Woven Geo Fabric
1.Corrosion resistance: Generally, it has the characteristics of acid resistance, alkali resistance, moth resistance, and mildew resistance. It can maintain stable performance in different chemical environments and is suitable for various complex soil and water quality conditions.
2.Water permeability: The size and distribution of its structural pores can be effectively controlled according to engineering requirements to achieve a certain degree of water permeability. It can not only allow water to pass through but also prevent the loss of soil particles, etc., playing the role of filtration and drainage.
3.Durability: Synthetic chemical fiber materials are not prone to deformation, decomposition, and weathering. They can maintain their original properties during long - term use, resist the influence of natural environmental factors such as ultraviolet rays, temperature changes, and humidity, and have a long service life.
4..High strength: High-strength synthetic fibers are used as raw materials, which inherently possess high original strength. After the weaving process, the fibers interweave and restrain each other, forming a stable structure. The comprehensive bearing capacity is further enhanced, enabling it to withstand large tensile forces, pressures, and shear forces, etc.
Product Introduction:
Woven Geo Fabric is a kind of geotechnical material made from high-strength industrial synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, polyester, and nylon through a weaving process.
Structural Features
Warp and Weft Interwoven Structure: It is formed by the interweaving of two sets of filaments or flat strips, creating a regular interwoven structure. This structure endows the geotextile with good mechanical properties in both the warp and weft directions, enabling it to withstand external forces from different directions.
Highly Designable: By adjusting the types, specifications, yarn counts, densities of raw materials and the weaving process, the structure and properties of geotextiles can be precisely controlled to meet the needs of different projects. For example, for projects requiring higher strength, the fiber density can be increased or thicker yarns can be used.
Product Parameters:
| project | metric | |||||||||||||
| Nominal strength/(kN/m) | ||||||||||||||
| 35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | ||||
| 1 Tensile strength per (kN/m) ≥ | 35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | |||
| 2. Weft tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | After tensile strength is multiplied by 0.7 | |||||||||||||
| 3 | Maximum elongation at maximum load/% | warp direction ≤ | 35 | |||||||||||
| broadwise ≤ | 30 | |||||||||||||
| 4 | Top penetration force /kN is greater than or equal to | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10.5 | 13 | 15.5 | 18 | 20.5 | 23 | 28 | ||
| 5 | Equivalent aperture O90 (O95)/mm | 0.05~0.50 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10⁵~102) where: K=1.0~9.9 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -1 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | Tear strength in both directions /kN ≥ | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.7 | ||
| 9 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | ||||||||||||
| 10 | Length and width deviation rate/% | ±2 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | Joint/seam strength a/(kN/m) ≥ | Nominal strength x 0.5 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | Anti-acid and alkali properties (strong retention of warp and weft Rate) a /% ≥ | Polypropylene: 90; other fibers: 80 | ||||||||||||
| 13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) b | The strength retention rate in both directions is /%≥ | 90 | |||||||||||
| 14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescencePhotometric ultraviolet lamp method) | The strength retention rate in both directions is /%≥ | 90 | |||||||||||
Product Applications:
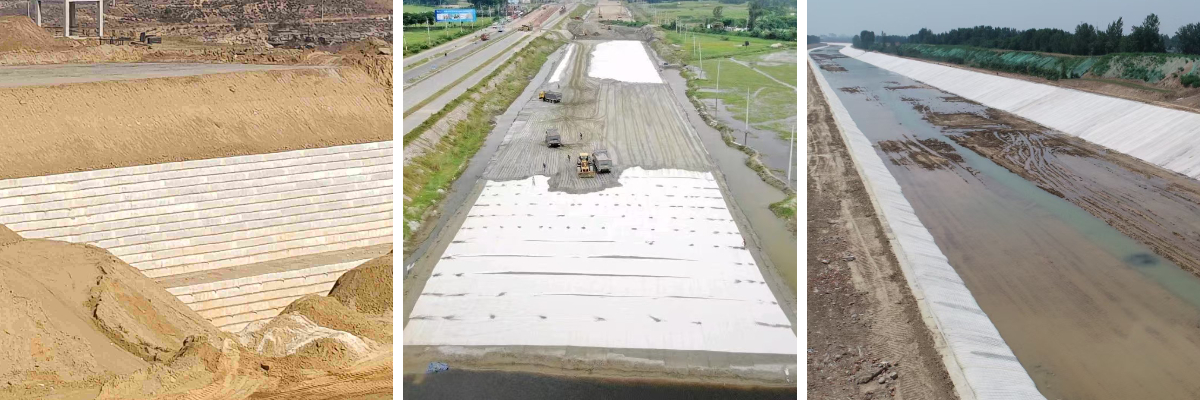
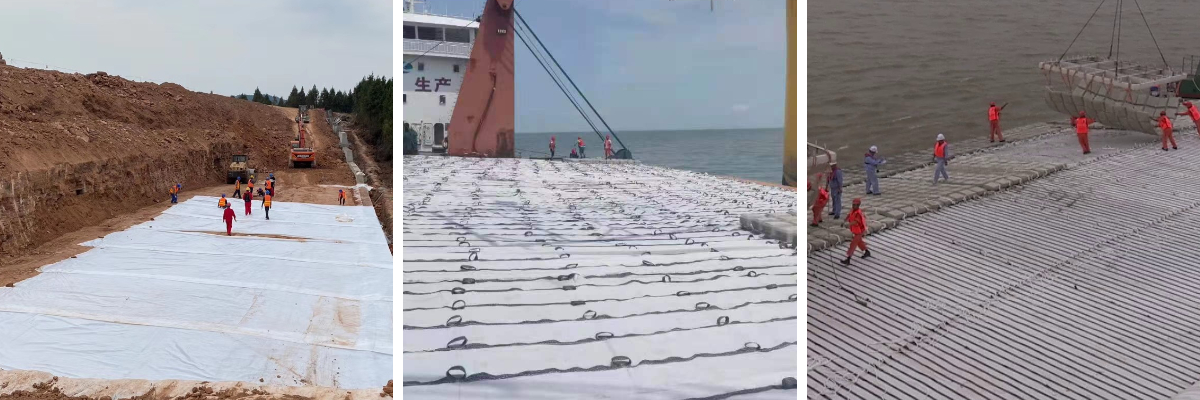
1.Hydraulic Engineering: It is used for river slope protection, coastal embankment construction, anti-seepage, filtration, and reinforcement of reservoir dams, as well as anti-seepage of channels. It can prevent the scouring of soil by water flow, protect the stability of embankments and dam bodies, and at the same time play the role of filtration and drainage to ensure the safe operation of hydraulic facilities.
2.Traffic Engineering: In the construction of highways and railways, it can be used for subgrade reinforcement, soft soil foundation treatment, and prevention of reflective cracks on road surfaces. It can effectively disperse and transfer the load borne by the subgrade, enhance the overall stability of the subgrade, prevent subgrade settlement and deformation, and extend the service life of roads and railways.
3.Environmental Protection Engineering: In the construction of landfills, it is used for anti-seepage, filtration and drainage at the bottom and sides to prevent the leachate from polluting the groundwater. At the same time, it provides good drainage and air permeability to protect the surrounding environment.
4.Mining Engineering: It is used for the construction and reinforcement of mine tailings dams, as well as the waterproofing and drainage of mine shafts. This can prevent environmental pollution caused by tailings leakage and ensure the safe operation of mining engineering.
5.Ocean Engineering: In the construction of seaports, docks, artificial islands, etc., it is used for anti-erosion layers, isolation layers, and reinforcement layers to resist the erosion of coastal areas and buildings by marine dynamic factors such as waves and tides, and improve the stability and durability of ocean engineering.
Woven geotextiles, with their high strength, durability, and designable functions, play key roles such as reinforcement, anti - seepage, filtration, drainage, and isolation in civil engineering. They are important functional materials in fields such as water conservancy, transportation, and environmental protection.