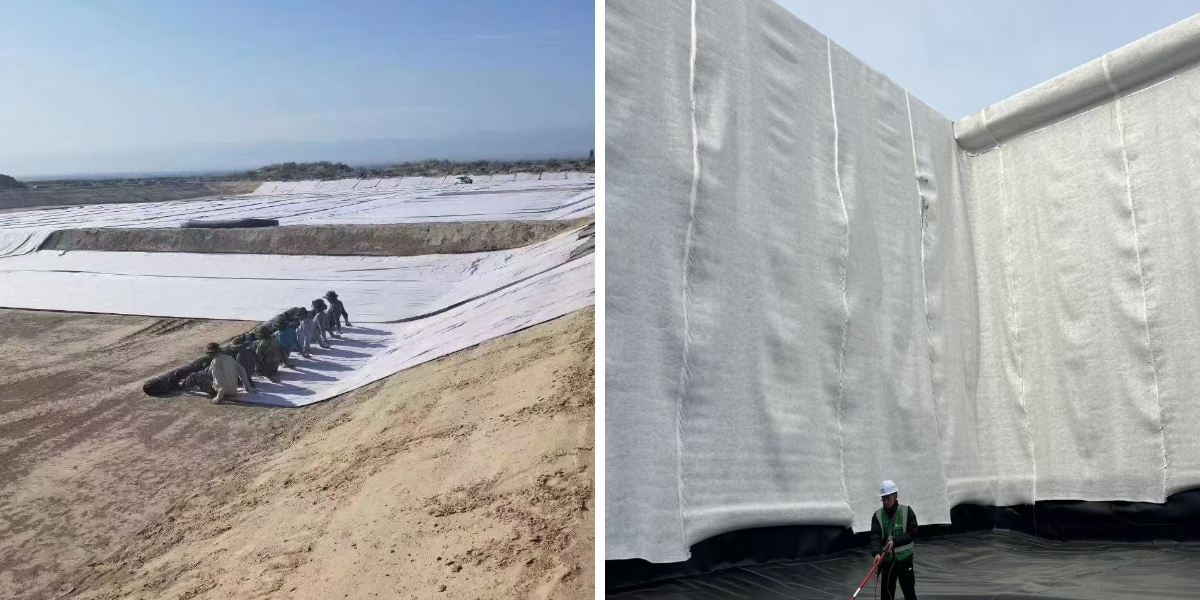
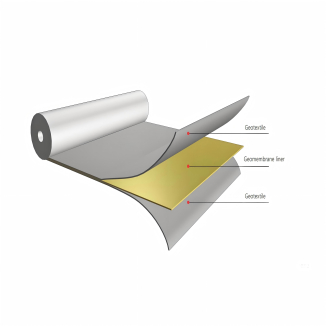
Geotextile Protection
Excellent Separation: Separate different soil layers or materials to prevent mixing of roadbed filling and soft soil, ensuring even stress distribution on the roadbed and extending the lifespan of the road.
Excellent filtration: When water flows through, it blocks soil particles, which can drain water without allowing sediment to flow away, maintaining stability.
Fast drainage: The porous structure can quickly drain rainwater or groundwater in a timely manner, avoiding water immersion, settlement, and overturning of the roadbed.
Impact and corrosion resistance: The material has high strength, wear resistance, acid and alkali resistance, UV resistance, and long service life.
Environmental Protection and Ecology: Non toxic and pollution-free, pores are conducive to plant rooting and growth, can form an ecological slope protection system, and promote ecological restoration.
Product Introduction
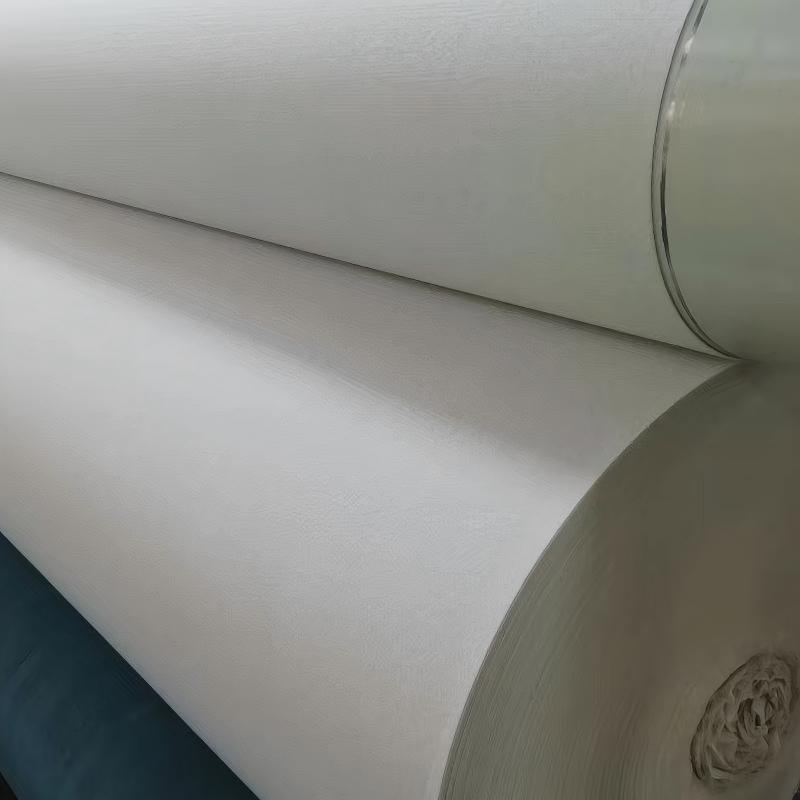
Geotextile protection products, crafted from synthetic fibers like polyester or polypropylene, are a type of permeable fabric designed for diverse civil engineering and construction applications. They come in two main types: woven and non-woven. Woven geotextiles, made by interlacing yarns, offer high strength and are great for separation tasks. Non-woven geotextiles, created through needle punching or heat bonding of fibers, excel in filtration and drainage due to their random fiber arrangement.
These products have several key properties. They possess high tensile strength, allowing them to withstand significant pulling forces without breaking. Their excellent water permeability enables efficient water flow through the fabric, while their filtration ability ensures that soil particles are retained, preventing clogging in drainage systems. Additionally, geotextiles are resistant to chemicals, UV radiation, and biological degradation, ensuring long-term durability even in harsh environmental conditions.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications
1.Road Construction
Subgrade Separation: Geotextiles are placed between the subgrade soil and the base course materials. In areas with soft soil subgrades, they prevent the mixing of the soft soil with the coarser base materials. This separation function ensures that the base course maintains its integrity and load - bearing capacity, reducing the risk of road settlement and improving the overall lifespan of the road. For example, in new road construction projects in marshy or low - bearing - capacity soil areas, geotextiles act as a barrier, allowing for proper compaction of the base layers.
Pavement Reinforcement: They can be incorporated within the pavement structure, such as between asphalt layers or in the base of concrete pavements. By adding geotextiles, the tensile strength of the pavement is enhanced, which helps to resist the formation and propagation of cracks. This is especially important in areas with heavy traffic or temperature - induced stress, as it can significantly extend the time between pavement rehabilitation or replacement.
Edge Protection: Along the edges of roads, geotextiles are used to prevent soil erosion caused by water runoff. They help to hold the soil in place, maintaining the stability of the road shoulders and preventing the undermining of the pavement edges.
2.Hydraulic and Coastal Engineering
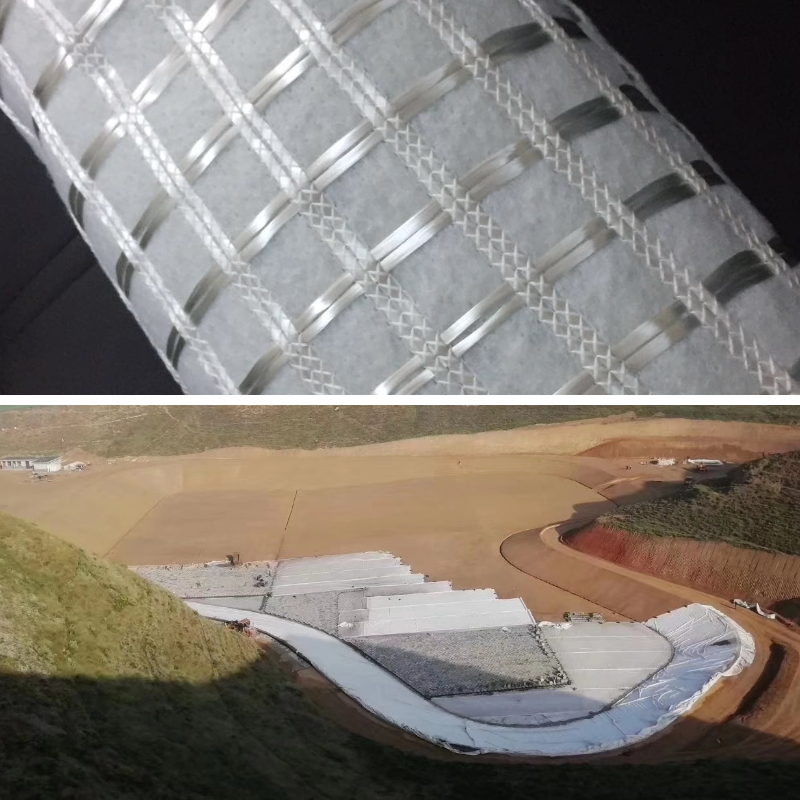
Dams and Embankments: Geotextiles are used in dam construction for multiple purposes. They are placed on the upstream and downstream faces of earth - filled dams to provide filtration. This allows water to drain through while preventing the loss of fine soil particles, which could lead to internal erosion and potential dam failure. In embankment construction, they can be used as reinforcement layers to increase the stability of the embankment against sliding forces, especially in areas with high water tables or near water bodies.
Coastal Protection: In coastal areas, geotextiles are deployed to protect beaches, dunes, and seawalls from erosion. They can be used in beach nourishment projects, where they are placed beneath the new sand fill to prevent the sand from being washed away by waves and currents. For seawalls, geotextiles are installed between the seawall structure and the soil to prevent erosion at the base of the wall, and they can also be used in combination with rip - rap (armor stones) to create a more stable and durable coastal protection system.
Riverbank Stabilization: Along rivers, geotextiles help to stabilize riverbanks by preventing soil erosion caused by flowing water. They can be used in the form of erosion control mats or as part of a gabion wall system, where they are placed behind the gabions to filter water and retain soil, maintaining the integrity of the riverbank.
3.Landfill and Waste Management
Liner Protection: Geotextiles are placed above and below landfill liners (such as geomembranes) to protect the liners from punctures. The rough surfaces of the underlying soil or waste materials can potentially damage the liner, but the geotextile acts as a buffer, distributing the stress and preventing direct contact that could lead to holes or tears in the liner. This is crucial for preventing the leakage of leachate, a highly polluted liquid generated in landfills, into the surrounding soil and groundwater.
Leachate Collection and Filtration: They are also used in leachate collection systems. Geotextiles are placed around perforated pipes within the landfill to allow the leachate to enter the pipes while filtering out solid particles. This filtration function helps to keep the pipes clear, ensuring efficient leachate collection and preventing clogging of the drainage system.
4.Slope Protection and Erosion Control
Steep Slopes: On steep slopes, geotextiles are used to prevent soil erosion and slope failure. They can be installed as a surface cover, either as a single layer or in combination with other materials like vegetation. The geotextile helps to hold the soil in place, reducing the impact of rainfall and surface runoff on the slope. In addition, for vegetated slopes, the geotextile provides a supportive structure for the growing plants, protecting the young roots and helping to establish a stable vegetative cover that further enhances slope stability.
Construction Sites: During construction activities, temporary geotextiles are often used to control erosion on exposed soil areas. They prevent soil from being washed away by rain or construction - related water runoff, protecting nearby water bodies from sediment pollution and maintaining the integrity of the construction site.
5.Agriculture and Horticulture
Soil Erosion Control in Fields: In agricultural fields, especially on sloping land or in areas with high - intensity rainfall, geotextiles can be used to prevent soil erosion. They are placed along the edges of fields or in areas prone to erosion, such as around irrigation channels. By reducing soil loss, they help to maintain soil fertility and prevent sedimentation in waterways, which can have negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
Greenhouse and Nursery Applications: In greenhouses and nurseries, geotextiles are used for weed control. They are laid on the ground between plants or in walkways to block sunlight from reaching the soil surface, inhibiting weed growth. At the same time, their permeability allows for proper water drainage and aeration of the soil, creating a suitable environment for plant growth.
Geotextile Protection products are permeable fabrics made of synthetic fibers such as polyester and polypropylene. They are divided into woven types with good strength and toughness, suitable for separation scenarios, and non-woven types with randomly arranged fibers that are good at filtering and drainage. They are suitable for multiple engineering scenarios; This product has high tensile strength, strong permeability and filtration, as well as chemical corrosion resistance, UV resistance, and biodegradation resistance. It can be used for a long time in harsh environments. Its applications cover five major fields: road construction (roadbed separation, road surface reinforcement, etc.), water conservancy and coastal engineering (dam protection, coastal and riverbank stability), landfill management (liner protection, leachate treatment), slope protection (erosion and landslide prevention), and agricultural horticulture (soil erosion control, weed prevention). It can effectively solve structural stability and ecological protection problems in various scenarios.