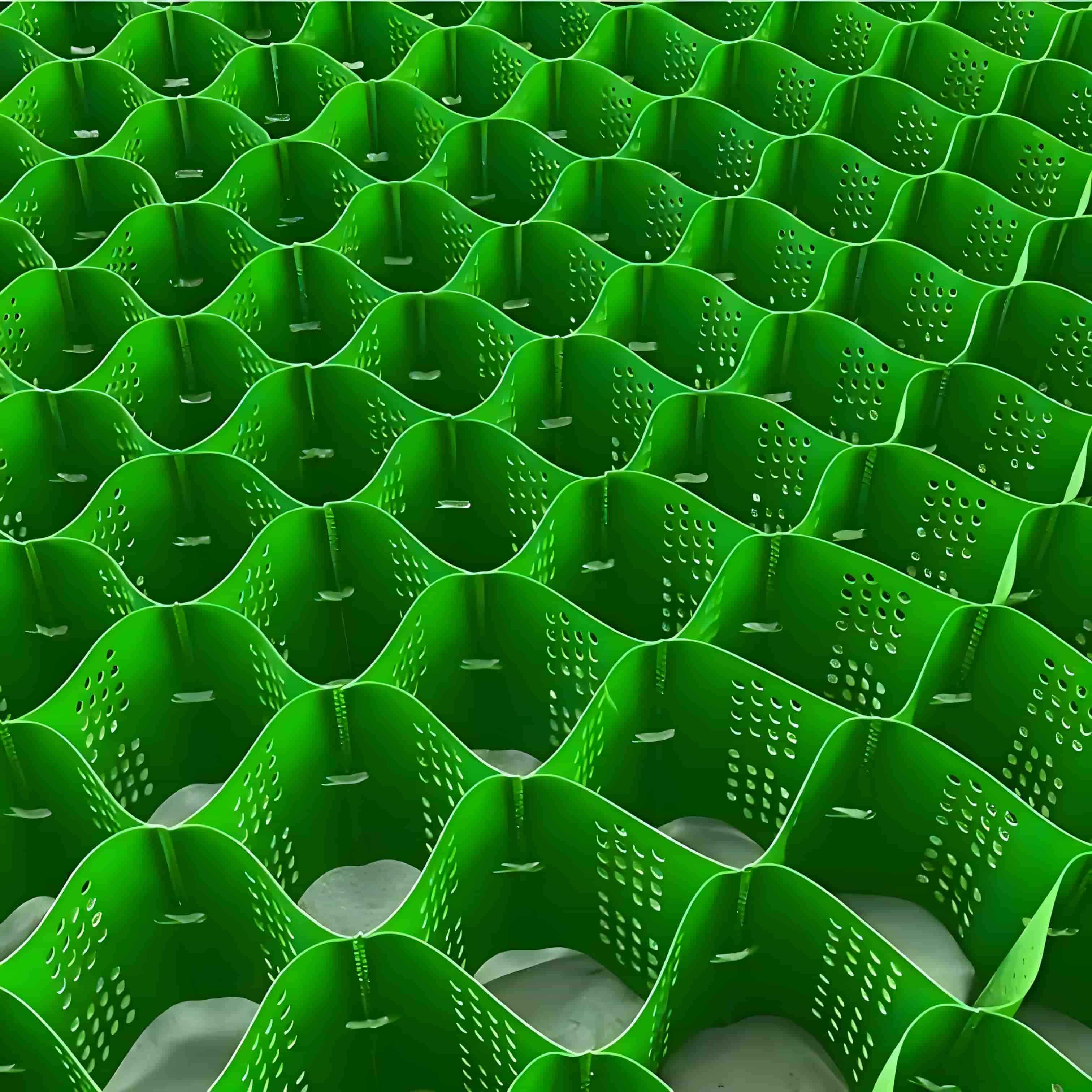
Geocell Pavers
1. Improving engineering stability: By constraining the soil, reducing lateral displacement and settlement of the soil, enhancing the stability of structures such as foundations and slopes, and reducing the risk of collapse.
2. Save material costs: Compared with traditional reinforcement methods such as sand and gravel cushion layers, it can reduce the amount of sand and gravel materials used and lower engineering costs.
3. Simplify the construction process: The construction process is relatively simple and does not require complex large equipment. After unfolding, filling materials can be used, which can shorten the construction period.
4. Good environmental friendliness: The materials are recyclable and have minimal disturbance to the surrounding environment during the construction process, which is in line with the concept of green engineering.
Product Introduction:
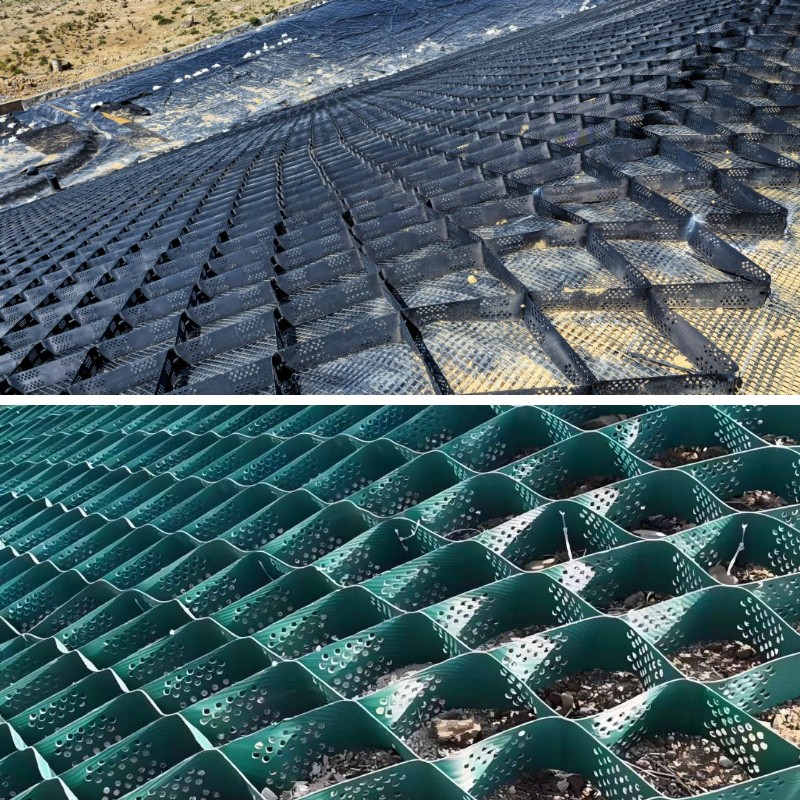
Geocell Pavers is a new type of geosynthetic material that is formed by using high-strength polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP) sheets to form a three-dimensional mesh grid structure through ultrasonic welding, riveting, and other processes. The core principle is to use three-dimensional structures to form lateral constraints on fillers (such as soil, sand, and gravel), enhancing the overall stiffness and bearing capacity of the material. According to engineering requirements, some lattice sheets will be perforated to enhance permeability or promote vegetation growth.
characteristic
1. Three dimensional structure
Unlike the planar structure of traditional geotechnical materials such as geotextiles and geogrids, geogrids form three-dimensional supports through honeycomb grids, significantly improving shear strength and lateral restraint capabilities. Experiments have shown that under its limiting effect, the apparent cohesion of medium dense sand can be increased by more than 30 times.
2. Lightweight, High Strength, and Durability
The material has low density but high tensile strength, stable chemical properties, acid and alkali resistance, light and oxygen aging resistance, and a service life of several decades. For example, in saline or expansive soil areas, its corrosion resistance can meet the requirements of high-grade highway construction.
3. Flexibility and adaptability
Adjustable size: Parameters such as grid height and welding distance can be customized according to engineering requirements to adapt to different slopes and geological conditions.
Convenient construction: It can be folded and compressed during transportation, and stretched into a net and filled with fillers during construction, greatly reducing the construction period. For example, after laying on a muddy soft foundation, it can be directly compacted without pre-treatment.
4. Eco friendliness
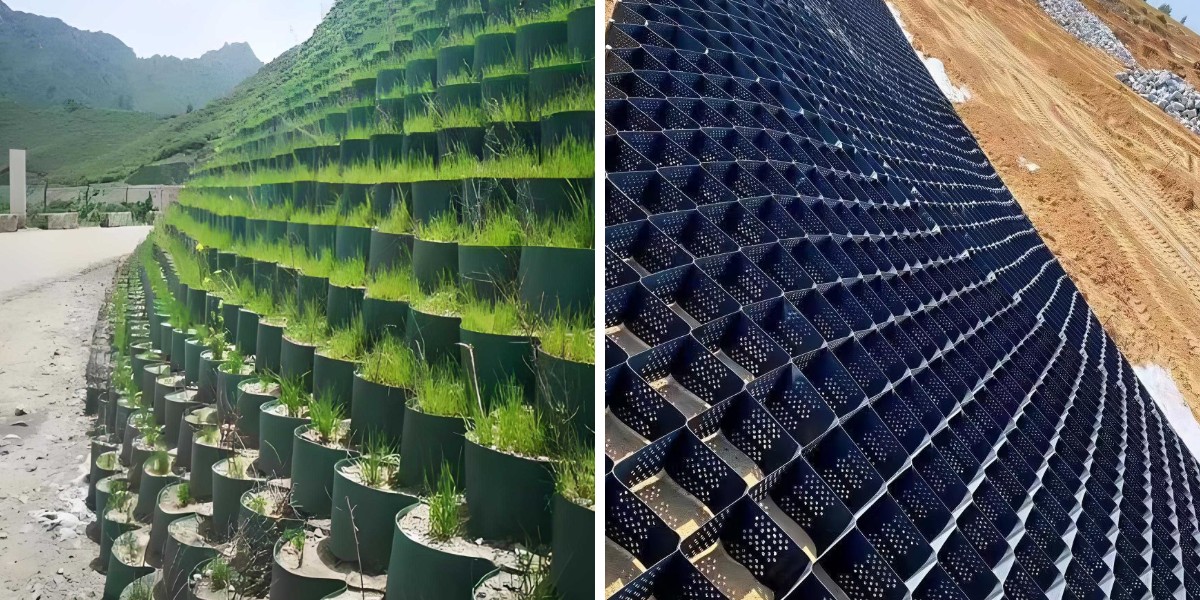
Permeable hole design promotes drainage and prevents soil erosion; The grid structure provides anchoring space for vegetation roots, assisting in ecological restoration projects such as wetland restoration and desert greening.
Product Parameters:
order number | raw and processed material | |||||||
test item | unit | polytene | sulan | polyester | ||||
Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | |||
1 | tensile strength | kN/m | ≥20 | ≥100 | ≥23 | ≥100 | ≥30 | ≥120 |
2 | Tensile yield strain | % | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | - |
3 | Tensile fracture strain | % | — | 8~ 20 | — | 6~ 15 | — | 8~ 20 |
4 | Carbon black content a | % | 2. 0~ 3. 0 | |||||
5 | Carbon black dispersion a | — | There should be no more than one level 3 data item in ten data items and no level 4 or 5 data items | |||||
6 | 200℃ oxidation induction time | min | ≥20 | ≥20 | — | |||
7 | Tensile load stress cracking | h | ≥300 | — | ||||
8 | B. Resistance to artificial climate aging retention rateb | % | ≥80 | |||||
9 | Chemical resistance performance retention rate c | % | — | ≥80 | ||||
Product Applications:
1. Transportation Engineering
Roadbed treatment: solving special geological problems such as weak foundation, collapsible loess, saline soil, etc. For example, in loess collapsible sections, grid cells can increase the foundation bearing capacity to 1.5 times the design requirements.
Supporting structure: replacing traditional retaining walls, reducing land occupation and lowering costs.
2. Water conservancy engineering
River management: As a revetment structure, it enhances soil erosion resistance and protects riverbank vegetation. For example, in the management of the Yellow River beach area, grid protection can reduce soil erosion by more than 80%.
Embankment reinforcement: prevent embankment settlement and landslides, and improve flood control standards.
3. Environmental Engineering
Ecological restoration: Fill renewable materials in desert greening and wetland restoration to promote vegetation growth. For example, in the Kubuqi Desert control project, the grid structure increased vegetation coverage from 5% to 60%.
Pollution control: Limit the spread of pollutants and prevent soil and groundwater pollution.
4. Agriculture and Horticulture
Soil improvement: Improve soil structure, enhance water and fertilizer retention capacity, and promote crop yield increase. For example, in paddy field irrigation, grid cells can reduce water leakage by 30%.
Greenhouse construction: As a lightweight support structure, it reduces construction costs.
Geogrids have become indispensable "multifunctional warriors" in modern engineering due to their unique three-dimensional structure, excellent mechanical properties, and wide adaptability. From transportation infrastructure to ecological restoration, its innovative applications continue to drive technological innovation in civil engineering materials, providing strong support for sustainable development.