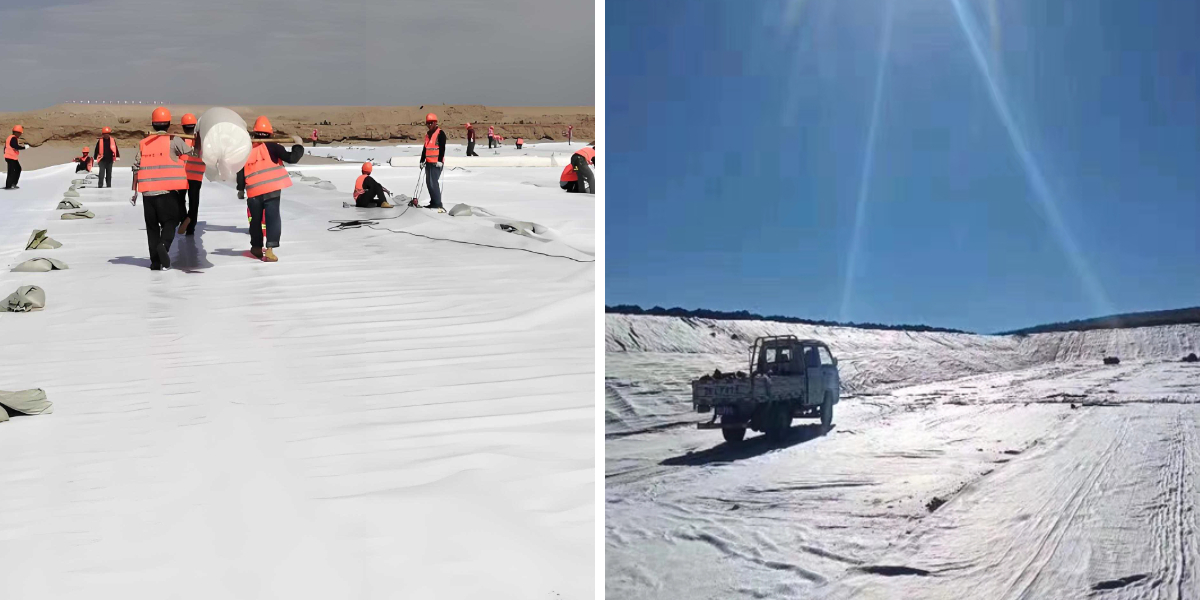
Geotextile for Soil Stabilization
Significantly Enhanced Structural Stability: Relying on the high tensile strength and creep resistance of synthetic fibers, the product can effectively disperse the upper load to a larger soil range, increasing the bearing capacity of the soil by 30–50%. In unpaved road projects, it can reduce rutting depth by about 35% and avoid road surface subsidence; in embankment and slope engineering, it can effectively inhibit deep-seated sliding of the soil and reduce the risk of engineering failure. For example, in soft soil foundation reinforcement of expressway subgrades, the use of this product can reduce the settlement of the subgrade by more than 40% compared with traditional methods.
Outstanding Cost and Time Efficiency: It can significantly reduce the amount of earthwork construction by 20–40%, avoiding the high cost of over-excavation and replacement of large quantities of aggregates in traditional methods. The product is lightweight and easy to lay, with an installation speed 3–5 times faster than traditional materials, which can shorten the construction period by 20–30% for large-scale projects. In terms of long-term operation, it can reduce maintenance costs by 50–70% due to its excellent durability, such as reducing the frequency of road repair and embankment reinforcement.
Superior Hydraulic Control Performance: The product is designed with controlled porosity, with a permeability coefficient of 10⁻¹–10⁻³ cm/s, which can quickly drain the pore water in the soil and reduce hydrostatic pressure by about 50%. This effectively avoids soil softening and strength reduction caused by water accumulation. At the same time, it can intercept soil particles and prevent soil erosion, reducing soil loss by 40–50% in slope and coastal engineering. In river bank protection projects, it can effectively resist the scouring of water flow and protect the stability of the bank slope.
Long-Term Durability and Environmental Adaptability: The synthetic fiber material (PET/PP) has excellent resistance to UV radiation, chemical corrosion (acid, alkali, salt, and organic solvents), and biological degradation (mold, insect damage). It can maintain stable performance in harsh environments such as high temperature, strong radiation, and coastal saline-alkali areas, with a service life of more than 20 years. The product also has good mechanical damage resistance, which can withstand the extrusion and impact of construction machinery and aggregates during installation and use.
Products Introduction:
Product Features:
This product has multiple core technical features, and the technical performance, principles, and application impacts of each feature are as follows:
First, it has high tensile strength, with a longitudinal tensile strength of 10–1000 kN/m, a transverse tensile strength of 5–100 kN/m, and a tensile modulus of not less than 1000 kN/m at 2% elongation. This performance comes from high-tenacity synthetic fiber materials and special weaving/needling processes, which can withstand the tensile force generated by soil deformation and upper loads, ensuring the reinforcement effect of the soil structure. It is suitable for heavy-load engineering scenarios such as highway subgrades, airport runways, and heavy-duty parking lots.
Second, it has controlled porosity, with an Aperture Size (AOS) of 0.075–0.2 mm, a porosity of 40–90%, and a permeability coefficient of 10⁻¹–10⁻³ cm/s. The pore size is precisely controlled through the production process, which can retain soil particles to prevent loss while ensuring smooth water passage for drainage. It avoids blockage of permeable channels caused by excessively large pores or drainage failure caused by excessively small pores, ensuring the long-term effectiveness of filtration and drainage functions.
Third, it has excellent chemical resistance, being able to withstand pH 3–11 acid-base environments, showing no significant performance degradation after 1000 hours of immersion in 5% sodium chloride salt solution, and can also resist erosion by organic solvents such as diesel and engine oil. The chemical stability of synthetic fibers enables the product to be used in harsh chemical environments such as industrial waste yards, landfills, coastal saline-alkali areas, and chemical plant foundations, avoiding performance degradation or damage caused by chemical corrosion and ensuring the service life of the project. In addition, the product also has good flexibility and conformability, with an elongation at break of 10–30%, a weight of 200–500 g/m², and a thickness of 1–5 mm. It is lightweight and highly flexible, able to closely fit uneven terrains such as undulating subgrades and irregular slopes without wrinkles or gaps. This not only simplifies the installation process and improves construction efficiency but also ensures full contact between the product and the soil, exerting uniform reinforcement and filtration effects. At the same time, it has excellent creep resistance. After 1000 hours of testing at 50% of the ultimate tensile strength, the creep deformation is less than 5%, and the creep rupture strength is not less than 80% of the ultimate tensile strength. Creep resistance refers to the ability to resist permanent deformation under long-term sustained loads. It can ensure that the product maintains stable structural integrity and reinforcement performance for a long time, avoiding engineering failure problems such as subgrade settlement and slope sliding caused by material creep deformation in long-term service projects.
Finally, the product has strong puncture resistance and wear resistance, with a dynamic puncture resistance of 1000–2000 N and a mass loss of less than 5 g after 500 cycles of wear testing. During construction and operation, it can resist puncture by aggregates and rocks as well as wear by construction machinery, preventing product damage and ensuring functional integrity. It is particularly suitable for engineering scenarios with large aggregate particle sizes and frequent construction machinery operations, such as highway base reinforcement and pipeline trench backfilling.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
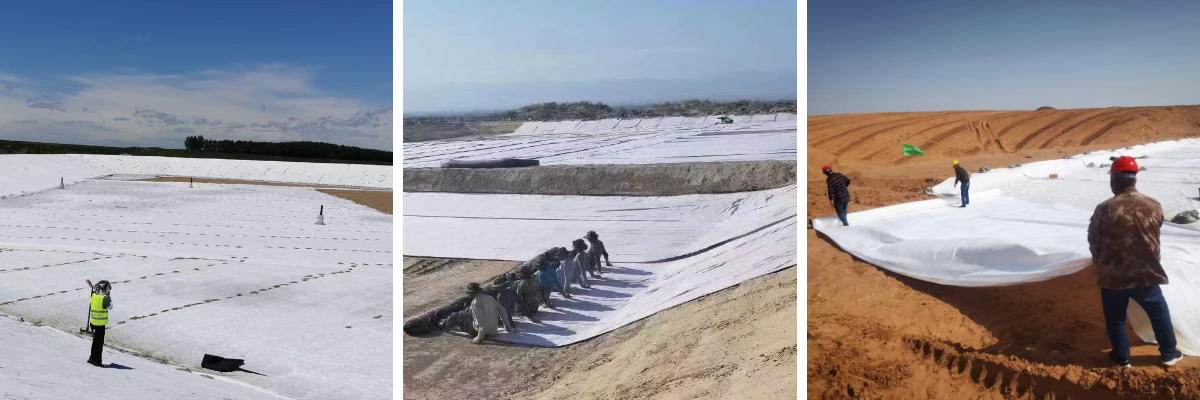
Product Applications:
1 Transportation Infrastructure Engineering
Road Engineering: Used for the stabilization of road subgrades and bases. For soft soil subgrades, it can enhance the bearing capacity of the subgrade, reduce settlement, and avoid road surface cracking and rutting. For example, in the construction of rural highways and expressways in soft soil areas, the use of this product can reduce the thickness of the base course, save construction costs, and improve the service life of the road.
Railway Engineering: Applied to the separation and reinforcement of railway ballast. It can prevent the mixing of ballast and subgrade soil, avoid ballast settlement and deformation, and ensure the stability of the railway track. At the same time, it can improve the drainage performance of the ballast layer, reduce the impact of groundwater on the subgrade, and ensure the safe operation of the railway.
Airport and Port Engineering: Used for the foundation improvement of airport runways and taxiways, enhancing the bearing capacity of the foundation to meet the take-off and landing requirements of large aircraft. In port and wharf engineering, it is used for the treatment of soft soil foundations of wharf platforms and approach bridges, reducing foundation settlement and ensuring the stability of port facilities.
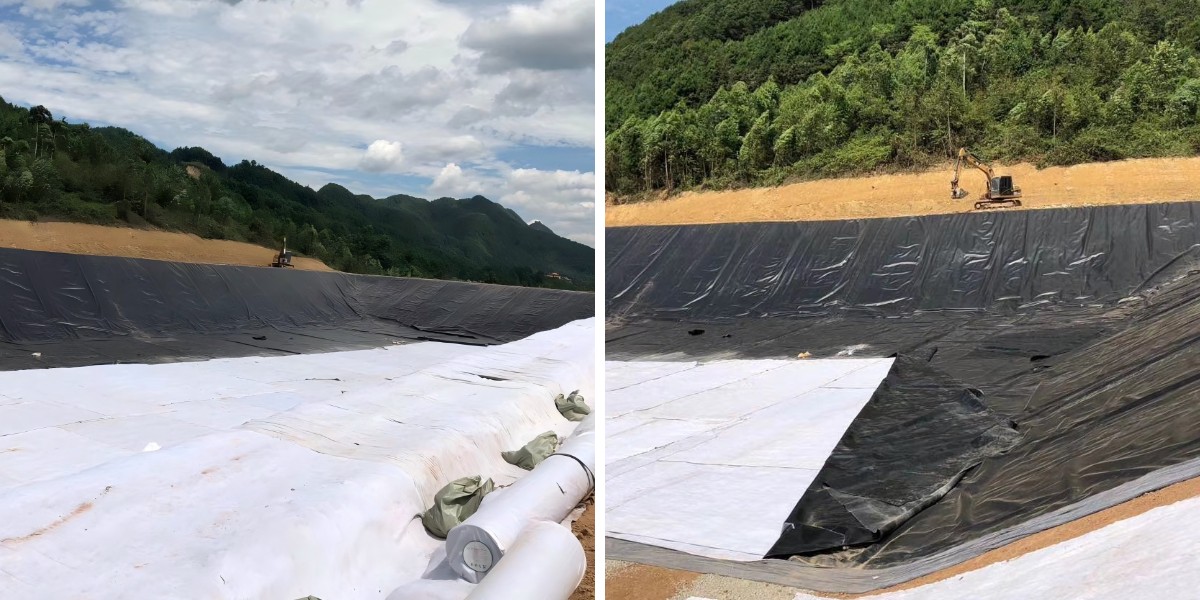
2 Water Conservancy and Coastal Engineering
Dam and Levee Engineering: Used for the anti-seepage, filtration, and slope protection of dams and levees. It can prevent soil erosion on the slope of dams and levees caused by water scouring, enhance the stability of the dam body, and reduce the risk of dam collapse. At the same time, it can drain the seepage water in the dam body, reduce hydrostatic pressure, and avoid dam body softening.
River and Coastal Bank Protection: Applied to the protection of river banks and coastal shorelines. It can resist the scouring of river water and sea waves, prevent bank collapse and coastal erosion, and protect the ecological environment of the river and coastal areas. For example, in the ecological restoration project of river banks, the combination of geotextiles and vegetation can achieve both soil stabilization and ecological greening effects.
Reservoir and Channel Engineering: Used for the filtration and drainage of reservoir bottoms and channel linings. It can prevent soil loss in the reservoir and channel, avoid the silting of the reservoir and channel, and ensure the normal operation of water storage and water delivery. At the same time, it can protect the channel lining from damage caused by soil deformation.
3 Environmental and Geotechnical Engineering
Landfill Engineering: Used for the protection of landfill liners and the drainage of leachate. It can prevent the landfill liner from being punctured by garbage and soil, ensuring the anti-seepage effect of the landfill. At the same time, it can drain the leachate in the landfill, reduce the pressure on the liner, and avoid the leakage of leachate and environmental pollution.
Mining Engineering: Applied to the stabilization of mining tailings dams. It can enhance the stability of the tailings dam, prevent dam collapse and tailings leakage, and protect the surrounding environment and human life safety. In addition, it can be used for the treatment of goafs and the reinforcement of mining area foundations.
Soil Remediation Engineering: Used for the isolation of contaminated soil. It can prevent the spread of contaminated soil and groundwater, ensuring the effectiveness of soil remediation. At the same time, it can provide reinforcement and drainage functions for the remediation site, facilitating the construction of remediation projects.
4 Urban and Agricultural Engineering
Urban Construction: Used for the reinforcement of retaining walls, basement foundations, and subway pit slopes. It can enhance the stability of retaining walls and slopes, prevent collapse, and ensure the safety of urban construction projects. In addition, it can be used for the drainage of urban green spaces and square bases, improving the waterlogging resistance of urban areas.
Landscaping and Sports Facilities: Applied to the stabilization of landscaping slopes and the base drainage of golf courses, football fields, and other sports facilities. It can prevent soil erosion on landscaping slopes and ensure the flatness and stability of the base of sports facilities. At the same time, it can improve the drainage performance of the base, avoiding water accumulation and affecting the use effect.
Agricultural Engineering: Used for the anti-seepage and soil conservation of farmland irrigation canals and terraced fields. It can reduce water seepage in irrigation canals, save water resources, and prevent soil erosion on terraced fields, improving the utilization rate of agricultural land.
Geotextile stabilization, as a multifunctional and efficient engineering material, plays a crucial role in various engineering fields such as roads and railways, slope protection, water conservancy and transportation, construction and municipal engineering, and mining environment restoration due to its high strength, good filtration and drainage performance, excellent durability, lightweight and easy construction, and environmental protection. It can not only effectively solve the problems of soil stability, settlement, and soil erosion in traditional engineering, improve the safety and durability of engineering structures, but also reduce engineering costs, shorten construction periods, and meet the efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly requirements of modern engineering construction.
With the continuous development and progress of engineering technology, the performance of Geotextile Stabilization products will be further optimized, and their application areas will continue to expand. In future engineering construction, it will become an important supporting material for achieving engineering safety, environmental protection, and sustainable development, providing more reliable technical support for various infrastructure construction and environmental governance projects.