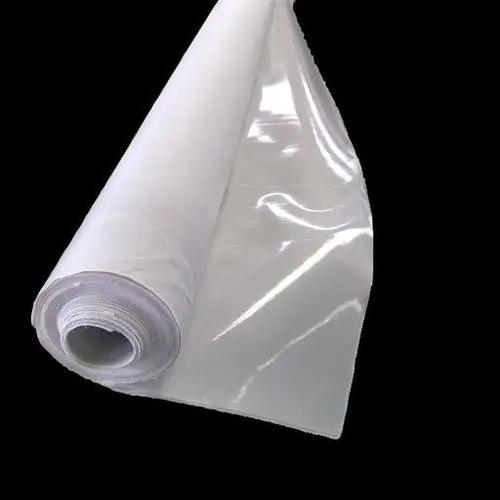
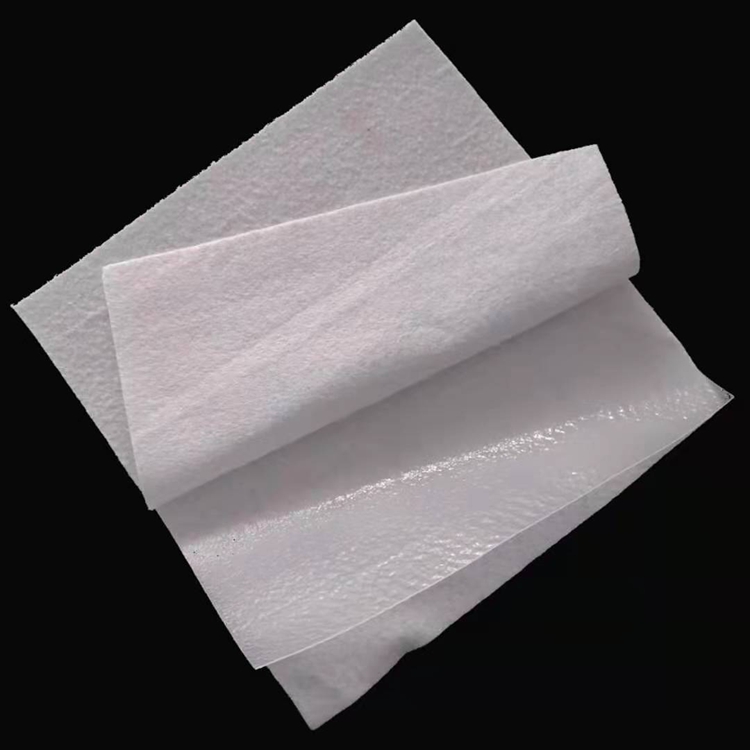
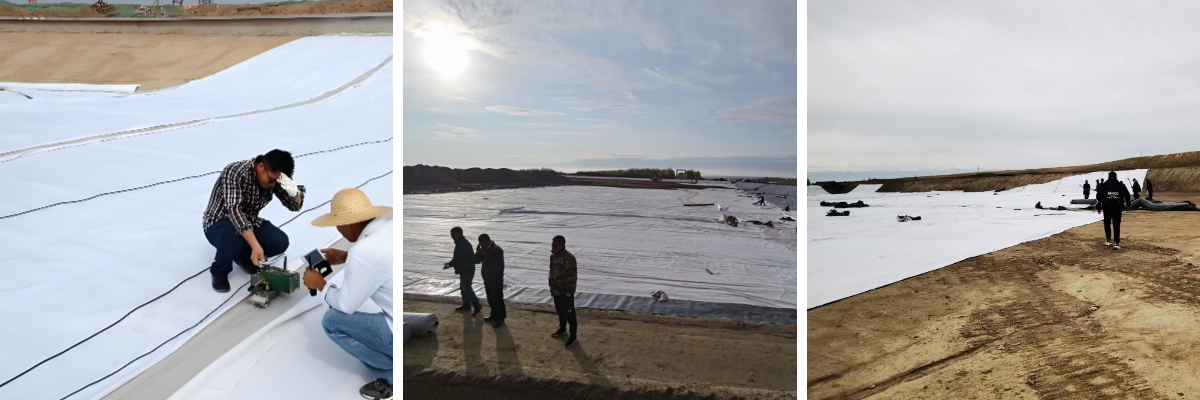
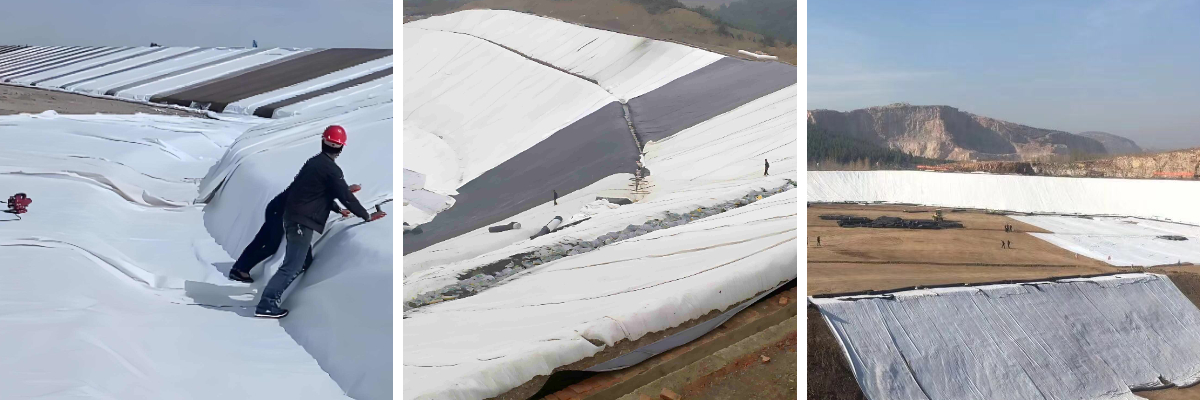
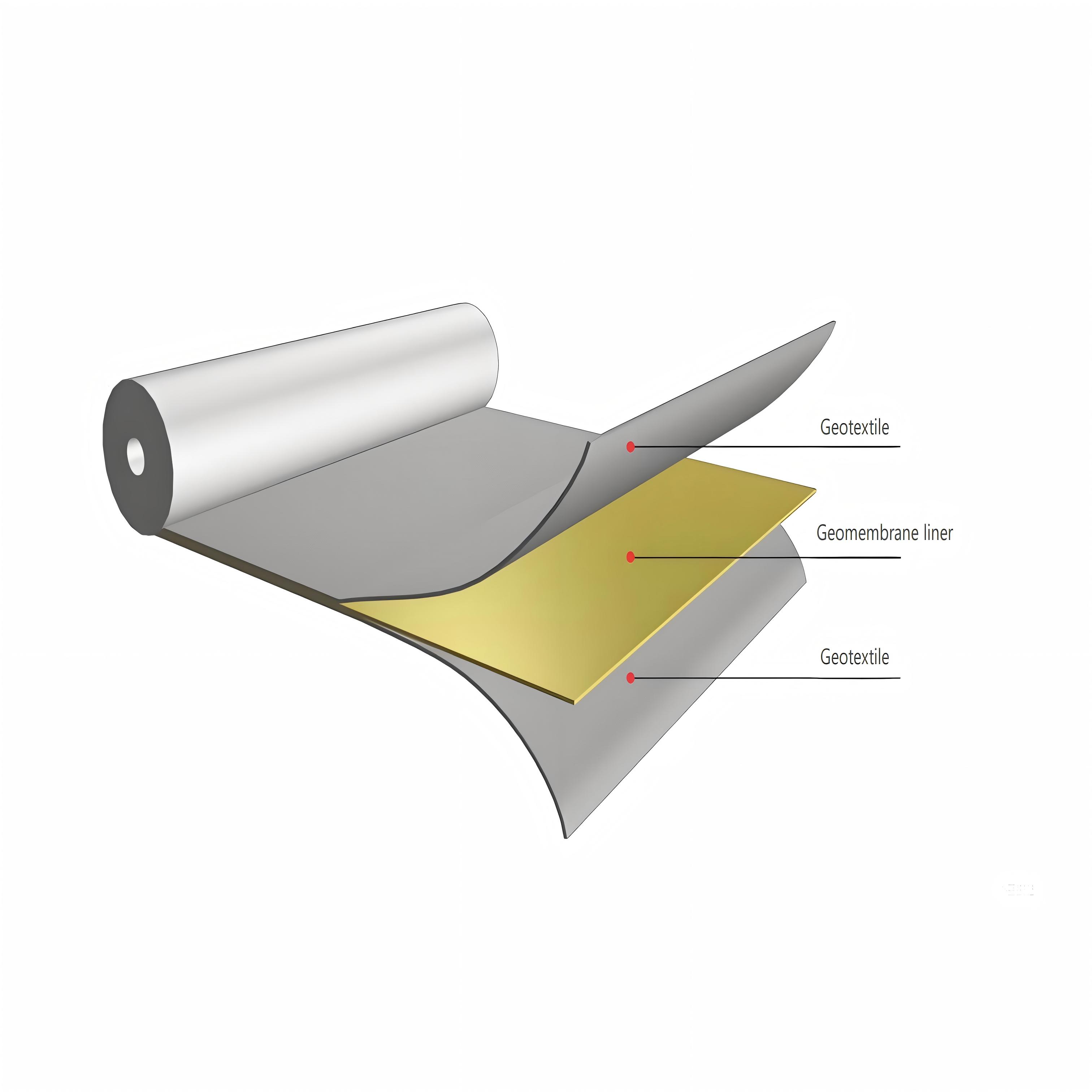
HDPE Composite Geomembrane
1.Superior Impermeability: The dense HDPE film structure effectively blocks water, gas, and chemical seepage, with a permeability coefficient as low as 1×10⁻¹² cm/s.
2.Enhanced Durability: Resists UV radiation, aging, corrosion (acid/alkali/salt), and microbial degradation, ensuring long-term performance (service life up to 50+ years in protected environments).
3.High Mechanical Strength: The geotextile composite layer improves tensile, tear, and puncture resistance, adapting to ground settlement and construction loads.
4.Easy Construction: Lightweight, flexible, and weldable (via thermal fusion), enabling efficient on-site installation with tight, leak-proof joints.
5.Cost-Effective: Combines impermeability and reinforcement functions in one material, reducing material types and construction costs.
Product Introduction:
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Composite Geomembrane is a high-performance engineered geosynthetic material designed for advanced impermeability, reinforcement, and protection applications in civil engineering and environmental projects. It is a multi-layer composite structure, typically consisting of a core HDPE geomembrane layer bonded with one or two layers of geotextiles (non-woven polypropylene or polyester geotextile, or woven geotextile) through advanced thermal lamination, hot-press bonding, or needle-punching technology. This integrated structure combines the intrinsic advantages of each component, creating a material that outperforms single-layer geomembranes or geotextiles in comprehensive performance.
The core HDPE film is manufactured from high-purity HDPE resin with added anti-UV stabilizers, anti-aging agents, and anti-oxidants, ensuring excellent chemical stability and long-term weather resistance. The thickness of the HDPE film layer can be customized from 0.2mm to 3.0mm, while the geotextile layer (either single-sided or double-sided) has a grammage range of 100g/m² to 600g/m², allowing precise matching to the specific requirements of different projects. The composite material features a smooth or textured surface (textured version enhances friction with soil and other materials) and exhibits excellent flexibility, enabling it to conform to irregular ground surfaces and adapt to slight ground settlement without cracking.
Key physical and mechanical properties of HDPE Composite Geomembrane include: tensile strength ≥ 15kN/m (depending on specifications), elongation at break ≥ 400%, puncture resistance ≥ 300N, and a permeability coefficient as low as 1×10⁻¹² cm/s, which meets or exceeds international standards such as ISO 10818 and GB/T 17643.
Core performance characteristics
Excellent anti-seepage ability: The HDPE membrane itself has an extremely low permeability (close to zero), and the composite structure further prevents pore leakage, making it suitable for liquid anti-seepage projects (such as reservoirs and landfills).
High Strength and Durability: High tensile strength (≥15MPa), tear-resistant, puncture-resistant, and can withstand foundation settlement or external impacts. Strong anti-aging performance, resistant to ultraviolet rays, high and low temperatures (-70℃~+70℃), and the service life can reach more than 50 years.
Outstanding chemical stability: Resistant to the corrosion of acid, alkali, salt solutions and organic solvents, suitable for complex environments such as chemical pollution sites and tailings ponds.
Construction convenience: The material has good flexibility, can adapt to uneven terrain, and has various splicing methods (hot melt welding, gluing). The welding strength is more than 80% of the base material. It is lightweight (1000 - 3000g/m²), and the transportation and laying efficiency is high.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||
| Nominal fracture strength/(kN/m) | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | |
| 1 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength/(kN/m) ≥ | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
| 2 | Longitudinal and transverse standard strength corresponding elongation/% | 30~100 | |||||||
| 3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 3 | 3.2 |
| 4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN ≥ | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.7 |
| 5 | Peel strength/(N/cm)> | 6 | |||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | As required by design or contract | |||||||
| 7 | Width deviation /% | -1 | |||||||
| project | film thickness /mm | ||||||||
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
| Resistant to static water pressure /MPa ≥ | One cloth, one membrane | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| Two cloth and one film | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | |
| Note: If the film thickness is between adjacent specifications in the table, the corresponding assessment index shall be calculated by linear interpolation; if it exceeds the range in the table, the assessment index shall be determined by negotiation between the supplier and the demander. | |||||||||
Product Applications:
1.Environmental Protection Engineering
• Landfills: Used as the main impermeable liner and capping material for municipal solid waste landfills, hazardous waste landfills, and industrial waste landfills. It effectively contains leachate (the toxic and harmful liquid produced by waste decomposition) and prevents it from seeping into the groundwater and soil, protecting the surrounding ecological environment. The composite structure provides reinforcement and puncture resistance, preventing damage from sharp waste particles.
• Sewage Treatment: Applied in the linings of sewage treatment ponds, oxidation ditches, and sludge storage lagoons. It prevents the seepage of sewage and sludge, ensuring the efficiency of sewage treatment and avoiding secondary pollution of groundwater.
• Remediation of Contaminated Sites: Used as a barrier layer in the remediation of contaminated soil and groundwater, preventing the spread of pollutants and facilitating the treatment of contaminated media.
2.Water Conservancy & Hydraulic Engineering
• Reservoirs & Ponds: Used as the impermeable liner for reservoirs, small ponds, and water storage tanks, reducing water seepage loss and improving water storage capacity. It is particularly suitable for arid and semi-arid regions where water conservation is critical.
• Canals & Irrigation Systems: Applied in the lining of irrigation canals, water transfer canals, and ditches. It reduces water seepage (seepage loss can be reduced by more than 90% compared to unlined canals), improving water use efficiency and reducing the cost of water diversion projects.
• Dams & Embankments: Used as a seepage control layer in earth-rock dams, slope protection of embankments, and anti-seepage reinforcement of old dams. It reduces seepage pressure, prevents dam foundation piping, and enhances the stability and safety of dams and embankments.
• Coastal & River Engineering: Applied in coastal revetments, riverbank protection, and tidal flat reclamation projects. It resists erosion by waves and currents, protects the bank slope, and prevents soil loss.
3.Mining Industry
• Tailings Ponds: Used as the impermeable liner for metal ore tailings ponds (such as iron ore, copper ore, and gold ore tailings ponds). It prevents the seepage of heavy metal-containing tailings water into the groundwater, protecting the ecological environment of mining areas.
• Heap Leaching Pads: Applied in the lining of heap leaching pads for metal ore processing. It resists corrosion by acidic leaching solutions (such as sulfuric acid solutions) and prevents the seepage of leachate, ensuring the efficiency of heap leaching and avoiding environmental pollution.
• Coal Mine Goafs: Used as a sealing and impermeable material in coal mine goafs (abandoned mining areas), preventing the seepage of groundwater and the spread of harmful gases (such as methane).
4.Agricultural Engineering
• Irrigation & Water-Saving Agriculture: Used as the liner for agricultural irrigation ponds, drip irrigation systems, and greenhouse soil moisture retention layers. It reduces water seepage, improves water use efficiency, and promotes water-saving agriculture.
• Aquaculture: Applied in the lining of fish ponds, shrimp ponds, and other aquaculture ponds. It prevents water seepage, maintains stable water levels, and avoids soil contamination of the aquaculture environment. The smooth surface also facilitates pond cleaning and reduces the growth of algae and bacteria.
5.Infrastructure & Other Fields
• Land Reclamation: Used in the impermeable lining of reclaimed land (such as coastal land reclamation and industrial wasteland reclamation), preventing saltwater intrusion and improving soil quality.
• Subway & Tunnel Engineering: Applied as a waterproof layer in subway tunnels, road tunnels, and underwater tunnels. It provides reliable waterproofing and resists the pressure of groundwater.
• Rooftop Gardens & Landscape Engineering: Used as a waterproof and impermeable layer in rooftop gardens, artificial lakes, and landscape ponds. It prevents water seepage into the building structure and protects the roof from damage.
• Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applied in the linings of anaerobic ponds, aeration ponds, and sludge dewatering areas, ensuring the containment of wastewater and sludge and preventing environmental pollution.