Geotextile De Drainage
1.Efficient drainage and flood prevention: The three-dimensional structure features high porosity and rapid drainage, while lowering the water level to prevent deformation and prevent seepage.
2.Two-way protection: Filters sediment to prevent clogging, reduces loads and protects the base material, extending the life of the project.
3.Weather and corrosion resistance: The polymer raw material is treated to withstand temperature fluctuations, acidity, and alkali, ensuring stable performance in harsh environments.
4.Convenient and low-cost: The single roll is lightweight and wide, making it easy to lay and cut manually, reducing costs by over 30%.
Product Introduction
I. Basic Properties
Material Composition: Geotextile De Drainage are made from high-molecular-weight polyethylene or polypropylene through a special process, combining flexibility with structural stability.
Physical Form: They feature a three-dimensional mesh structure with widths up to 6-8 meters. A single roll weighs only 20-50 kg, making them easy to transport and deploy.
Environmental Adaptability: Treated for anti-aging and UV resistance, they operate stably within a temperature range of -40°C to 80°C. They are also acid- and alkali-resistant and resistant to microbial attack, making them suitable for a variety of complex environments.
II. Core Functions
Efficient Drainage and Waterlogging Prevention: With a high porosity of 70%-90%, they achieve a vertical drainage rate exceeding 5 × 10⁻³ m/s, rapidly draining excess soil moisture, lowering the groundwater level and preventing structural deformation caused by waterlogging and softening.
Bidirectional Protection: Its compact fiber structure filters sediment from the water, preventing soil fines from eroding and clogging drainage channels. It also buffers external loads, reducing frictional damage to underlying geomembranes, drainage blind pipes, and other materials, extending the project lifespan by 3-5 years.
Cost Optimization and Savings: It can be quickly laid manually without the need for complex construction machinery. Its flexible, easy-to-cut material conforms to irregular terrain, such as slopes and trenches, minimizing material waste and reducing construction costs by over 30% compared to traditional gravel drainage layers.
III. Key Features
High Performance and Efficiency: Its drainage rate and protective effectiveness far exceed those of traditional materials, quickly resolving core issues such as waterlogging and blockages in projects and ensuring structural stability.
Ease of Use: Its lightweight design and wide width simplify the construction process, reducing labor and equipment reliance and shortening the construction period.
Durability: High-quality raw materials and specialized processing techniques provide it with strong weather and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term functionality in harsh environments and reducing ongoing maintenance costs.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1. Transportation Infrastructure
Highway and Railway Roadbed: Laid between the subgrade soil layer and the cushion layer, it utilizes its high porosity to quickly drain rainwater and groundwater, reducing the subgrade's moisture content and preventing subgrade settlement and cracking caused by soil softening. It also filters sediment and prevents drainage blockage, ensuring long-term structural stability and reducing the need for subsequent maintenance.
Bridge and Tunnel Engineering: Laid between bridge abutments and tunnel sidewalls and backfill, it drains water around the structures, preventing erosion of bridge piers and tunnel linings. It also mitigates frictional damage from backfill loads, extending the service life of bridges and tunnels.
2. Water Conservancy and Municipal Engineering
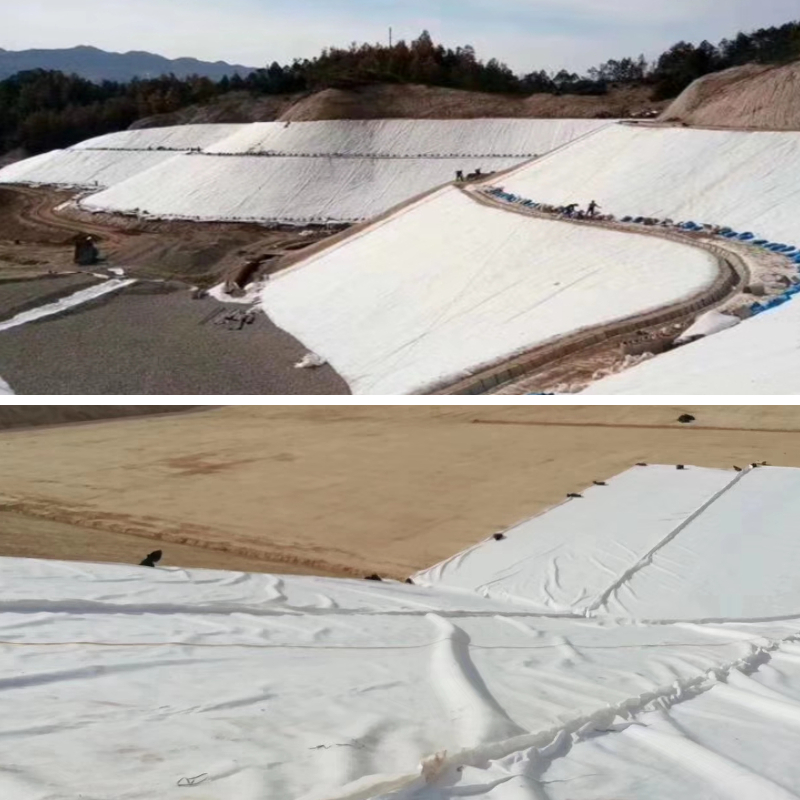
Dyke and River Management: Used outside the impermeable layer of dykes or for river slope protection, it rapidly drains excess water from dyke and slope soil, enhancing soil stability and preventing landslides, piping, and other disasters. It also filters sediment and prevents siltation in rivers. Its acid, alkali, and microbial resistance make it suitable for the complex, long-term water-related environments of water conservancy projects.
Municipal Drainage and Sponge Cities: They serve as a filtration and drainage layer in underground drainage systems for urban sidewalks and squares, or as rainwater infiltration systems in parks and green spaces. They quickly collect and channel surface rainwater, replenish groundwater, and alleviate urban flooding. They also filter impurities and prevent clogging of drainage pipes, meeting the sponge city's "infiltration, retention, storage, utilization, and drainage" construction requirements.
3. Environmental Protection and Construction
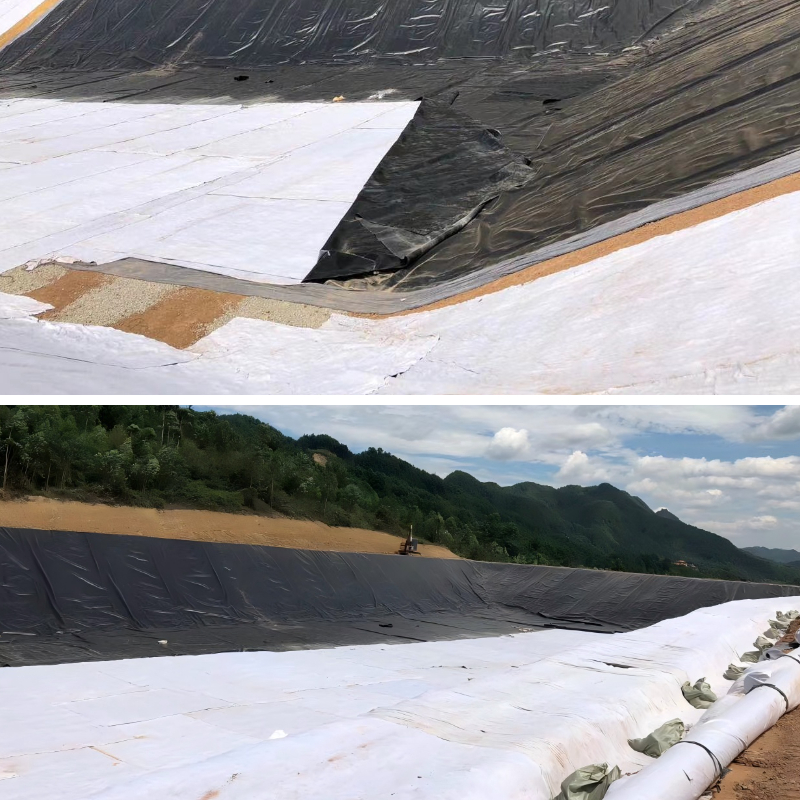
Landfills: They are laid above the impermeable membrane at the bottom of the landfill reservoir. They channel leachate, preventing damage to the membrane caused by accumulation. They also filter solid impurities from the leachate, preventing clogging of drainage blind pipes, ensuring efficient operation of the leachate collection system, and reducing soil and groundwater contamination.
Building Foundation Pits and Underground Garages: Used in the foundation pit slope support layer or underground garage roof backfill layer, it quickly drains seepage from the foundation pit and rainwater from the roof, reducing the moisture content of the surrounding soil and preventing pit collapse. It also protects the support structure and roof waterproofing layer, reduces groundwater erosion on the building structure, and improves the waterproofing and moisture-proofing of the construction project.
4. Agriculture and Gardening
Farmland Water Conservancy and Saline-Alkali Land Improvement: Lay it around irrigation channels and drainage ditches to divert excess irrigation water or groundwater, preventing waterlogging and crop root rot. In saline-alkali land improvement projects, it accelerates the removal of salt from the soil with water, reducing soil salinity and improving the growing environment for crops. It also filters sediment and keeps channels clear.
Landscaping and Rooftop Gardens: Used for slope drainage of landscape water bodies (such as artificial lakes and ponds) or as drainage layers in rooftop gardens, it quickly drains accumulated water from slope soil and rooftop plantings, preventing plant root rot. Its lightweight and easy-to-cut design makes it suitable for installation in areas with limited roof space and irregular terrain, reducing roof loads.
Drainage geotextiles, with their core advantages of efficient drainage, two-way protection, weather and corrosion resistance, and easy installation, have been widely adopted in key projects across various sectors, including transportation, water conservancy, environmental protection, construction, and agricultural landscapes. They not only address specific challenges such as water accumulation, erosion, and blockage in various scenarios, ensuring the safety and long-term stability of project structures, but also simplify construction processes and reduce maintenance costs, providing crucial support for the efficient construction and sustainable operation of various projects. They have become an indispensable functional material in modern engineering construction.