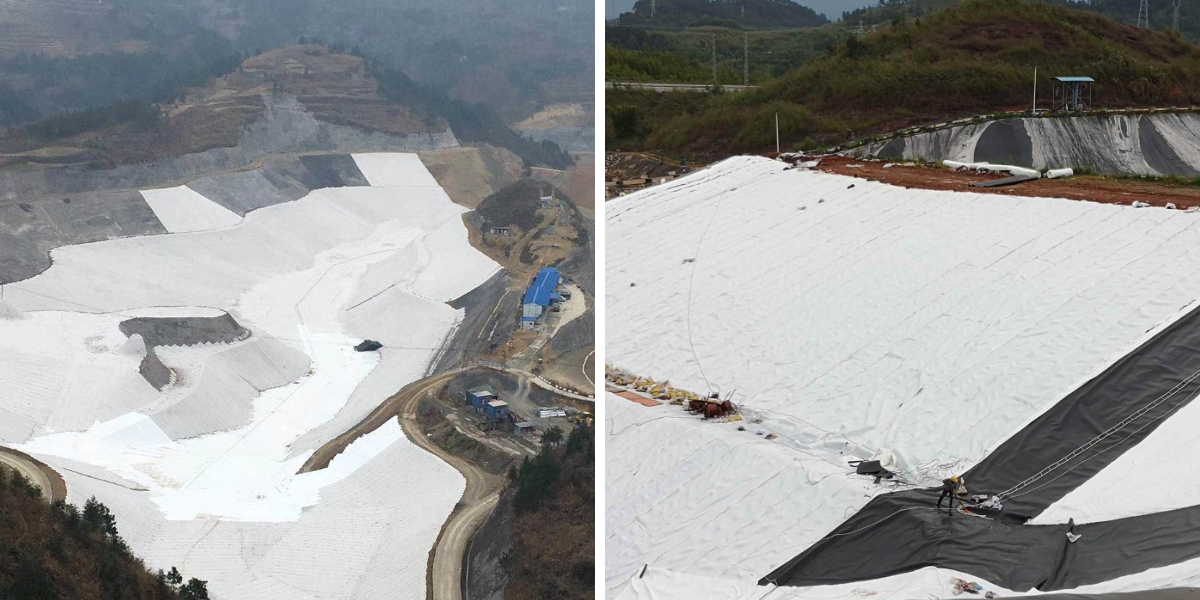
Geotextile Fabric for Road Stabilization
1.Strengthening roads and minimizing damage: It can disperse road pressure, reduce roadbed settlement and pavement cracking, make roads more durable, especially suitable for truck roads
2.Drain accumulated water and maintain stability: It can quickly drain water from the roadbed, prevent soil from becoming soft and bearing capacity from decreasing, and also block sediment from entering the roadbed
3.Fast construction, cost saving: Directly laid between the roadbed and road surface, without the need for traditional sand and gravel cushion layer, with fewer steps, shorter construction period, and can also save material and labor costs
4.Anti erosion and roadbed protection: It can block rainwater and groundwater from washing away the roadbed, avoiding soil loss along the roadside. It is more suitable for use in rainy areas or on roads with slopes
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Geotextile Fabric for Road Stabilization made of polymer synthetic materials, commonly made of polypropylene, polyester, etc; The shape is mostly rolled and can be trimmed according to the width of the road; Has certain tensile strength and weather resistance, can adapt to rolling and stretching during road construction, and is not easily corroded or aged when exposed or buried underground for a long time.
2、 Core functions
Structural enhancement: disperses road surface loads, reduces local stress concentration on the roadbed, avoids roadbed settlement and pavement cracking, and enhances the overall bearing capacity of the road;
Drainage and soil filtration: Quickly drain the accumulated water inside the roadbed, prevent moisture retention and soften the soil, while blocking the infiltration of surface sediment into the roadbed, maintaining the stability of the roadbed structure;
Protection and damage resistance: resist the erosion of rainwater and groundwater on the roadbed, reduce soil erosion on the slope, and protect the integrity of the roadbed edge and bottom structure.
3、 Main features
Strong practicality: Suitable for different road conditions (heavy-duty roads, rural roads, etc.), without the need for complex construction equipment, it can be directly laid between the roadbed and surface layer for use;
Economic advantages: can replace some traditional sand and gravel cushion layers, reduce material usage and construction steps, and lower construction costs;
Good durability: acid and alkali resistant, UV resistant, not easily degraded or damaged after long-term use, extending the road maintenance cycle.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1、 Application by road type
Heavy duty roads (such as freight roads, industrial park roads)
Placed between the top and bottom layers of the roadbed, it disperses the concentrated load generated by heavy vehicles such as trucks, avoids uneven stress on the roadbed, reduces road cracks, and extends the service life of the road against heavy loads.
Rural/low-grade roads
Replace some traditional sand and gravel cushion layers and directly lay them on the plain soil subgrade to enhance the overall integrity of the subgrade, prevent soil from softening due to rainwater immersion, reduce construction costs, and improve road foundation stability.
Expressway/High grade Highway
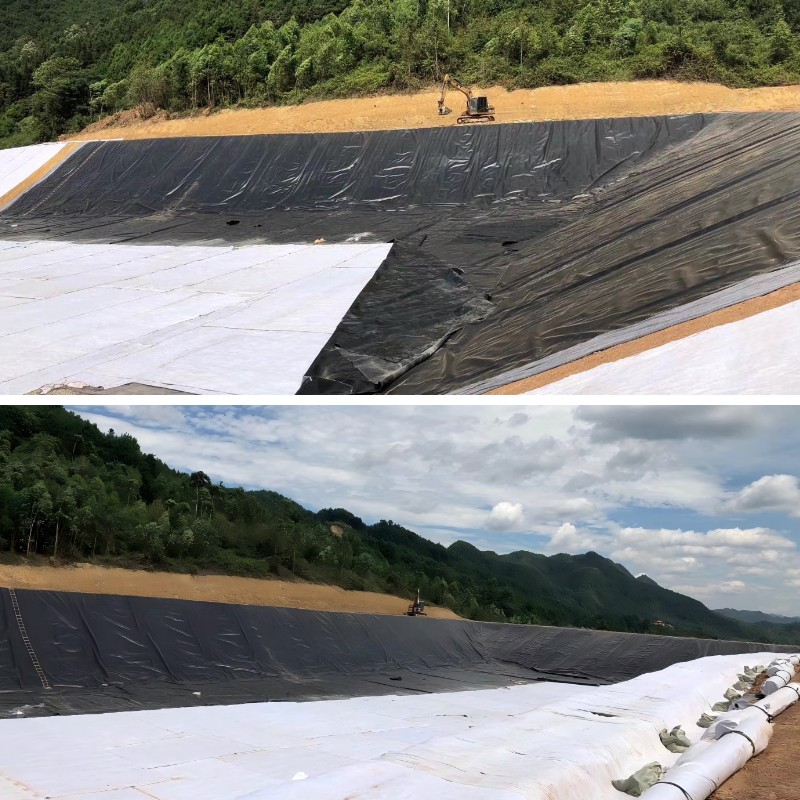
Used for roadbed slopes and central dividers, on the one hand to resist rainwater erosion of slopes and reduce soil erosion; On the other hand, during the layered filling of the roadbed, it is laid to enhance the interlayer bonding and avoid the decrease in pavement smoothness caused by layered settlement.
Old Road Renovation Project
Placed between the old road surface and the new surface layer, it serves as a "reinforcement buffer" to alleviate the upward reflection of cracks from the old road base to the new road surface, while improving the force transmission between the new and old structural layers and reducing road surface damage after renovation.
2、 Application according to the construction process
Roadbed treatment stage
For soft soil roadbeds, geotextiles are laid before filling to use their tensile strength to constrain lateral deformation of the soil, accelerate roadbed consolidation, and reduce later settlement; Simultaneously filter the fine particles in the filler to avoid clogging the roadbed pores.
Construction of Road Base/Subbase
Placed between the base layer and the sub base layer, to prevent the two layers of materials from experiencing "interlayer displacement" due to compaction and load, and to enhance the overall structural integrity; And it can drain the accumulated water inside the base layer, avoiding the loosening of the base material due to water damage.
Slope protection construction
Laying on the slopes on both sides of the road, combined with anchor rods or soil compaction fixation, forms a "fabric protective layer" to resist rainwater erosion and groundwater infiltration, prevent slope collapse and soil erosion, especially suitable for rainy areas or slopes with high fill.
In summary, the application of geotextiles for road stability has always revolved around "solving the structural stability problem of the entire life cycle of roads" - whether it is adapting to the differentiated needs of different types of roads such as heavy-duty, rural roads, highways, or covering key construction links such as roadbed treatment, base construction, slope protection, etc., they can all rely on the core role of "enhancing structure, drainage and soil filtration, and protection against damage", which not only reduces the cost of road construction and renovation, but also extends the service life of roads and reduces the frequency of later maintenance. Especially in scenarios where structural hazards are prone to occur, such as soft soil roadbeds, rainy areas, and old road renovations, its advantages as a "low-cost, efficient, and stable solution" are more prominent, becoming an important auxiliary material for improving structural reliability in road engineering.