Heavy Duty Woven Geotextile Fabric
1.High Strength: High-density craftsmanship and strong fibers withstand heavy loads, resist breakage, and ensure stable construction.
2.Durability: Resistant to wear, acid, alkali, and sunlight, it lasts 15-20 years with minimal maintenance.
3.Excellent Filtration: Uniform pores ensure rapid soil drainage, and the pore shape is stable for long-lasting effectiveness.
4.Easy Installation: Dimensions remain stable, the material adapts to the terrain, and it can be cut and laid quickly.
Product Introduction
1. Basic Properties
Heavy Duty Woven Geotextile Fabric are made from high-strength fibers (such as polyester and polypropylene) through a high-density weaving process. They are thick and compact, boasting high tensile strength and low shrinkage. They are dimensionally stable under normal conditions and offer outstanding resistance to wear and acid and alkali.
2. Core Functions
Heavy-duty support: Distributes heavy loads in roadbeds, embankments, and other applications, preventing structural deformation and collapse.
Filtration and drainage: Uniformly woven pores filter soil particles and prevent clogging, while also rapidly draining accumulated water.
Protection and isolation: Separates different materials (such as sand and soil) to protect engineering structures and reduce wear and damage.
3. Key Features
Durability: Sun- and corrosion-resistant, with a service life of 15-20 years and low maintenance costs.
Adaptability: Flexible enough to conform to complex terrain, such as steep slopes and curved surfaces, making it easy to cut and efficient.
Stable performance: Resistant to damage under load, with a durable pore structure, ensuring long-term reliable filtration and support.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
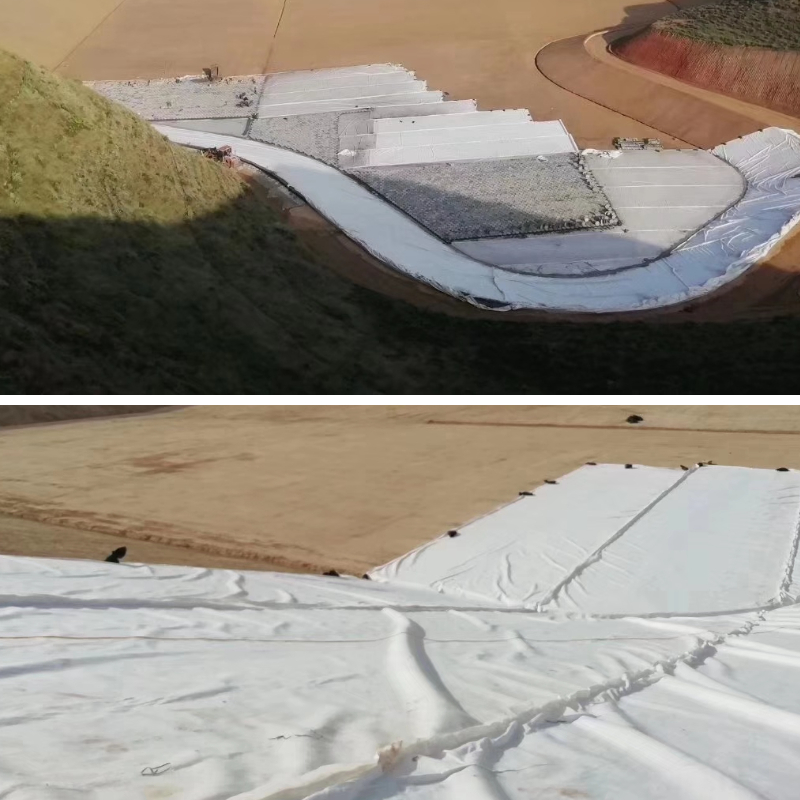
Product Application
1. Transportation Infrastructure
Heavy-Load Roadbed Reinforcement: Used as the subgrade layer of highways, freight railways, and port yards, its high tensile strength distributes the load pressure of heavy vehicles and containers, preventing roadbed settlement and cracking. It is particularly suitable for soft soil or roads with frequent heavy loads.
Pavement Base Isolation: Sandwiched between the asphalt layer and the gravel base layer, it separates the different materials and prevents the mixing of gravel and asphalt, which can lead to a loosened pavement structure. It also drains water from the base layer through its pores, reducing freeze-thaw damage and extending the service life of heavy-load pavement.
Slope Protection and Reinforcement: Used on steep slopes of mountain roads and railways, it provides both protection and reinforcement, securing the slope soil and resisting rainwater erosion and gravity landslides. It is suitable for applications with steep slopes and high load pressure.
2. Water Conservancy and Flood Control Projects
Dyke and Flood Control Reinforcement: Installed on the waterfront slopes of dams or within the embankment, it enhances the embankment's stability against scour and sliding, dissipates water pressure on the embankment, and simultaneously drains accumulated water through filtration and drainage, reducing pore water pressure and preventing embankment failure.
River and Reservoir Bank Protection: Used for river channel regulation and reservoir bank protection, it resists bank erosion and collapse caused by water flow, intercepts soil particles, and prevents siltation in river channels. It is suitable for water environments with fast currents and strong scouring forces.
Drainage Filtration: Serves as a filter layer in drainage ditches, blind ditches, and water conservancy project drainage systems. It encapsulates gravel drainage bodies, preventing sediment from entering and clogging pipes, ensuring smooth drainage. It is suitable for drainage scenarios with high sediment content and relatively turbid water quality.
3. Industrial and Environmental Engineering
Mine and Tailings Pond Protection: Installed on the bottom and slopes of mine yards and tailings ponds, it isolates tailings from the soil, preventing the infiltration of heavy metal contaminants. It also withstands the heavy load pressure of the tailings, prevents deformation and leakage in the pond, and ensures the safety of the surrounding environment.
Landfill Reinforcement and Isolation: Applied to the outer surface of the anti-seepage system of large landfills, it serves as a reinforcement and protective layer to enhance the anti-sliding stability of the landfill slopes, withstand the pressure of the waste pile, protect the anti-seepage membrane from being punctured by sharp debris, and assist in the drainage of leachate.
Industrial Site Foundation Treatment: Installed on the foundations of heavy-duty factories, warehouses, and logistics centers, it improves the bearing capacity of weak foundations, distributes the heavy load pressure of equipment and cargo, and prevents uneven foundation settlement. It is suitable for industrial applications requiring high foundation stability.
4. Agricultural and Ecological Restoration Projects
Large-Scale Irrigation Channel Protection: Used for the slopes and bottoms of large-scale irrigation channels and main water supply canals for farmland. This protects against channel collapse caused by water erosion, reduces soil loss, and filters impurities in irrigation water, preventing channel siltation and clogging of irrigation equipment.
Ecological Slope and Wetland Restoration: In scenarios requiring a balance between strength and ecology, such as mine reforestation and riverbank ecological belts, this geotextile, combined with vegetation planting, stabilizes the soil in the restoration area and withstands slope loads. Its porosity also ensures soil permeability and promotes plant growth, achieving a combination of ecological restoration and structural stability.
Heavy-duty woven geotextiles, with their core properties of high strength, heavy-load resistance, stable drainage, and durability, have become a key geotextile in various fields, including transportation, water conservancy, industrial environmental protection, and agricultural ecology. Whether it's addressing the structural reinforcement of heavy-loaded infrastructure, anti-scour protection of water conservancy projects, or the dual "strength + ecology" needs of environmental isolation and ecological restoration in industrial scenarios, it can accurately adapt to complex working conditions, improving project stability and reducing maintenance costs while taking into account environmental benefits, providing strong support for the long-term and reliable operation of various projects.