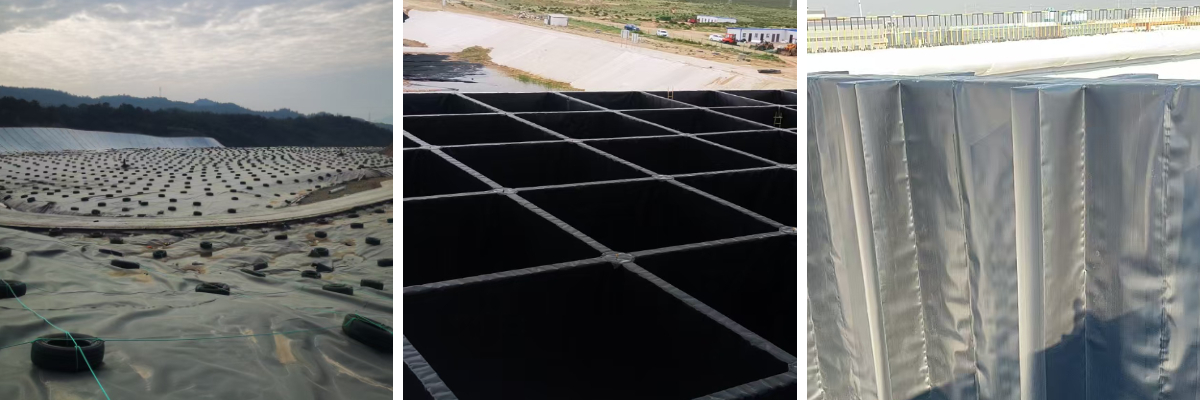
HDPE Sheet for Pond
1. Extremely high efficiency: Its anti-seepage effect is millions or even tens of millions of times that of high-quality compacted clay.
2. Space saving: The thickness is usually between 0.5mm and 3.0mm, which requires much less space than the clay lining layer that requires a large thickness.
3. Fast construction speed: significantly reducing complex processes such as soil excavation and compaction, mechanized laying and welding, and short construction period.
4. Strong adaptability to deformation: Good flexibility enables it to adapt well to the settlement and deformation of the foundation, and is not easily cracked.
5. Controllable quality: It is an industrialized production product with uniform and stable quality, while the quality of clay is greatly affected by soil sources and is difficult to control.
Product Introduction:
HDPE Sheet for Pond is a thin and flexible material with extremely low permeability, mainly made from high molecular weight polymers such as polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), etc. It is classified as an anti-seepage and isolation material in the geosynthetics family.
Its core function is to block the migration of fluids (liquids or gases) and act as an artificial impermeable barrier in engineering, thereby controlling the movement path of fluids and preventing leakage and pollution.
Main Features
The characteristics of geomembranes are mainly reflected in their material and engineering properties:
1. Extremely low permeability: This is its most core characteristic, with a permeability coefficient usually less than 10 ⁻¹¹~10 ⁻¹³ m/s, almost considered impermeable.
2. Excellent anti-seepage performance: It can effectively prevent the leakage of fluids such as water, chemical solutions, biogas, volatile gases, etc.
3. Good durability and aging resistance: by adding carbon black, antioxidant, anti ultraviolet agent, etc., it can resist ultraviolet radiation, temperature change, chemical and biological erosion, and its service life can reach decades or even longer.
4. High strength and ductility: It has good tensile, tear, and puncture resistance, and can adapt to uneven settlement and deformation of the foundation.
5. Strong chemical stability: able to resist corrosion from various acids, bases, salts, and oils, suitable for various complex environments, especially in landfills and chemical fields.
6. Easy construction and high cost-effectiveness: Compared to traditional anti-seepage structures such as concrete and clay, geomembranes are lightweight, easy to transport, and have fast construction speed, resulting in lower overall costs.
Common types
According to the differences in raw materials and manufacturing processes, they are mainly divided into the following categories:
1. HDPE geomembrane (high-density polyethylene geomembrane):
Features: High strength, extremely strong resistance to chemical corrosion, good resistance to UV aging, long service life.
Application: It is the most widely used type, especially suitable for projects with strict environmental requirements, such as landfills, hazardous waste disposal sites, mining tailings ponds, etc.
2. LLDPE geomembrane (linear low-density polyethylene geomembrane):
Features: softer than HDPE, better ductility, stronger resistance to stress cracking, and better adaptability to uneven settlement.
Application: Suitable for occasions with high deformation requirements, such as landfill closure, artificial lakes, landscape water bodies, etc.
3. PVC geomembrane (polyvinyl chloride geomembrane):
Features: Good flexibility, easy welding, low cost. But its UV resistance and resistance to certain organic solvents are not as good as HDPE.
Application: Commonly used in water conservancy projects (channels, reservoirs), garden landscapes, basement anti-seepage, etc.
Product Parameters:
metric | ASTM | unit | test value | Minimum test frequency | ||||||
test method | 0.75 mm | 1.00 mm | 1.25 mm | 1.50 mm | 2.00 mm | 2.50mm | 3.00 mm | |||
Minimum average thickness | D5199 | mm | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | Per volume |
Minimum value (any one of 10) | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | |||
minimum density | D 1505/D 792 | g/cm3 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 90,000 kg |
Minimum average tensile performance (1) | D638 Type IV | |||||||||
Breakage strength, | N/mm | 20 | 27 | 33 | 40 | 53 | 67 | 80 | 9,000 kg | |
yield strength | N/mm | 11 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 29 | 37 | 44 | ||
Strain extension, | % | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | ||
yield extension | % | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | ||
Minimum strength of right-angle tear | D 1004 | N | 93 | 125 | 156 | 187 | 249 | 311 | 374 | 20,000 kg |
Minimum puncture strength | D4833 | N | 240 | 320 | 400 | 480 | 640 | 800 | 960 | 20,000 kg |
Constant tensile load stress cracking (2) | D5397 | hour | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | Based on GRI GM-10 |
Carbon black content | D 1603(3) | % | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 9,000 kg |
Carbon black dispersion | D5596 | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | 20,000 kg | |
Oxygen induction time (OIT) (5) | D3895 | minute | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90,000 kg |
(a) Standard OIT | D5885 | minute | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | |
(b) high-handed OIT | ||||||||||
85℃ Oven aging (minimum average) (5)(6) | Per formula | |||||||||
(A) Standard OIT is retained after 90 days | D 5721 | % | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | |
(B) High voltage OIT is retained for 90 days | D 3895 D5885 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | |
Ultraviolet resistance (7) | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Note (8) 50 | Per formula | ||
(a) standard OIT | D3895 | |||||||||
(b) Retention of high pressure OIT after 1600 hours (9) | D5885 | % |
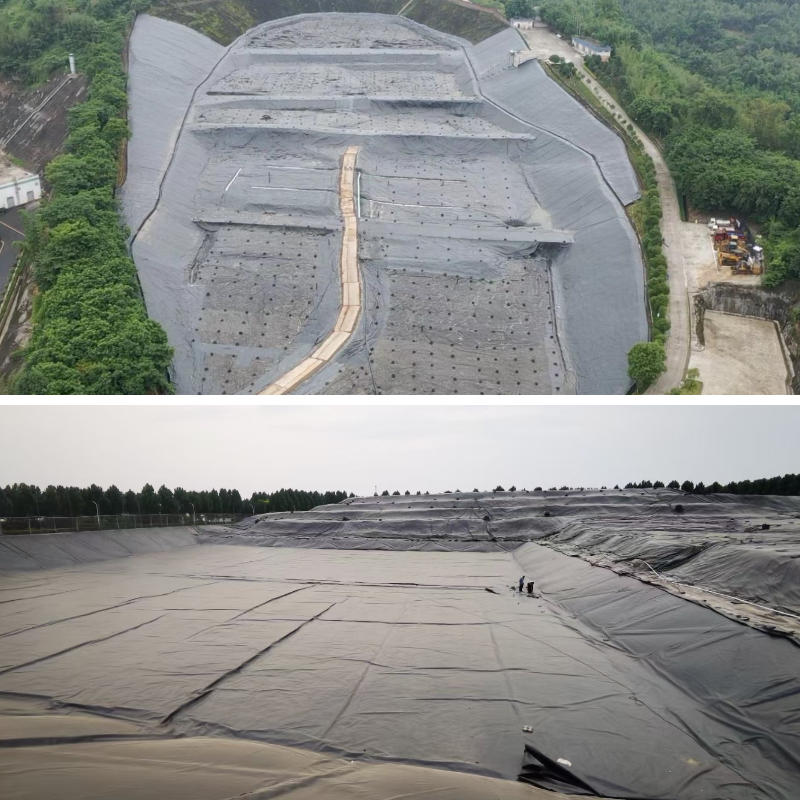
Product Applications:
1. Water conservancy engineering
The anti-seepage treatment of reservoirs and dams to prevent dam leakage;
Preventing seepage in channels and irrigation systems to reduce water resource depletion;
The anti-seepage lining of rivers and lakes is used to control soil erosion.
2. Municipal and environmental engineering
The anti-seepage layer of landfill sites (household waste, industrial waste) is used to prevent soil and groundwater pollution caused by leachate;
Anti seepage measures for sewage treatment tanks and oxidation ponds to prevent sewage leakage;
The anti-seepage of artificial lakes and landscape water pools ensures stable water levels.
3. Mining Engineering
The anti-seepage of tailings pond to prevent the infiltration of tailings liquid and pollution of the surrounding environment;
The anti-seepage of heap leaching tanks and sedimentation tanks, and the recovery of useful minerals.
4. Transportation Engineering
The roadbed of highways and railways is anti-seepage to prevent groundwater from rising and affecting the stability of the roadbed;
Waterproof lining for tunnels and culverts to reduce water seepage hazards.
5. Agriculture and Aquaculture
The anti-seepage of reservoirs and fish ponds improves the utilization rate of water resources and prevents the loss of aquaculture water bodies.
6. Other fields
Anti seepage measures in the petrochemical storage tank area to prevent oil leakage;
Anti seepage layers for golf courses, rooftop gardens, etc.
As an efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly anti-seepage material, geomembrane plays an irreplaceable role in civil engineering, environmental protection, water conservancy, and other fields due to its excellent performance and wide adaptability. It is one of the core materials for achieving anti-seepage and isolation functions in modern engineering.