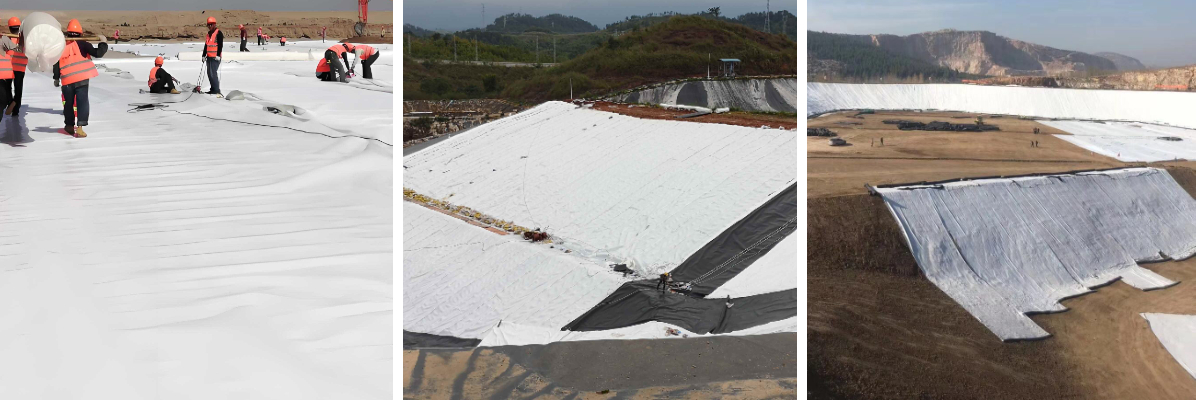
Non Woven Geotextile Filter Fabric
Excellent filtration performance
Prevent the loss of soil particles, while allowing water to permeate and drain, maintaining the stability of the soil structure.
Strong mechanical properties
High tensile strength, tear resistance, aging resistance, UV resistance, adaptable to soil deformation, and durable in the long term.
Good corrosion resistance
Resistant to acid, alkali, and microbial erosion, adaptable to different geological and water quality conditions, and has a long service life.
Ecology and Economy
Reduce the use of natural sand and gravel, which is environmentally friendly; can be combined with vegetation greening, and has a low maintenance cost.
Product Introduction:
Non Woven Geotextile Filter Fabric is a kind of geosynthetic material made from polymer materials such as polyester and polypropylene through processes like needle punching and weaving. It has unique functions such as filtration, isolation, and drainage, and is widely used in the engineering field.
Core Materials and Structure
Materials: Mainly use high - molecular polymers such as polyester (PET) and polypropylene (PP), which have the characteristics of chemical corrosion resistance, UV resistance, and anti - aging.
Structure: A porous structure is formed through fiber needling or weaving. The size and distribution of the pore diameters can be designed according to requirements, achieving the dual functions of "blocking particles + water permeability".
Main Functions and Advantages
Efficient Filtration: Prevents the loss of soil particles while allowing water to penetrate, preventing the soil structure from being damaged by water flow scouring (such as dam piping and roadbed settlement).
Isolation and Stabilization: Separates soil layers of different particle sizes to avoid mixing and maintain the stability of the soil structure (such as the isolation between the roadbed and the gravel layer).
Drainage and Seepage Guidance: Serves as a drainage channel to accelerate the discharge of water from the soil and is often used in the drainage systems of dams and slopes.
Excellent Mechanical Properties: High tensile strength and good flexibility, can adapt to soil deformation, and is not easily damaged during long - term use.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
| Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
| 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
| 1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
| 2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
| 3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
| 4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
| 5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
| 7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
| 8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
| 9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
| 10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
| 11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
| 12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
| 13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
| 14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
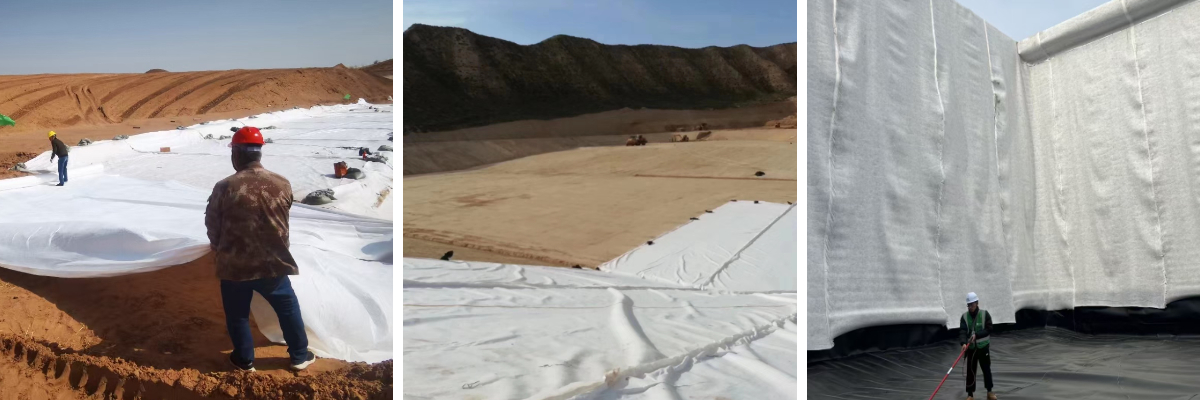
Water conservancy project:The filter layers of dams and cofferdams prevent soil erosion caused by water flow scouring; the drainage and filtration of drainage ditches and reservoirs.
Traffic engineering:Laying under road subgrades and railway roadbeds to filter water, protect the subgrades, prevent road surface settlement caused by waterlogging, and carry out slope protection.
Environmental protection engineering:Filter leachate in landfills to prevent the spread of pollutants; dewater sludge in sewage treatment plants to assist in the discharge of water.
Geotechnical engineering:Tunnel waterproofing and drainage, soft soil foundation reinforcement, slope greening (combined with vegetation to fix soil and promote plant growth).
Agriculture and Ecology:Farmland drainage, soil and water conservation, reducing irrigation water loss; salt drainage and filtration in saline-alkali land improvement.
Compared with the traditional sand and gravel filter layer, non woven geotextile filter fabric has advantages such as light weight, low cost, high construction efficiency, and environmental friendliness (reducing the exploitation of natural sand and gravel). It has become the preferred solution to replace traditional materials in modern projects, especially in complex terrains or ecologically sensitive areas, where it is more practical.