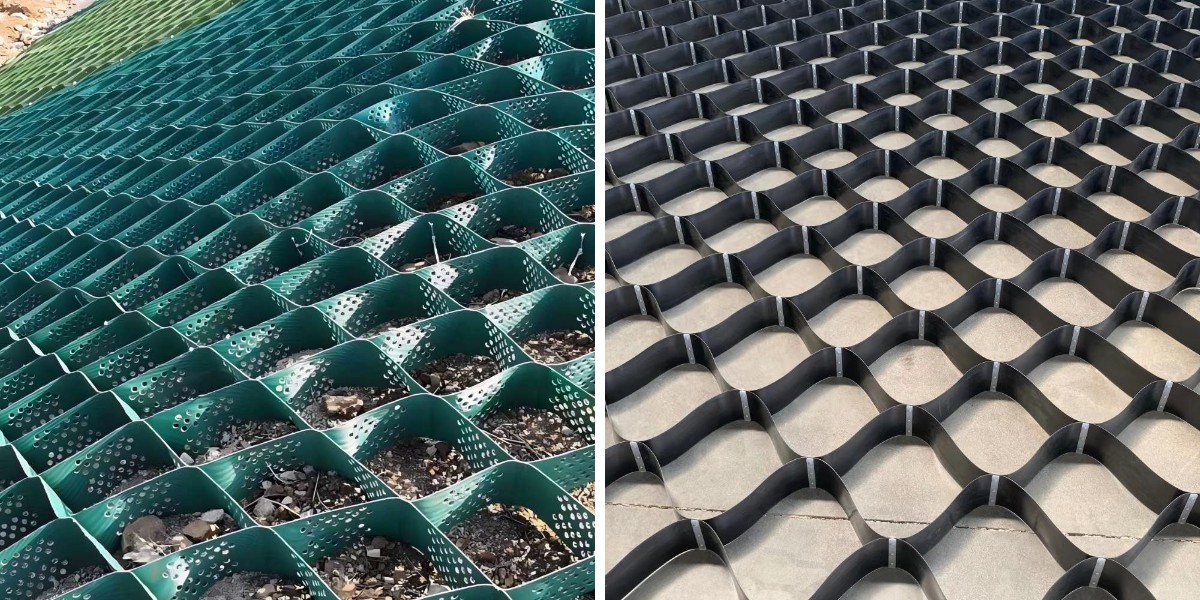
Top 5 Applications of Geocell in Civil Engineering
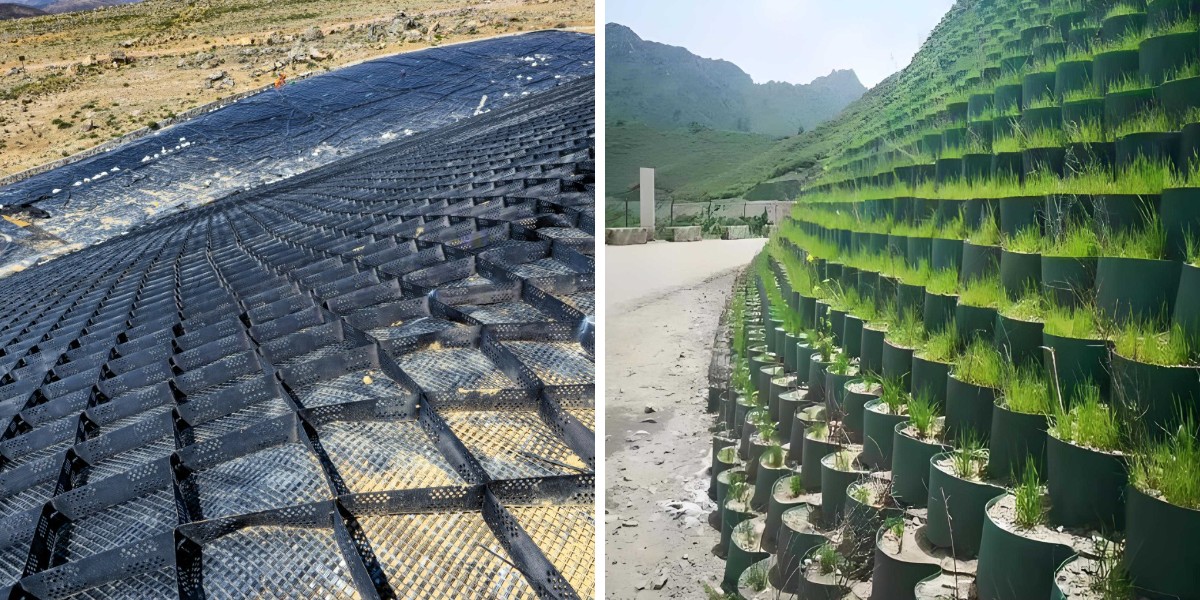
The development enterprise is undergoing a paradigm shift, pushed via revolutionary substances that beautify durability, limit costs, and limit environmental impact. Among these advancements, geocell technology—a third-dimensional cell confinement machine made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE)—has emerged as a game-changer. By developing a honeycomb-like shape that confines soil, gravel, or concrete, geocells distribute masses greater efficiently, forestall erosion, and stabilize slopes. This article explores the pinnacle 5 purposes of geocell in civil engineering, with a center of attention on geocell street construction, slope stabilization, and different imperative use cases.
1. Geocell Road Construction: Reinventing Unpaved and Heavy-Duty Roads
The Challenge of Soft Soil and Heavy Traffic
Unpaved roads in rural areas or industrial zones regularly go through from rutting, dust, and erosion due to susceptible subgrade soils and repeated site visitors loads. Traditional options like thick gravel layers or concrete slabs are high-priced and time-consuming. Similarly, heavy-duty roads in ports, mining sites, or army zones require strong foundations to face up to excessive masses besides immoderate settlement.
How Geocell Roads Work
Geocells tackle these challenges by way of developing a semi-rigid mat that distributes masses laterally. When stuffed with granular cloth (e.g., gravel, beaten stone), the geocell street structure:
Reduces vertical stress on the subgrade by using up to 60%, minimizing deformation.
Enhances resilient modulus (a measure of stiffness) through 40–60%, enhancing fatigue resistance.
Prevents lateral migration of infill material, lowering renovation needs.
Case Study: Mining Road in Australia
A 2024 learn about on a haul avenue in Western Australia tested that geocell-reinforced gravel roads decreased rutting by means of 75% in contrast to unreinforced sections, even underneath 100-ton haul trucks. The assignment additionally reduce fabric charges with the aid of 30% through the usage of domestically sourced recycled asphalt as infill.
2. Geocell Slope Stabilization: Protecting Lives and Infrastructure
The Threat of Erosion and Landslides
Steep slopes (exceeding 1:1 gradient) are susceptible to erosion, specially in waterfront areas or areas with heavy rainfall. Conventional strategies like riprap or concrete blocks are regularly ineffective or visually intrusive.
Geocell Slope Solutions
Geocells stabilize slopes by:
Confining soil or vegetation inside cells, stopping slippage.
Increasing shear energy via interlocking cells and root reinforcement.
Allowing herbal drainage whilst lowering hydraulic pressure.
Case Study: Colorado Highway Slope Protection
In 2023, the Colorado Department of Transportation used geocells to stabilize a 45° slope alongside Interstate 70. The system, crammed with native topsoil and planted with deep-rooted grasses, decreased erosion via 90% and reduce upkeep charges by way of 60% in contrast to typical methods. The assignment additionally blended seamlessly with the surrounding landscape, maintaining herbal aesthetics.
3. Retaining Walls: Building Stronger Structures with Less Material
The Limitations of Traditional Retaining Walls
Concrete gravity partitions or robotically stabilized earth (MSE) partitions require vast excavation, formwork, and reinforcement. In far flung or environmentally touchy areas, these strategies are impractical due to price or logistical constraints.
Geocell Retaining Walls: Lightweight and Flexible
Geocells enable the building of modular conserving partitions by:
Using on-site fill fabric (e.g., soil, gravel) rather of imported concrete.
Reducing excavation depth by using leveraging the wall’s flexibility to take in minor settlements.
Withstanding seismic endeavor higher than inflexible structures, as validated in a 2025 earthquake simulation study.
Case Study: Indian Railway Embankment
In 2024, Indian Railways used geocell-reinforced partitions to stabilize a 10-meter-high embankment in a seismic zone. The device withstood a 7.2-magnitude earthquake besides failure, thanks to its capacity to dissipate electricity via cellphone deformation. The assignment additionally decreased carbon emissions by using 45% with the aid of fending off cement production.
4. Channel and Riverbank Protection: Preventing Erosion in Waterways
The Problem of Hydraulic Erosion
Rivers, canals, and stormwater channels are prone to scouring, specially at bends or outlets. Hard armor options like riprap or gabions are susceptible to displacement below high-velocity flows.
Geocell Erosion Control
Geocells shield waterways by:
Anchoring infill cloth (e.g., riprap, soil) with high-tensile-strength cells.
Reducing turbulence thru a smooth, vegetated surface.
Promoting sediment deposition to rebuild eroded banks naturally.
Case Study: Mississippi River Flood Control
In 2023, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers used geocells to fortify a 200-meter part of the Mississippi River’s left bank. The system, crammed with nearby limestone and planted with wetland grasses, decreased scour depth by way of 80% at some stage in a 100-year flood event. The task additionally created habitat for fish and birds, incomes reward from environmental groups.
5. Temporary Construction Platforms: Rapid Deployment on Soft Ground
The Need for Speed in Construction
In soft-soil areas like swamps or reclaimed land, constructing transient roads or crane pads for building initiatives is time-consuming and expensive. Traditional strategies (e.g., bushes mats, metal plates) frequently sink or shift beneath load.
Geocell Platforms: Instant Stability
Geocells allow speedy deployment by:
Creating a load-bearing floor in hours, no longer days.
Distributing factor masses (e.g., crane outriggers) throughout a broad area.
Requiring minimal excavation—just clear the web site and unfold the cells.
Case Study: Dubai Desert Solar Farm
In 2025, a photo voltaic farm in the Dubai desolate tract used geocell systems to aid 50-ton cranes throughout panel installation. The system, crammed with wasteland sand, executed a bearing potential of 350 kPa in simply 4 hours, reducing venture timelines by way of 30%.
Conclusion: The Future of Geocell in Civil Engineering
From geocell avenue development to slope stabilization and beyond, this technological know-how is redefining infrastructure resilience. By combining strength, flexibility, and sustainability, geocells tackle the industry’s most urgent challenges: lowering costs, minimizing environmental impact, and extending asset lifespans.
As lookup continues—such as the improvement of clever geocells with embedded sensors for real-time monitoring—the functions will solely expand. For engineers, contractors, and planners, embracing geocell science is no longer simply a choice; it’s a necessity in an generation of local weather uncertainty and aid constraints.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province