Synthetic Geotextile
1.Strong Durability: Anti-aging, acid and alkali resistant, not easy to corrode, with longer service life than natural materials.
2.Effective Water Filtration: Can retain soil particles and drain water quickly, preventing subgrades/dikes from damage caused by water accumulation.
3.Good Reinforcement: Tensile-resistant and not easy to deform; when laid in soil, it stabilizes slopes and improves bearing capacity.
4.Easy Construction: Light in weight, easy to cut and transport; quick to lay without complex equipment, saving costs and time.
Product Introduction
1. Basic Properties
Material: Synthetic Geotextile are made from synthetic polymers such as polypropylene (PP) and polyester (PET).
Durability: Anti-aging, acid and alkali resistant, non-biodegradable, and with a service life longer than natural geotextiles.
Physical Properties: Lightweight and flexible fiber structure, ensuring basic use in complex environments.
2. Core Functions
Filtration and Drainage: Retains soil particles to prevent clogging, quickly drains seepage water, and stabilizes the soil structure (preventing damage to roadbeds and embankments due to water pressure).
Reinforcement: High tensile strength resists deformation. When laid in the soil, it transfers stress, constrains soil movement, and improves the bearing capacity of slopes and roadbeds.
3. Key Features
Easy Installation: Easy to cut and transport in rolls, ensuring efficient on-site installation without the need for complex equipment (reducing project costs and time).
Adaptability: Compatible with a variety of substrates, including soil and sand and gravel, making it suitable for a variety of projects, including water conservancy projects, roads, and landfills.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
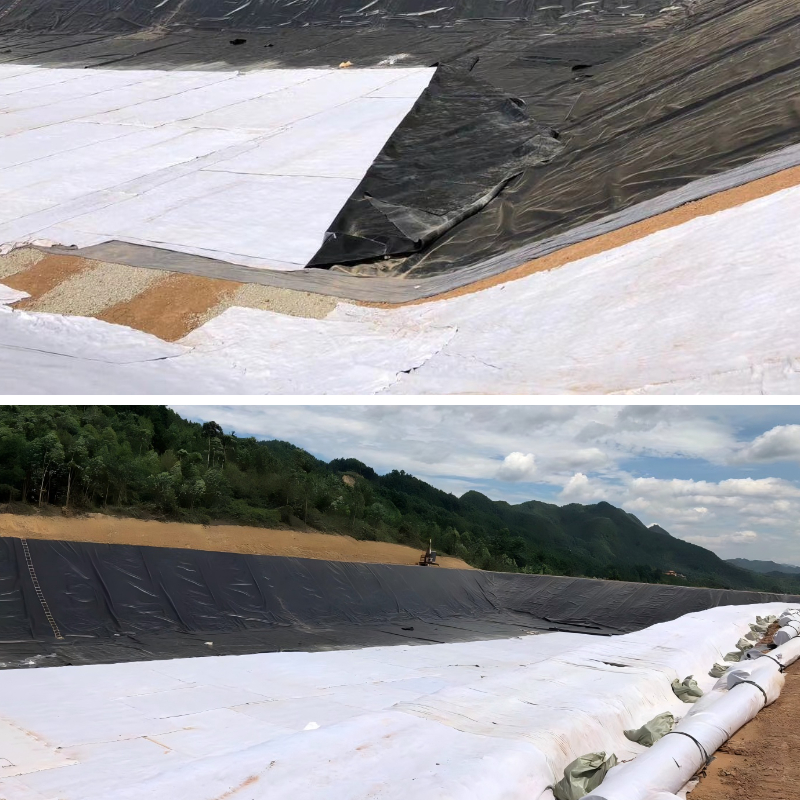
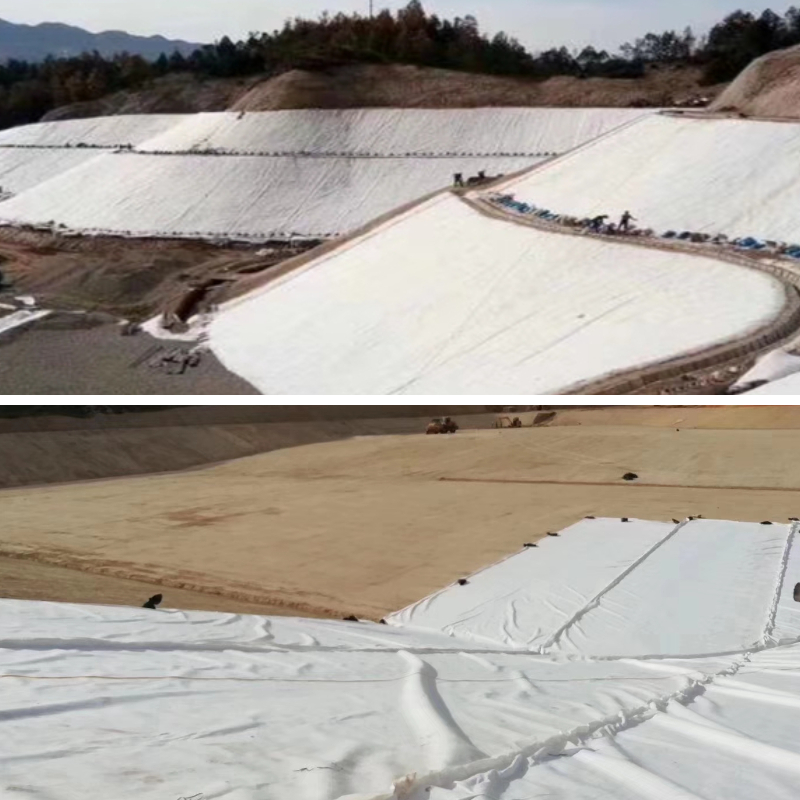
Product Application
1. Water Conservancy Projects
Dam/Riverbank Protection: Installed on the inside of dams or slopes, it combines filtering and anti-seepage functions—it intercepts soil particles to prevent loss while simultaneously draining away seepage, preventing pipe bursts and collapses caused by excessive water pressure.
Reservoir/Channel Anti-seepage: Used in conjunction with anti-seepage membranes, it enhances anti-seepage effectiveness, reduces water seepage, and its acid and alkali resistance protects against long-term erosion.
River Management: Used for ecological revetments along river slopes, it maintains soil stability while allowing water infiltration, achieving both ecological and protective benefits.
2. Transportation Engineering
Highway/Railway Roadbed: Laid between the roadbed base and the soil, it serves as an isolation and reinforcement layer—isolating different soil layers and preventing mixing. It also constrains soil displacement through tensile strength, reducing roadbed settlement and cracking.
Airport Runway/Parking Lot Base: Improves the bearing capacity of the base, filters water seepage, prevents structural damage caused by accumulated water, and extends the service life of runways and parking lots.
Tunnel/Culvert Drainage: Laid in blind drains on both sides of tunnels, it filters groundwater impurities, prevents blind drain clogging, ensures smooth drainage, and prevents tunnel water seepage.
3. Environmental Engineering
Landfills: Serves as a supplementary layer in anti-seepage systems—laid below the anti-seepage membrane (to protect it from sharp impurities) and above it (to filter impurities in the leachate and prevent clogging of the drainage system). Its corrosion resistance protects against chemical attack from landfill leachate.
Sewage Treatment Plants: Serves as a filter layer in sedimentation tanks and filter beds, intercepting suspended impurities in wastewater and improving water purification. It is easy to clean and has a long service life.
Mine Ecological Restoration: Covering abandoned mine slopes stabilizes soil and prevents soil erosion, while allowing plant roots to penetrate and aid ecological restoration.
4. Construction and Municipal Engineering
Underground Building Drainage: For example, underground garage roofs and basement side walls, laid outside the waterproofing membrane, drains structural water seepage and prevents damage to the waterproofing layer due to water pressure.
Rooftop/Courtyard Greening: Serves as a filter layer between the planting layer and the drainage layer, intercepting soil particles, preventing clogging of the drainage layer and ensuring smooth drainage in the green area.
Municipal Road Drainage: Used in drainage ditches on both sides of roads or in sidewalk subgrades, it quickly drains rainwater from the road surface, reduces surface water accumulation, and protects road structures.
Synthetic geotextiles, with their core properties of filtration and drainage, reinforcement, corrosion resistance, and durability, are widely applicable in four core engineering fields: water conservancy, transportation, environmental protection, and construction and municipal engineering. In various scenarios, they can address key issues such as soil stability, waterproofing and anti-seepage, and impurity filtration. They can also reduce project costs and extend facility life through convenient construction. In some scenarios, they can also address ecological protection needs, making them a crucial material for improving structural safety and cost-effectiveness in modern engineering construction.