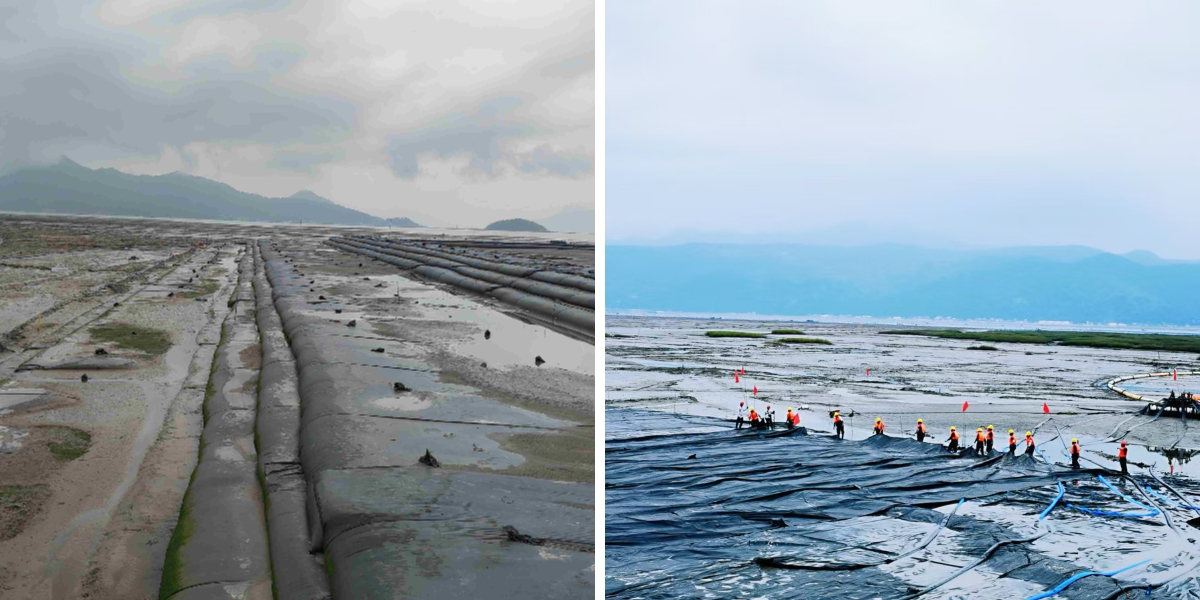
Coastal Geotextile Tubes
1. Convenient construction
Geotextile bags can be stacked for transportation, allowing for quick on-site filling and shortening the construction period.No need for complex machinery, suitable for remote areas or emergency rescue projects.
2. Outstanding cost-effectiveness
Sludge dewatering does not require electricity and has significant energy-saving and emission reduction effects.
3. Strong adaptability
It can handle various materials such as high moisture sludge (moisture content>90%), industrial waste residue, and river sludge.
4. Multifunctionality
It has functions such as drainage, reinforcement, filtration, and isolation, meeting diverse engineering needs.
Product Introduction:
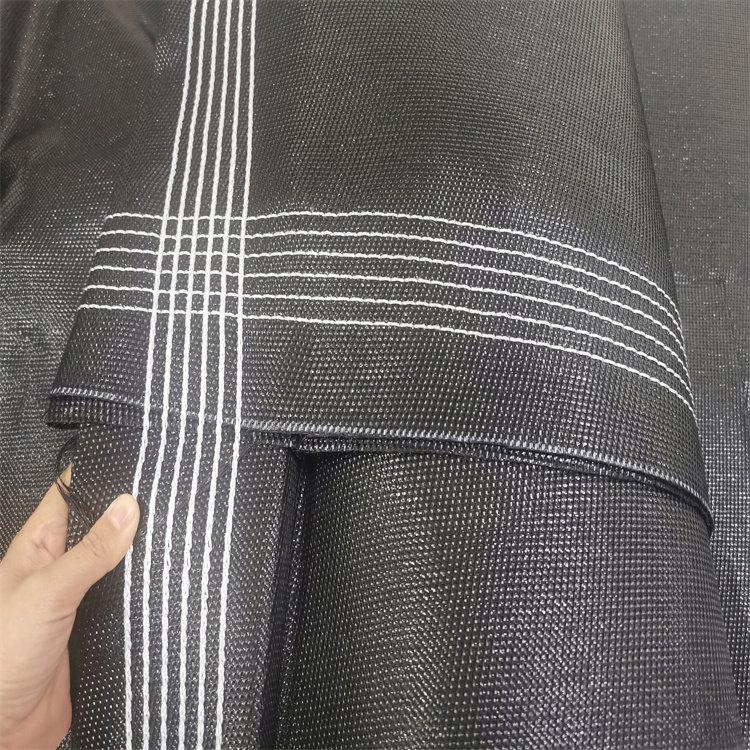
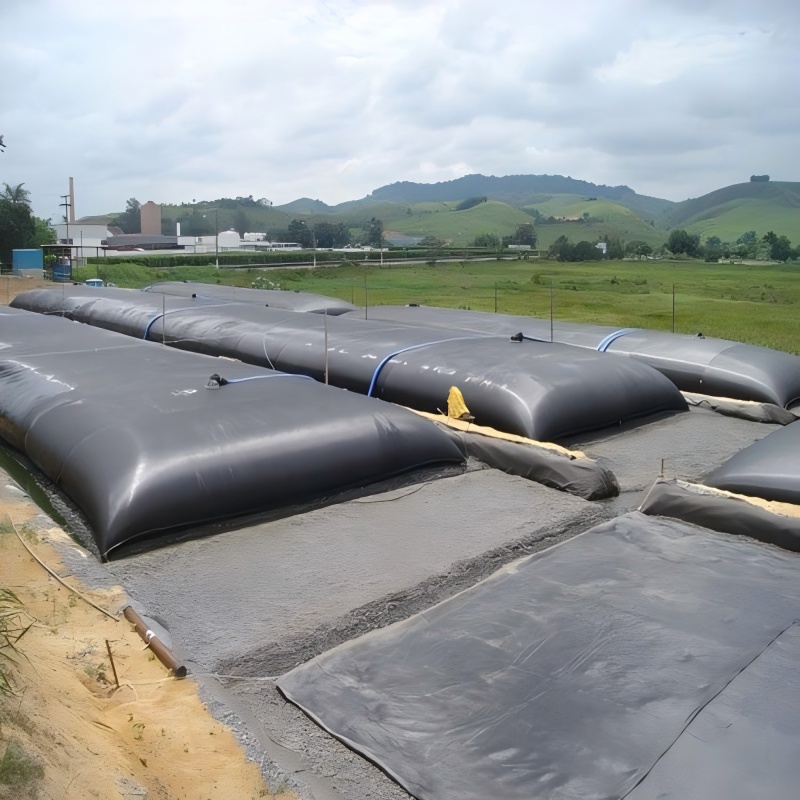
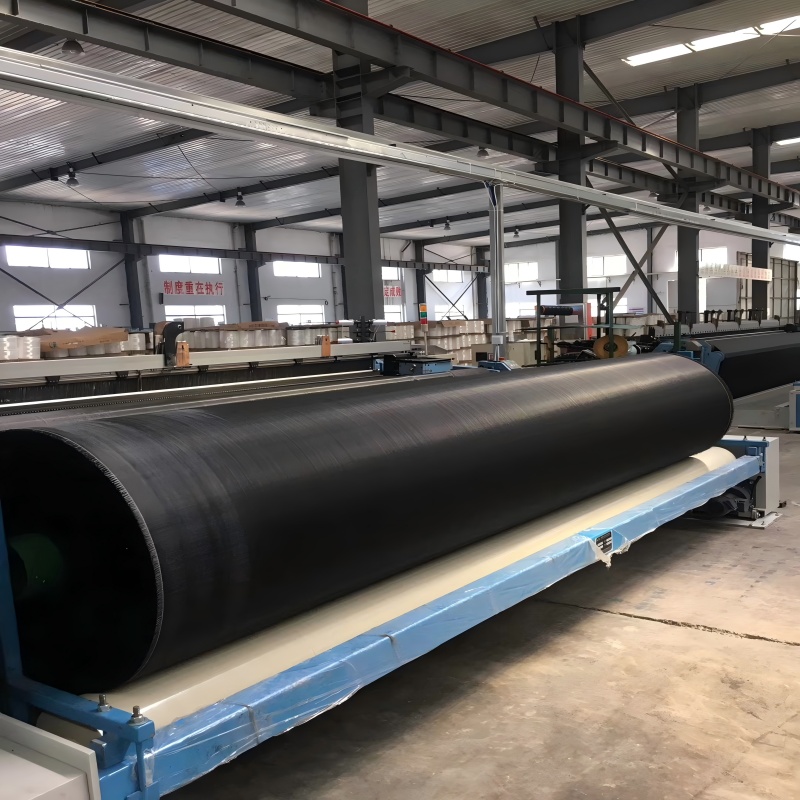
Coastal Geotextile Tubes are large tubular package made of high-strength geotextile fabric (such as polypropylene) through special sewing process. Its diameter and length can be flexibly customized according to engineering needs, and the longest can reach tens of meters. It achieves solid-liquid separation by filling materials such as sediment and sludge, utilizing the filtering performance of geotextiles, and ultimately forming a stable structure, which is widely used in fields such as water conservancy, environmental protection, and marine engineering.
Core Features
1. High strength and durability
The tensile strength reaches 45-200kN/m and can withstand high-pressure filling and long-term loads.
UV resistant, acid and alkali resistant (pH 2-13), resistant to microbial erosion, and adaptable to harsh environments.
The suture site has high strength, low risk of bag bursting, and a service life of several decades.
2. Flexibility and customizability
The diameter and length can be adjusted as needed, supporting multiple splices to adapt to different site sizes.
The filling height is usually 2/3 of the diameter to ensure structural stability.
3. Environmental Protection and Economy
Fully enclosed construction, no noise, no secondary pollution, meets the requirements of green engineering.
No need for large equipment or factory investment, only a small number of non professional personnel are required to operate, reducing labor costs.
4. Efficient dehydration and volume reduction
The pore size of geotextile can intercept solid particles and discharge water, and the sludge volume can be reduced by more than 90% within one month.
Dehydrated sludge can be directly used for slope protection, greening, or agriculture, achieving resource utilization.
Product Parameters:
project | unit | CWGD50S | CWGD90/120 | CWGD90S | CWGD100S | CWGD120S-B | CWGD120S-C | CWGD130S | CWGD200S-C | |
Tensile strength-radial | kN/m | 55 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 220 | |
Tensile strength-Weft | 50 | 120 | 90 | 100 | 120 | 120 | 130 | 210 | ||
Strain elongation-radial | % | 16±1 | 12±1 | 9±1 | 10±1 | 10±1 | 10±1 | 10±1 | 12±1 | |
Extensional elongation-Weft | 10±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | 8±1 | ||
Breakage strength at 2% elongation | warp direction | kN/m | 5/15 | 14/40 | 30/30 | 30/30 | 20/40 | 22/40 | 20/45 | 15 |
Breakage strength at 5% elongation | warp direction | kN/m | 14/33 | 38/90 | 75/75 | 75/75 | 80/100 | 84/40 | 80/110 | 90 |
mass area ratio | g/m² | 285 | 440 | 390 | 430 | 540 | 540 | 560 | 850 | |
Joint tensile strength | kN/m | 35 | 90 | 60 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 170 | |
Static Burst Strength (CBR) | KN | 5 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 22 | |
Dynamic perforation | mm | 10 | 8 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 8 | |
Equivalent aperture (0g0) | mm | 0.9 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.43 | 0.4 | |
Permeability (Q50) | L/m²/s | 200 | 40 | 20 | 15 | 12 | 6.5 | 15 | 15 | |
Ultraviolet resistance (500h strong storage rate ) | % | 90 | 90 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | |
Product Applications:
1. Water conservancy engineering
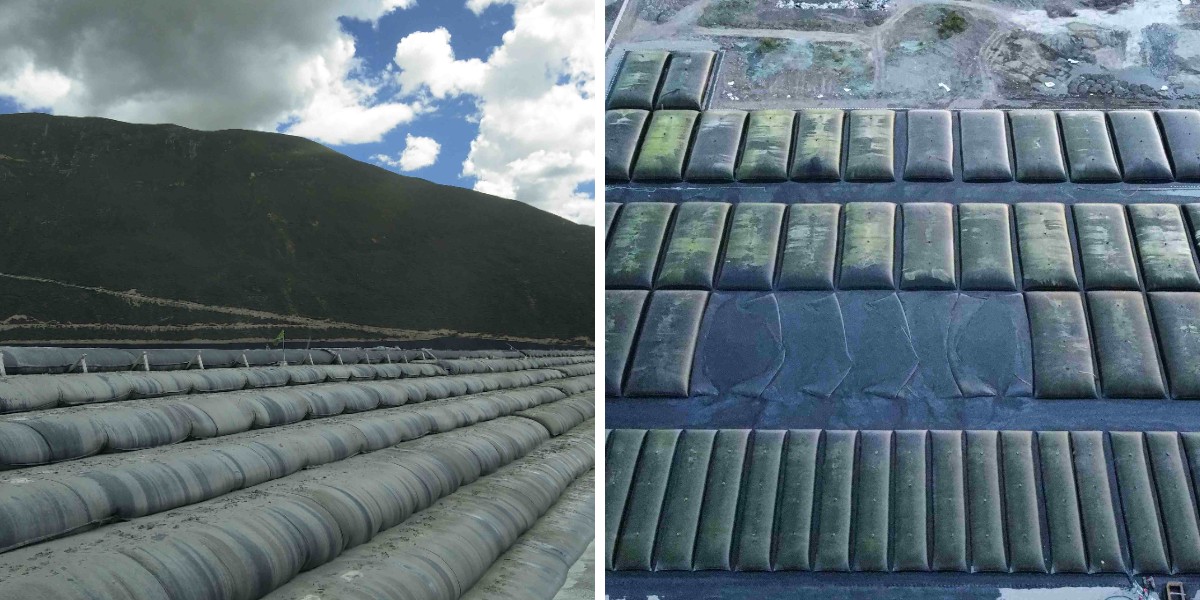
Embankment and Breakwater: As a core material for embankments, it can replace traditional stone throwing and reduce costs by more than 50% (such as the Amwaj Islands artificial island project in Saudi Arabia).
River treatment: used for sludge dewatering and solidification to prevent secondary pollution of sediment (such as the Taihu Lake Lake sediment treatment project).
Reservoir slope protection: Dehydrated silt is used as slope protection material to enhance slope stability.
2. Ocean Engineering
Artificial island construction: forming the core of an island by filling it with sea sand, such as the Buwana Ventura project in Colombia.
Dock protection: As a wave barrier structure, it resists the impact of tides and waves.
3. Environmental Protection Engineering
Industrial sludge treatment: treating highly polluted sludge from industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, printing and dyeing to achieve standard discharge.
Landfill closure: As a covering material, it isolates garbage from the external environment.
4. Agriculture and Municipal Affairs
Agricultural and pastoral wastewater treatment: purifying the wastewater from washing manure in the farm and recovering water resources.
Urban sludge dewatering: used for reducing sludge in sewage treatment plants and reducing landfill pressure.
5. Emergency rescue
Flood disaster: Quickly construct temporary dams to intercept the spread of floods.
Oil leakage: Fill with oil absorbing materials to form an isolation zone to control the pollution range.
Geotextile bags have become an indispensable flexible structural material in modern engineering due to their high strength, environmental friendliness, economy, and multifunctionality. From coastal protection to inland governance, from industrial processing to agricultural applications, its innovative technologies constantly expand the boundaries and provide efficient solutions for sustainable development. With the advancement of materials science, the performance of geotextile bags will be further improved, and their application scenarios will become more extensive.