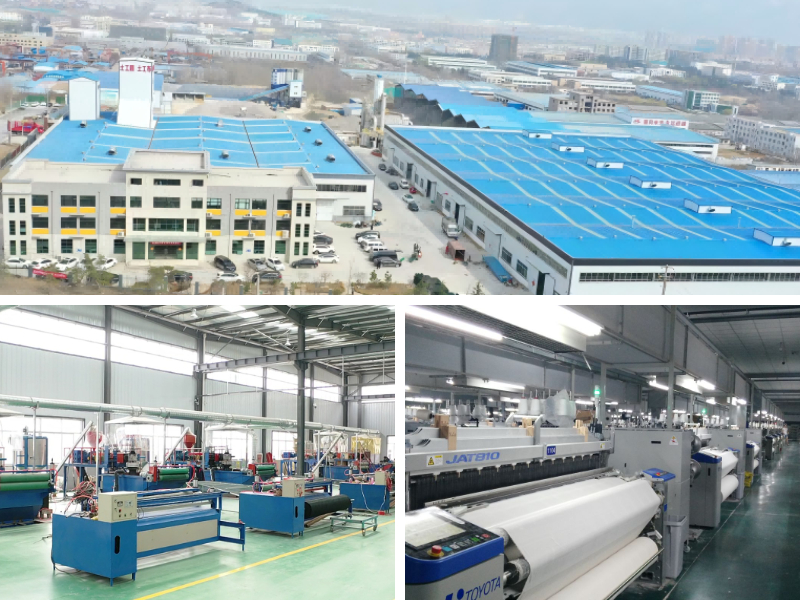
Geotextile White
1. High strength and durability: Synthetic fibers endow geotextiles with extremely high tensile, tear, burst, and puncture strength, capable of withstanding various stresses during construction and long-term use, corrosion resistance, microbial resistance, and long service life.
2. Permeability and Filtration: It has good permeability, allowing water to pass smoothly in the direction perpendicular to its plane, while effectively preventing excessive loss of soil particles and clogging, playing an excellent filtering role.
3. Easy construction and high efficiency: The finished product is a roll material, which is lightweight, easy to transport and lay, and can greatly reduce the amount of work, shorten the construction period, and reduce labor intensity.
Product Introduction:
Geotextile White is a permeable geosynthetic material made from synthetic fibers (such as polypropylene, polyester, nylon, etc.) through processes such as needle punching or weaving. It is essentially a fabric used in civil engineering and is one of the most widely used and fundamental materials in geotechnical engineering.
Main functions and functions
Geotextiles mainly play the following four roles in engineering, often with multiple functions working simultaneously:
1. Separation
Function: Separate two types of civil materials with different physical properties, such as soil and sand, to prevent them from mixing with each other.
Example: Laying geotextile between railway ballast and soft soil foundation can prevent the ballast from sinking into the soft soil, and also prevent soft soil particles from entering the ballast layer upwards, thereby maintaining their respective structural integrity and function, and extending the service life of the road.
2. Filtration
Function: While allowing liquid (water) to pass vertically, it effectively prevents excessive loss of soil particles.
Example: Behind a drainage system used for drainage ditches, revetments, or retaining walls. Water can be discharged smoothly, while the soil skeleton is preserved, preventing soil erosion and structural instability.
3. Drainage
Function: Utilize the pore channels inside the geotextile to discharge liquid (or gas) along its plane direction.
Example: In earth dams, tunnels, or underground structures, laying geotextiles can collect and guide water flow towards designated drainage outlets, reducing groundwater levels or pore water pressure.
4. Reinforcement
Function: Utilizing its high tensile strength and toughness, it disperses loads, improves the strength and stability of soil, similar to steel bars in concrete.
Example: Used to reinforce roadbeds on soft soil foundations, raise steep slopes, or construct reinforced soil retaining walls. Geotextiles transfer local loads to a larger area through friction with the soil, thereby reducing uneven settlement.
5. Protection
Function: As a buffer layer, it reduces the damage of external forces to waterproof materials (such as geomembranes) or structures.
Example: Laying geotextile on top and bottom of the anti-seepage geomembrane in a landfill can prevent sharp stones or debris from puncturing the anti-seepage membrane, playing a crucial protective role.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
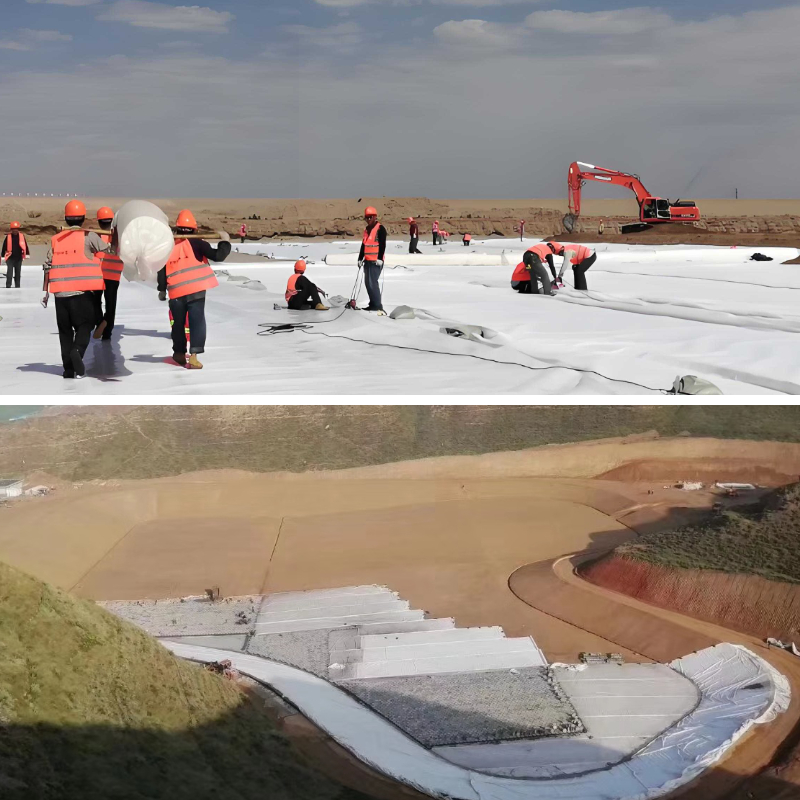
Product Applications:
1. Highway and railway subgrade engineering
Isolation: Installed between the roadbed and ballast to prevent soft soil from rising and stone from sinking, maintain clear structural layers, and extend service life.
Reinforcement: disperses loads, improves the bearing capacity and stability of the roadbed.
Drainage: Collecting and draining water from the foundation to reduce damage to the roadbed caused by water.
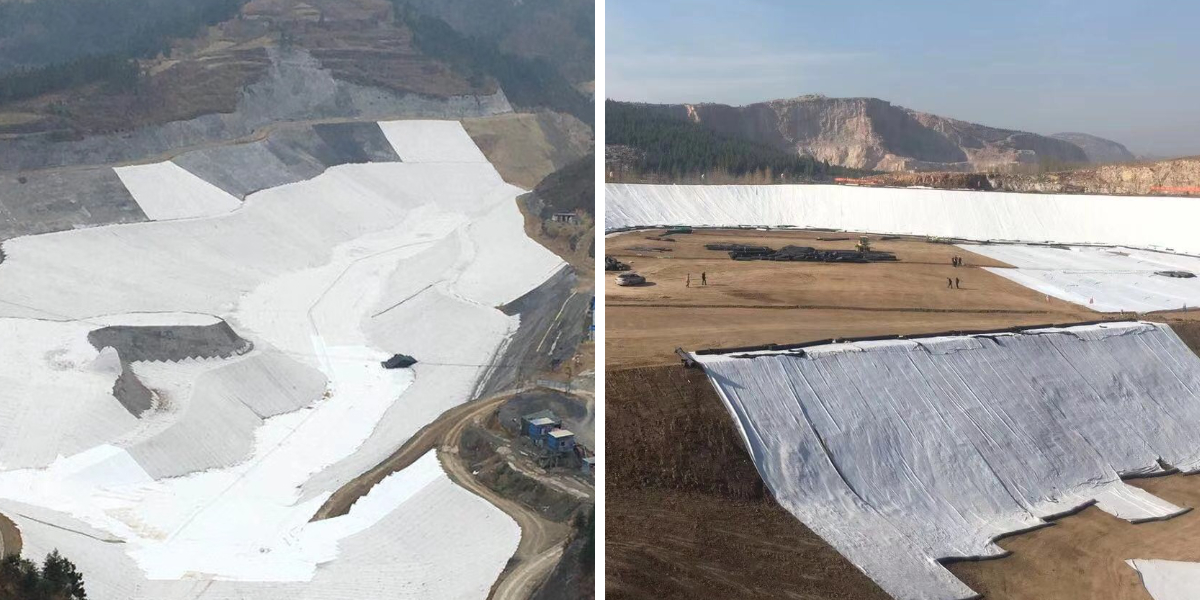
2. Water conservancy engineering (dams, rivers, coasts)
Anti filter layer: used for slope protection and downstream protection of earth rock dams, riverbanks, and seawalls, preventing soil from being washed away by water flow while allowing water to freely discharge. It is its most classic application.
Protection: prevent water flow and waves from scouring the bank slope and bottom.
Drainage: Form drainage channels behind the dam or retaining wall to reduce pore water pressure.
3. Landfills and environmental engineering
Isolation and protection: As a component of the bottom lining system of the landfill site, it prevents harmful substances from leaking and polluting the soil and groundwater.
Drainage and drainage: used to collect and guide the leachate and exhaust gas generated by garbage.
4. Construction Engineering
Foundation drainage: Lay around the building foundation for drainage and to keep the foundation dry.
Roof garden drainage: used for roof greening systems to filter and drain water.
5. Other applications
Tunnel engineering: used between primary and secondary lining to provide drainage and buffering protection.
Agriculture: used for drainage ditches, crop protection, etc.
Sports facilities: underground drainage systems such as football fields and golf courses.
In summary, geotextile, as an efficient geosynthetic material, plays a "multifunctional role" in modern engineering construction with its excellent mechanical, hydraulic, and durability properties, achieving safer, more economical, and environmentally friendly engineering results.