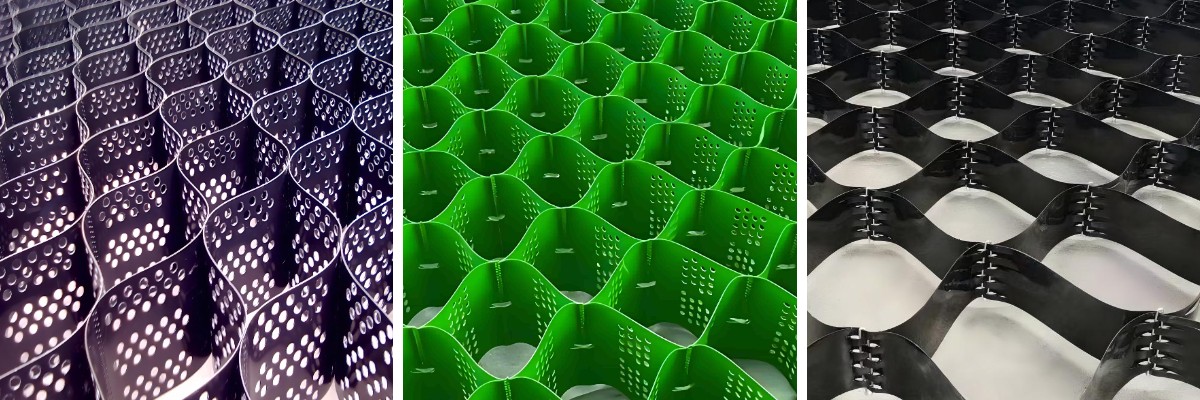
Design Considerations for Geocell Slopes: Slope Angle, Soil Type, and Load
Geocell slope safety has end up a go-to answer for stabilizing slopes in construction, transportation, and environmental projects—offering a stability of structural strength, cost-effectiveness, and ecological compatibility. However, the success of any geocell slope device hinges on three fundamental layout factors: slope angle, soil type, and utilized load. Overlooking these factors can lead to gadget failure, erosion, or slope instability, even with magnificent materials. This information delves into every consideration, explaining how they have an impact on sketch selections and highlighting the position of complementary options like Specifications of geotextile tubes and Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects in growing sturdy slope systems.
Why Design Precision Matters for Geocell Slope Protection
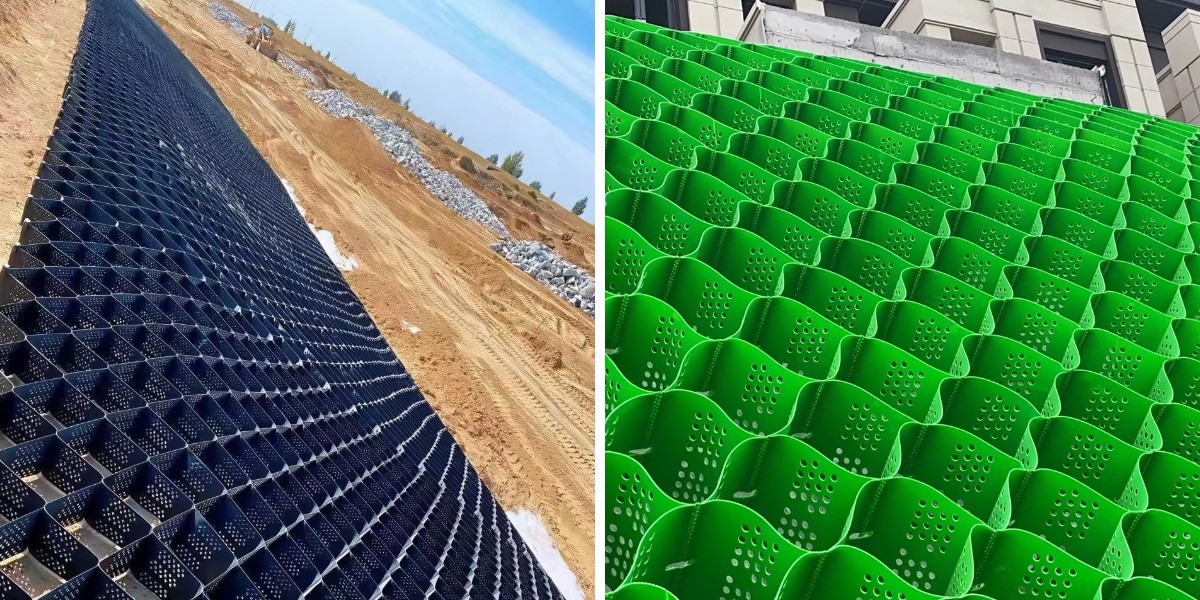
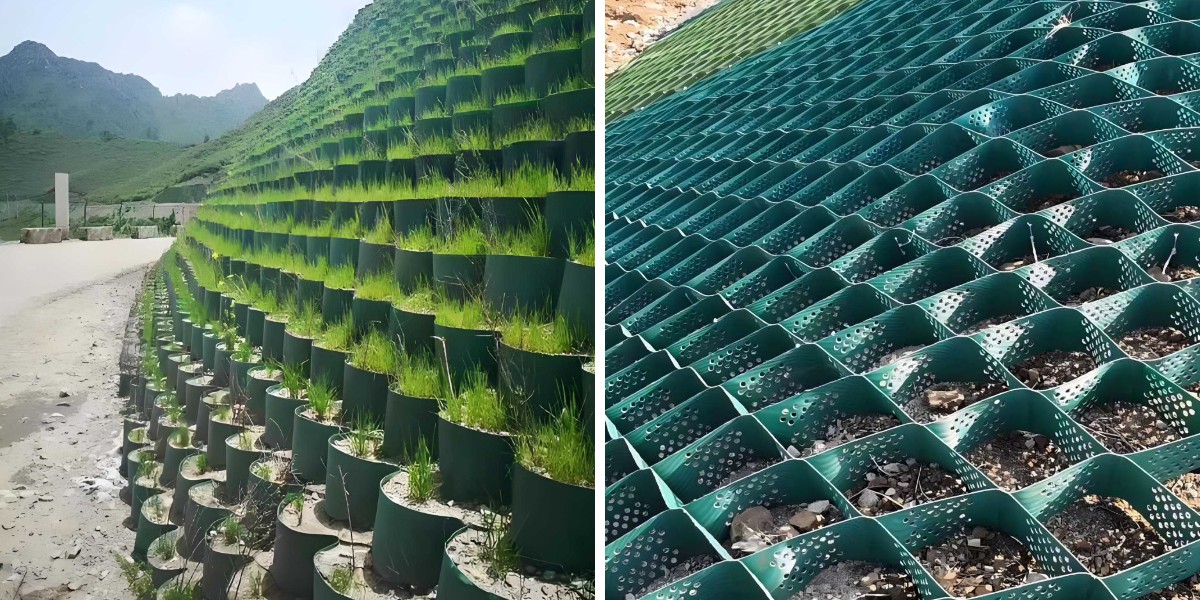
Geocell slope safety works via confining soil inside a third-dimensional honeycomb grid, distributing forces evenly and reinforcing the slope’s herbal stability. But this gadget isn’t one-size-fits-all—slopes with steep angles, terrible soil quality, or heavy hundreds require tailor-made designs to keep away from collapse. A well-designed geocell slope now not solely prevents erosion and landslides however additionally integrates seamlessly with surrounding environments. In initiatives the place sediment manipulate is necessary (e.g., close to waterways), pairing geocells with Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects ensures complete protection. By prioritizing format precision, engineers and contractors create slope structures that are durable, compliant, and constructed to face up to long-term environmental and operational stress.
Consideration 1: Slope Angle—Balancing Steepness and Stability
Slope attitude is the most seen format factor, as it immediately affects the geocell system’s load-bearing necessities and erosion risk. Gentle slopes (less than 1:3 gradient) exert minimal lateral stress on geocells, whilst steep slopes (up to 1:1 gradient) demand bolstered grids and extra stabilization measures. Exceeding a geocell system’s encouraged slope perspective can lead to soil slippage, grid deformation, or whole slope failure.
Design Strategies for Different Slope Angles
For mild slopes: Use standard-height geocells (10–20 cm) with a lightweight, woven geotextile material. The grid’s confinement on my own is regularly ample to forestall erosion, and vegetation can be brought to beautify aesthetics and long-term stability.
For average slopes (1:2 to 1:1.5): Opt for taller geocells (20–30 cm) and enhance the grid with anchor pins or geotextile underlays to face up to lateral movement.
For steep slopes (1:1.5 to 1:1): Incorporate bench terraces inside the geocell machine to minimize slope size and pressure. Pair with Specifications of geotextile tubes at the slope base to seize runoff and forestall toe erosion, growing a multi-layered safety system.
Consideration 2: Soil Type—Matching Geocells to Ground Conditions
Soil kind dictates the geocell’s confinement needs, drainage requirements, and fabric selection. Sandy soils, for example, drain shortly however lack cohesion, whilst clay soils keep water and are inclined to swelling. Loamy soils provide a stability however may also require extra reinforcement for heavy loads. Using the incorrect geocell format for soil kind can end result in terrible drainage, soil compaction, or grid separation.
Tailoring Geocells to Soil Characteristics
Sandy soils: Choose geocells with smaller telephone sizes to higher confine unfastened particles. Add a permeable geotextile liner to forestall soil loss whilst keeping drainage.
Clay soils: Use geocells with large mobile sizes to enhance water infiltration and decrease swelling. Incorporate drainage holes in the grid and pair with Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects if the slope is close to water—this captures fantastic clay sediments that may additionally wash off throughout heavy rain.
Loamy soils: Standard geocell designs work well, however make certain the grid cloth is UV-resistant and tear-proof to take care of reasonable loads. For all soil types, check compaction ranges earlier than set up to make certain the geocells sit down on a secure base.
Consideration 3: Applied Load—Designing for Static and Dynamic Forces
Geocell slopes ought to face up to two sorts of loads: static (e.g., soil weight, vegetation) and dynamic (e.g., foot traffic, development equipment, rainfall impact). Underestimating these masses leads to grid deformation, soil displacement, or slope collapse. For slopes in high-traffic areas (e.g., street embankments) or close to heavy machinery, load-bearing ability is a pinnacle priority.
Load-Bearing Design Tips
Static loads: Calculate the whole weight of soil and vegetation inside the geocell grid, and choose a geocell fabric with a tensile electricity that exceeds this load. For slopes with deep soil layers, use thicker geocell partitions to forestall bulging.
Dynamic loads: Reinforce the geocell gadget with a geotextile overlay to distribute strain from foot site visitors or equipment. For slopes close to development zones, set up brief limitations to redirect heavy equipment away from the geocell edges. In areas with extreme rainfall, layout the geocell grid to take care of accelerated runoff velocity—pair with Specifications of geotextile tubes alongside the slope crest to divert water and minimize erosion forces.
Complementary Solutions: Geotextile Tubes and Sedimentation Tubes
While geocells shape the core of geocell slope protection, complementary merchandise beautify universal machine performance:
Specifications of Geotextile Tubes
Specifications of geotextile tubes—such as diameter, length, and geotextile material—should align with slope plan needs. These tubes are frequently used at the slope toe or crest to act as electricity dissipators, lowering the influence of runoff. For steep slopes, pick out large-diameter tubes (1–2 meters) made from woven geotextile for most strength. They can additionally be crammed with neighborhood soil or sediment, making them a cost effective and eco-friendly stabilization tool.
Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects
When geocell slopes are section of dredging or waterfront projects, Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects play a quintessential function in shooting suspended sediments. These tubes forestall sediment from washing into waterways, defending aquatic ecosystems and complying with environmental regulations. Integrate them downstream of the geocell slope to create a filtration barrier, making sure that runoff from the slope is clear earlier than it enters herbal water bodies.
Conclusion: Holistic Design for Long-Lasting Geocell Slopes
Designing geocell slope safety requires a holistic method that bills for slope angle, soil type, and utilized load. By tailoring geocell specs to these factors—and incorporating complementary options like Specifications of geotextile tubes and Sedimentation Tubes for Dredging Projects—you create a slope device that is stable, durable, and environmentally responsible.
Whether you’re designing a slope for a highway, residential development, or environmental restoration project, precision is key. Consult geotextile professionals to check soil conditions, calculate load requirements, and pick out the proper materials. A well-designed geocell slope doesn’t simply stop problems—it provides value, improving website safety, lowering protection costs, and helping sustainable land use. For your subsequent slope stabilization project, prioritize these diagram considerations, and you’ll construct a gadget that stands the take a look at of time.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province