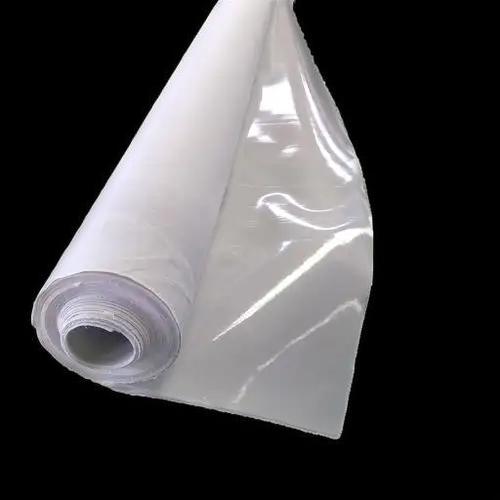
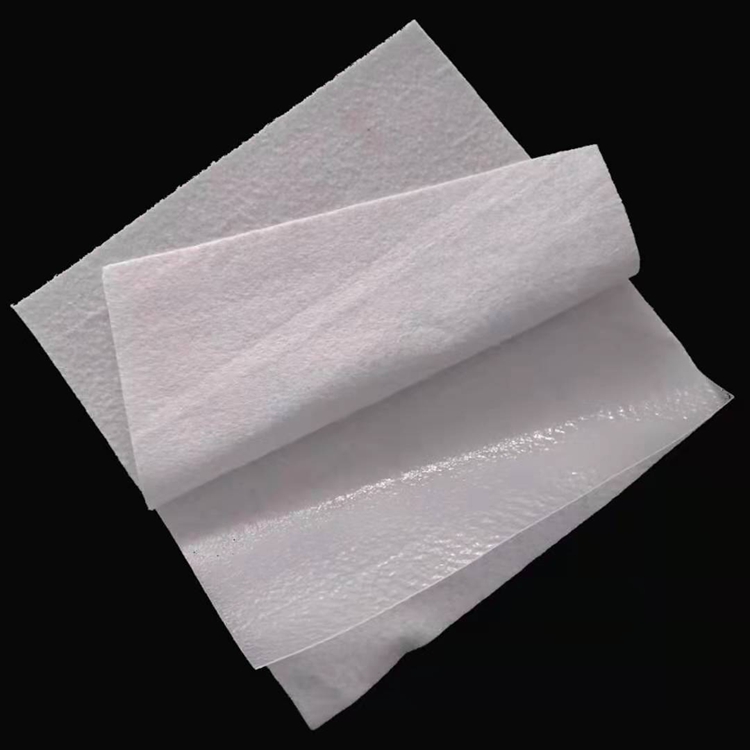
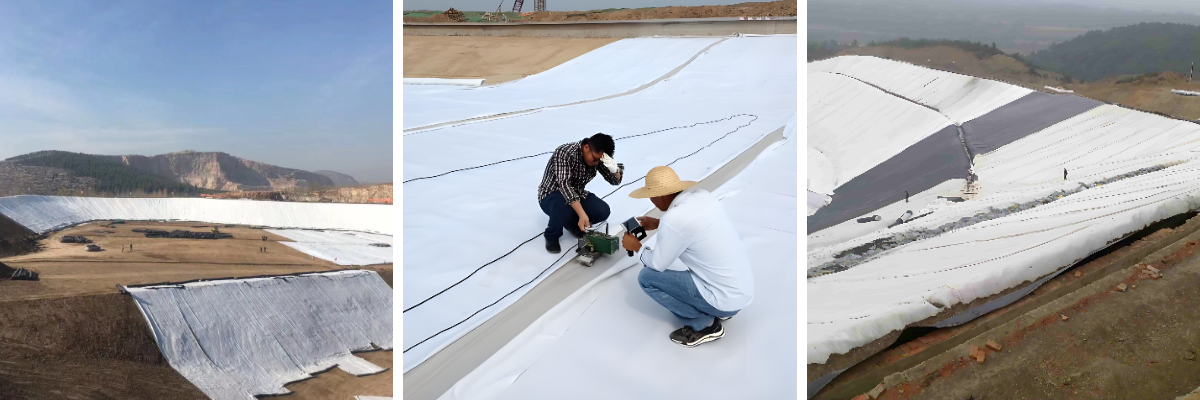
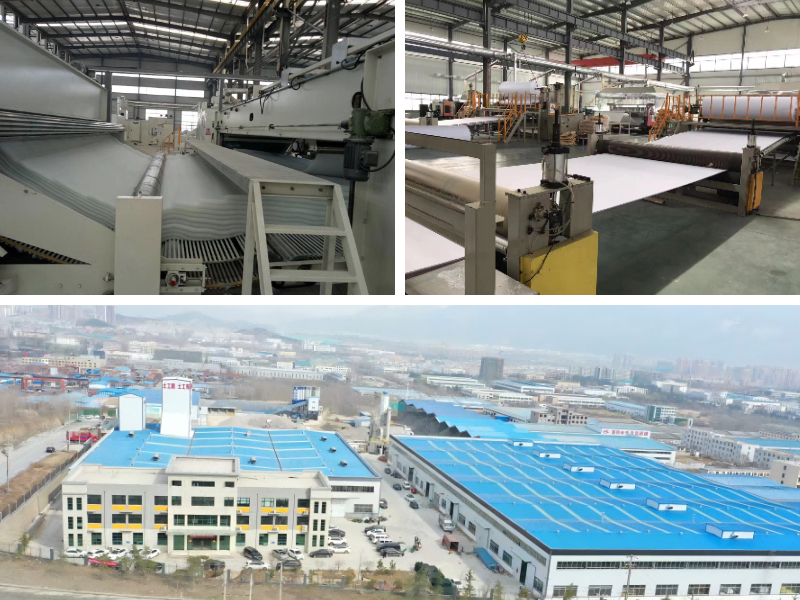
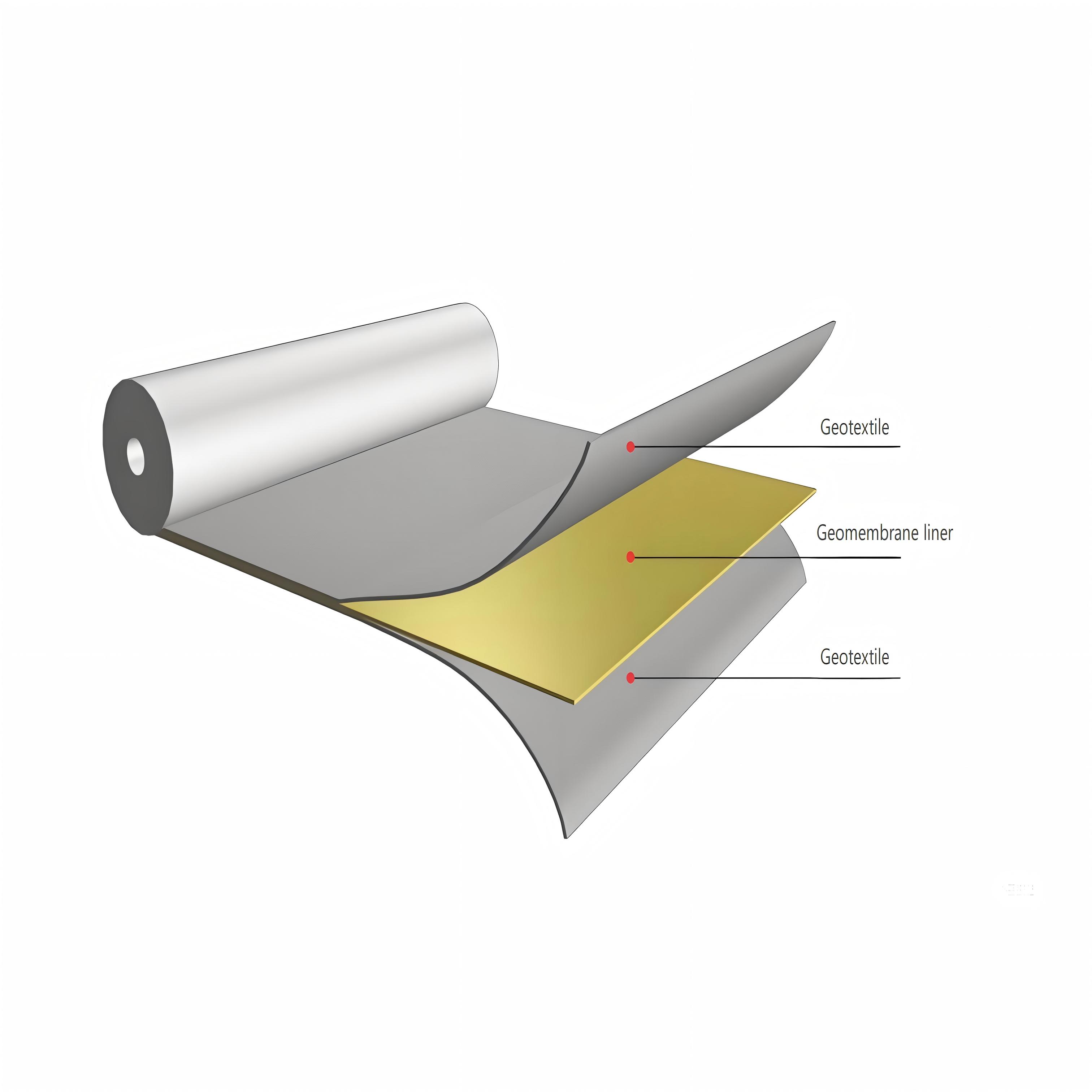
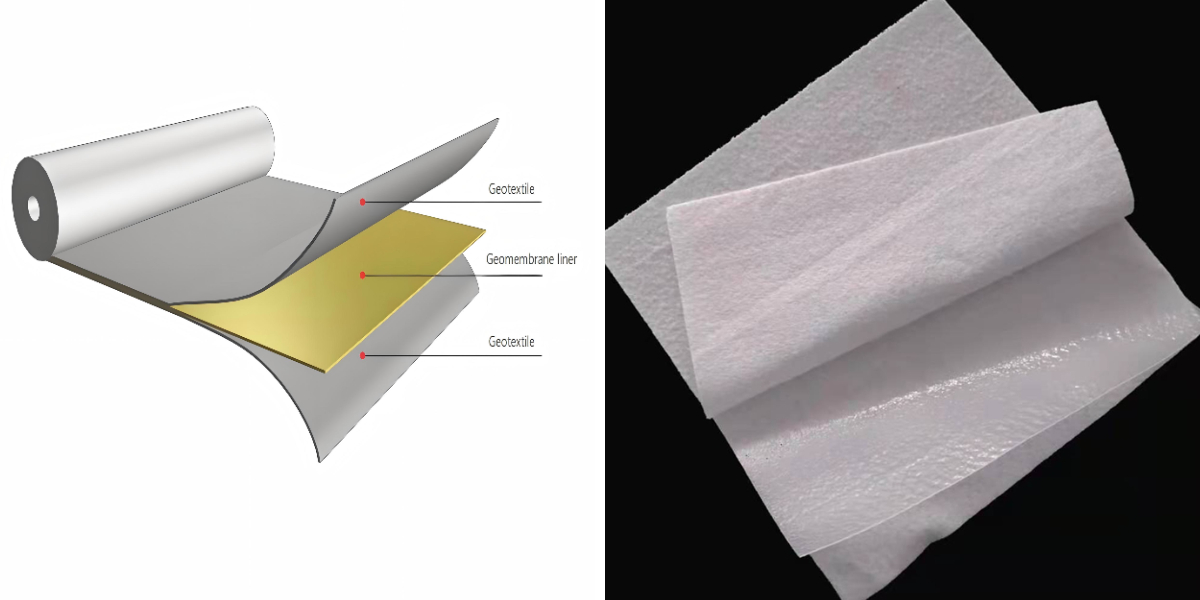
Irrigation Project Composite Geomembrane
1.Strong anti - seepage performance: High anti - seepage coefficient, effectively prevents water penetration, reduces soil erosion, and performs outstandingly in projects with high anti - seepage requirements such as water conservancy and environmental protection.
2.Good weather and corrosion resistance: Resistant to acids and alkalis, anti-corrosion. After adding anti-aging agents, it has excellent anti-aging performance, can be used for a long time in unconventional temperature environments, and its service life can reach 50 - 70 years.
3.Excellent physical properties: High physical and mechanical performance indicators such as tensile strength, tear resistance, and bursting strength. High strength, good extensibility, large deformation modulus, and can withstand large loads and external force damage.
Product Introduction:
Irrigation Project Composite Geomembrane is a geosynthetic material composed of geotextile and geomembrane through a specific process. Geotextiles (such as long - filament or short - filament non - woven geotextiles) provide mechanical properties such as tensile and tear resistance. Geomembranes (commonly high - density polyethylene HDPE and other polymer materials) play a role in anti - seepage.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||
| Nominal fracture strength/(kN/m) | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | |
| 1 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength/(kN/m) ≥ | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
| 2 | Longitudinal and transverse standard strength corresponding elongation/% | 30~100 | |||||||
| 3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 3 | 3.2 |
| 4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN ≥ | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.7 |
| 5 | Peel strength/(N/cm)> | 6 | |||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | As required by design or contract | |||||||
| 7 | Width deviation /% | -1 | |||||||
| project | film thickness /mm | ||||||||
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
| Resistant to static water pressure /MPa ≥ | One cloth, one membrane | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| Two cloth and one film | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | |
| Note: If the film thickness is between adjacent specifications in the table, the corresponding assessment index shall be calculated by linear interpolation; if it exceeds the range in the table, the assessment index shall be determined by negotiation between the supplier and the demander. | |||||||||
Product Applications:
Environmental Protection and Municipal Engineering
Landfill Seepage Control System: As the seepage control layer at the bottom and slopes of the landfill, it blocks the infiltration of leachate into the ground, preventing soil and groundwater pollution. A landfill in a certain state of the United States uses anti - ultraviolet composite geomembrane combined with GCL bentonite pads to form a multi - layer seepage control system, meeting the strict environmental protection requirements of the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency of the United States).
Seepage Control in Sewage Treatment Plants: It is used for the seepage control of sewage treatment tanks and regulating tanks, resisting the corrosion of acid - base sewage. In a German municipal sewage treatment project, LDPE composite geomembrane resistant to chemical corrosion is selected, with a service life of more than 20 years.
Industrial Waste Residue Disposal Sites: It isolates harmful substances such as heavy metals and chemical waste, avoiding the spread of pollution and meeting the EU CE certification and ISO 14001 environmental protection standards.
Mining and Energy Engineering
Tailings Dam Seepage Prevention: Seepage prevention at the bottom and slopes of mining tailings ponds to prevent the leakage of heavy metal - containing wastewater, which complies with the mining environmental protection regulations of countries such as Canada and Australia.
Petrochemical Seepage Prevention: Seepage prevention of the foundation in oil tank areas and chemical storage tank areas to prevent the leakage of oil or chemicals. In the shale gas development projects in the United States, composite geomembranes resistant to hydrocarbon corrosion are commonly used.
Water Conservancy and Hydropower Projects
Reservoir and Dam Seepage Prevention: It is used for the seepage prevention of reservoir dams and their foundations, blocking the infiltration of water into the dam body or underground, and avoiding dam stability problems caused by leakage. For example, in a large reservoir project in Africa, HDPE composite geomembrane was used as the core seepage prevention layer, effectively reducing water loss by more than 90%.
Irrigation Canal Seepage Prevention: In the agricultural irrigation system, it is laid at the bottom and slopes of the canals to prevent water from seeping into the soil and improve the utilization rate of water resources. In the irrigation project in the Ganges Plain of India, the use of composite geomembrane for seepage prevention has increased the water conveyance efficiency of the canals by more than 40%.
Reservoirs and Artificial Lakes: It is used for the seepage prevention of drinking water reservoirs and industrial reservoirs. At the same time, it has environmental protection characteristics (such as food - grade materials) and meets the drinking water project standards in Europe and America (such as FDA certification).
Transportation and Civil Engineering
Highway and Railway Subgrade Reinforcement: Laid between the subgrade and the foundation, it separates different soil layers, enhances the subgrade's anti-deformation ability, and reduces settlement. In a highway project in Southeast Asia, the combined use of composite geomembrane and geogrid increased the subgrade bearing capacity by 30%.
Tunnel and Subway Waterproofing: Used for the outer layer of tunnel lining to prevent seepage and stop groundwater from penetrating and causing structural damage. In the construction of a new subway line in Tokyo, Japan, self-adhesive composite geomembrane was adopted, simplifying the construction process and improving the waterproof reliability.
Agriculture and Aquaculture
Anti-seepage for Fish Ponds and Shrimp Ponds: Replace traditional clay pond bottoms to prevent water leakage, and facilitate pond cleaning and water quality management. After using composite geomembranes in Brazilian aquaculture farms, the water retention rate of ponds has increased to 95%, and the breeding density has increased by 20%.
Anti-seepage and Leakage Prevention for Biogas Digesters: In biomass energy projects, it blocks biogas leakage and resists the corrosion of fermentation liquid. It is commonly seen in rural energy projects in Africa and Southeast Asia.
Anti-seepage for Salt Pans: Used for the bottom anti-seepage of sea salt evaporation ponds, improving salt production and purity. Composite geomembranes resistant to high-salt corrosion are widely used in salt pan projects in the Middle East and Australia.