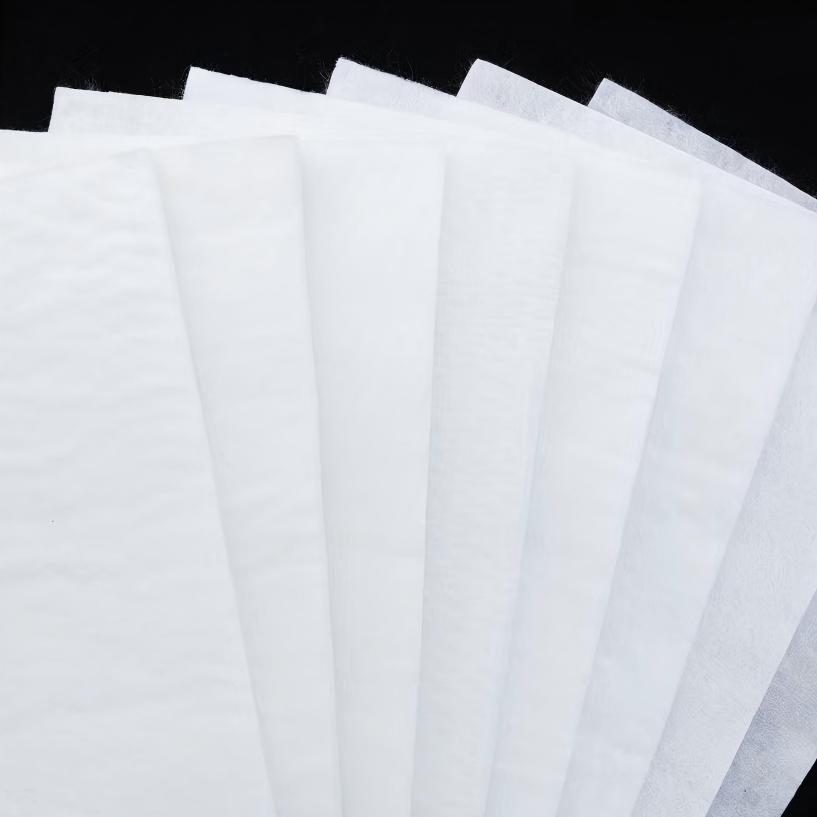
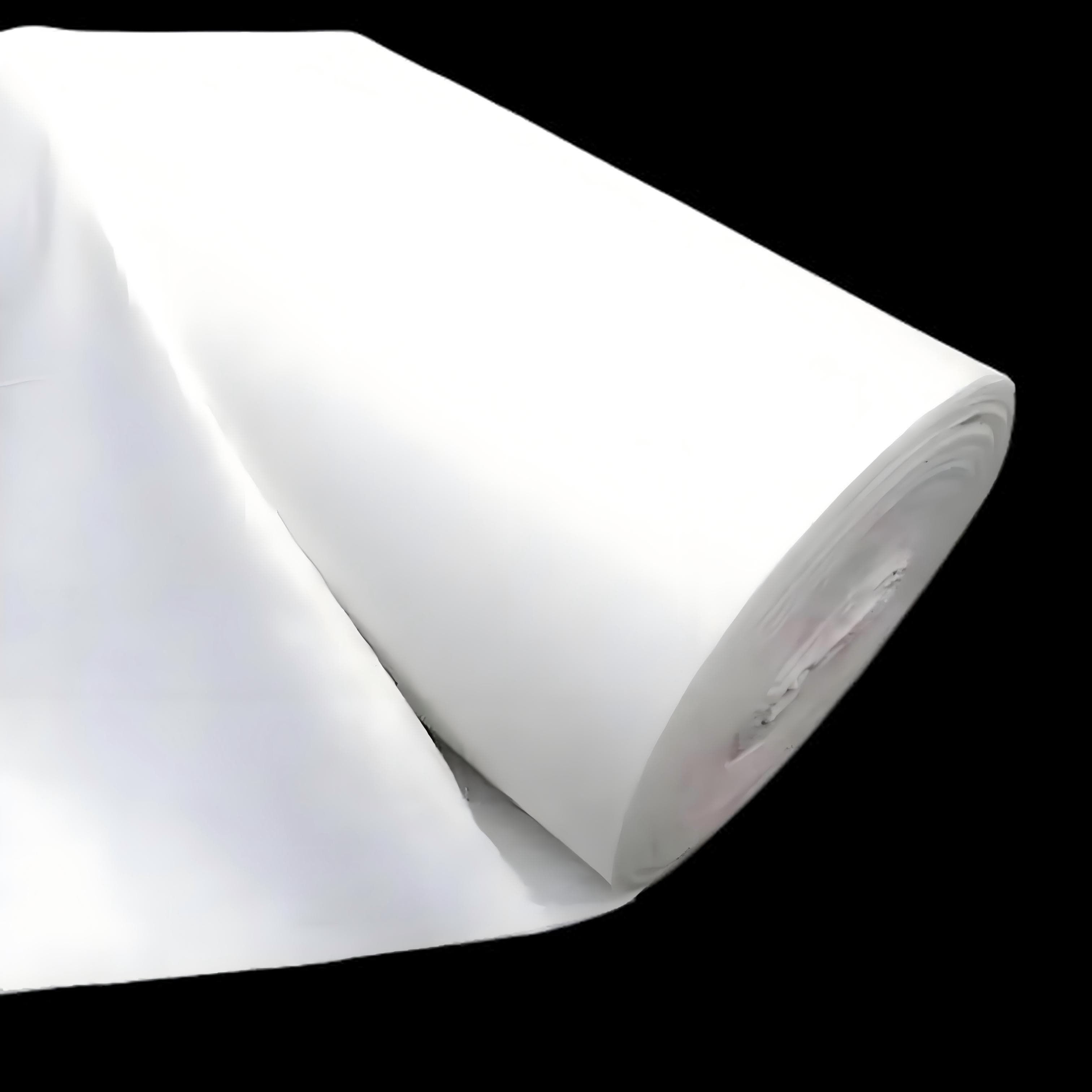
White Geotextile
1. High strength: corrosion resistance, microbial resistance, acid and alkali resistance.
2. Good flexibility: able to adapt to different terrains and uneven settlement.
3. Good permeability: Excellent drainage and filtration performance.
4. Easy to construct: lightweight, easy to transport, cut, and lay.
5. High cost-effectiveness: Long service life, can significantly reduce the use of traditional materials such as stone, lower engineering costs and maintenance expenses.
Product Introduction:
White Geotextile is a permeable geosynthetic material made from synthetic fibers (such as polypropylene, polyester, nylon, etc.) through processes such as needle punching or weaving. It is usually in the form of a roll and looks very much like thick cloth or non-woven fabric.
Geotextile is a very important basic material in geotechnical and civil engineering, known as the "clothing of civil engineering". Its main functions are separation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement, protection, and anti-seepage (when combined with other materials).
Main classifications of geotextiles
According to different manufacturing processes and structures, geotextiles are mainly divided into the following categories:
1. Non woven geotextile (non-woven geotextile)
Manufacturing process: Synthetic fibers are randomly arranged (in a mesh) and reinforced using methods such as mechanical needle punching, thermal bonding, or chemical bonding.
Features: The appearance is fluffy and fluffy, with good vertical permeability and flat drainage ability, high elongation rate, and strong deformation adaptability.
Main uses: drainage, filtration, isolation, and protection.
2. Woven geotextile (woven geotextile)
Manufacturing process: Weaving fiber filaments or flat strips in a certain direction, similar to traditional textile fabrics.
Characteristics: Tight structure, uniform pores, high tensile strength and modulus, but low elongation, and easy deformation of pores.
Main purpose: reinforcement, isolation, especially suitable for places that require high strength.
Manufacturing process: Composite non-woven fabric and woven fabric, or composite geotextile with geosynthetic materials such as geomembranes and grids.
Features: Combining the advantages of multiple materials to achieve the integration of multiple functions, such as integrated anti-seepage and drainage (e.g. sandwich structure of geotextile/geomembrane/geotextile).
Main use: Mainly used for projects that require both anti-seepage and drainage, such as landfills, artificial lakes, and channels.
The core function and principle of action of geotextile
1. Separation
Function: To permanently separate two types of soil or materials with different particle sizes (such as gravel and soft soil), prevent them from mixing with each other, and maintain their respective structures and properties.
Principle: After laying the geotextile, it acts as a barrier to prevent the upper gravel from sinking into the lower soft soil, while allowing water to freely pass through, thus ensuring the stability and bearing capacity of the structure. For example, when building roads on soft soil foundations, laying geotextiles can prevent the crushed stone base from sinking into the soft soil.
2. Filtration
Function: While allowing liquid (water) to pass vertically, it prevents excessive loss of soil particles, prevents soil erosion and piping phenomena.
Principle: Geotextile has countless tiny pores, the size of which allows water to pass through smoothly, but can effectively "intercept" soil particles, forming a natural filter layer. For example, a drainage filter layer used for dams and retaining walls to protect soil from being washed away by water flow.
3. Drainage
Function: Collect and discharge liquids (water or gas) along the interior or plane direction of the geotextile.
Principle: Non woven geotextile itself is a permeable three-dimensional structure that can form drainage channels to collect and guide water to drainage pipes for discharge. For example, used for underground drainage systems and drainage layers behind retaining walls.
4. Reinforcement
Function: Utilizing its high tensile strength to enhance the strength and stability of soil, disperse loads, and reduce deformation.
Principle: Geotextile is buried in the soil, and through its friction with the soil, it transfers local loads to a larger area, thereby limiting the lateral displacement and settlement of the soil. For example, used to reinforce steep slopes, embankments on soft foundations, and ground treatment.
5. Protection
Function: Provide cushioning protection for other anti-seepage materials (such as geomembranes) to prevent piercing by sharp objects.
Principle: Soft and resilient geotextile (usually non-woven fabric) can be used as a cushion layer to absorb and disperse external stress. For example, laying geotextile on top and bottom of HDPE anti-seepage film in a landfill site to protect it from being damaged by bottom layer gravel or upper layer garbage.
6. Anti seepage (composite with other materials)
Function: When geotextile is combined with geomembrane, an impermeable composite structure is formed to prevent liquid leakage.
Principle: Geomembrane provides the anti-seepage main body, while geotextile mainly plays a protective and drainage role.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
1. Transportation Engineering
Road base isolation and reinforcement
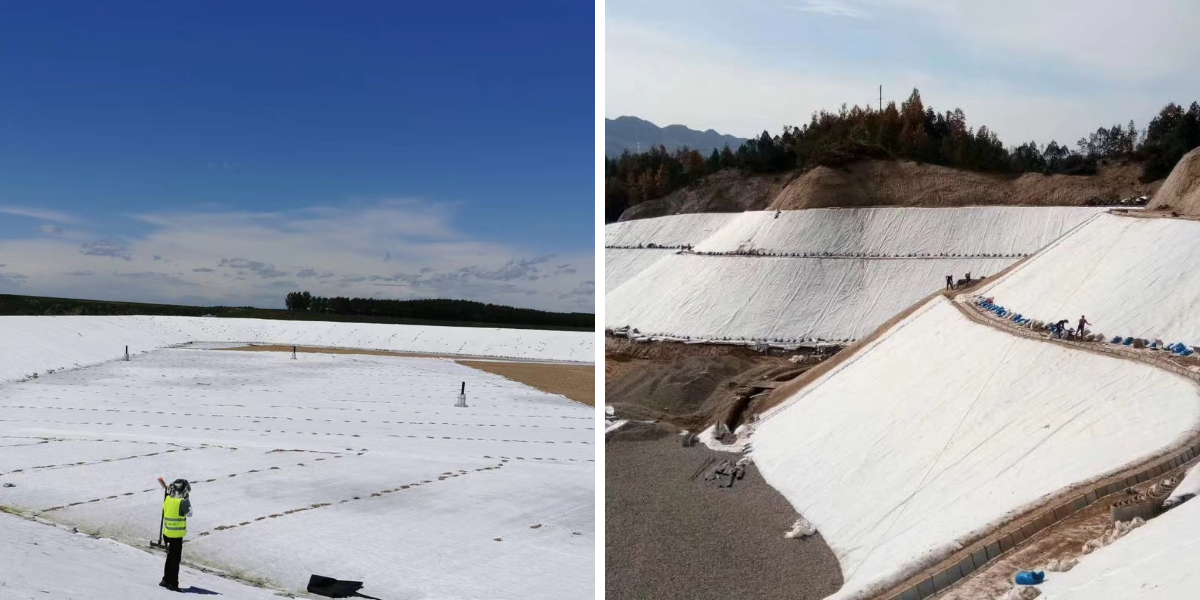
Application scenario: Constructing highways, railways, or airport runways on soft soil foundations.
Benefits: Reduce the amount of gravel used, lower the thickness of the project, save costs, and prevent early damage such as potholes and ruts on the road.
drainage system
Application scenarios: Inside road structures, shoulders, and behind retaining walls.
Function: The non-woven geotextile wraps around the drainage blind ditch or gravel drainage layer, playing a filtering role, allowing water to flow into the drainage pipe while preventing surrounding soil particles from being carried away by water and causing blockage.
2. Water conservancy engineering
Anti filter layer for bank protection
Application scenarios: Embankments, retaining walls, and underwater protective structures of rivers, lakes, and coasts.
Benefits: Replacing traditional graded sand and gravel filter layers, construction is faster, costs are lower, and performance is more stable.
drainage system
Application scenarios: inside earth and rock dams and embankments.
Function: Used as a vertical or horizontal drainage body inside the dam body, collecting seepage and guiding it to a safe zone, reducing the seepage line of the dam body, and increasing stability.
3. Environmental Protection Engineering
landfill
Application scenarios: Landfill bottom lining system, covering system.
Protection: Lay non-woven geotextile on both sides of the anti-seepage main material (HDPE geomembrane) as a protective layer to prevent sharp objects from piercing the geomembrane.
Drainage and filtration: Lay geotextile on top of the geomembrane, and together with the sand layer, form a leachate collection and drainage layer to quickly collect and guide the sewage generated by garbage; In the final covering layer, it is used for gas collection layer and surface drainage layer.
Artificial lake, sewage treatment tank
Application scenarios: Artificial water bodies and oxidation ponds that require anti-seepage measures.
Function: Using a composite structure of "non-woven fabric+geomembrane+non-woven fabric", the geotextile also serves to protect the anti-seepage membrane and facilitate drainage and air circulation.
4. Construction Engineering
foundation drainage
Application scenarios: around building foundations and outside basements.
Function: Lay a drainage board with geotextile on the outside of the foundation wall to form an efficient drainage system, introduce groundwater into the drainage pipe, effectively reduce groundwater pressure, and play a role in waterproofing and moisture-proof.
Roof garden drainage
Application scenarios: Green roofs, rooftop gardens.
Function: Lay geotextile between the planting soil and the lower drainage layer, allowing excess water to infiltrate and be discharged, while preventing soil particle loss from blocking the drainage system.
5. Other applications
Agricultural horticulture: used for soil and water conservation to prevent soil erosion; As a nursery ground cloth, it can inhibit weed growth while also providing water and air permeability.
Tunnel engineering: used between the initial and secondary lining of the tunnel as a drainage layer and buffer layer.
Emergency flood control: used for rapid repair of dams and making flood control bags (filled with sand and soil in geotextile bags).
In summary, the application of geotextiles is a microcosm of modern engineering technology progress. With its diverse functions, reliable performance, and economic cost, it has become the "behind the scenes hero" in building safe, durable, and sustainable infrastructure.