment plants, industrial wastewater treatment tanks, etc. to protect the surrounding environment from pollution.
3.Transportation engineering: waterproofing of roadbeds and railways, waterproofing and moisture proofing of tunnels, etc., can improve the durability of roads and tunnels, reduce water damage to roadbeds and structures.
4.Agricultural engineering: used for anti-seepage of irrigation channels, ponds, aquaculture ponds, etc., reducing water evaporation and leakage, and improving water resource utilization efficiency; It can also be used to prevent plant root penetration, protect underground pipelines and structures.
5.Mining engineering: anti-seepage treatment of tailings ponds to prevent harmful substances from leaking and polluting soil and water sources; It is also applied in drainage systems and heap leaching sites in mines.
The core advantages of geomembranes are "reliable anti-seepage, corrosion resistance, economic efficiency, and convenient construction", making them an irreplaceable anti-seepage material in modern engineering.