Non Woven Filter Fabric
1.Strong functional complexity: Combines filtration, drainage, isolation, reinforcement and protection, solving multiple engineering problems without extra materials, simplifying construction.
2.Stable physical performance: Good tensile strength, tear resistance, acid-alkali and corrosion resistance, maintaining stability in complex environments for long service life.
3.Convenient and efficient construction: Lightweight, easy to transport, simple to lay and splice, shortening construction time effectively.
4.Outstanding economic performance: Lower cost than traditional materials, reducing material and labor input, with low long-term maintenance costs and high cost-effectiveness.
5.Widely applicable: Customizable specifications for various scenarios in water conservancy, transportation, municipal engineering, environmental protection, etc.
Product Introduction
Basic attributes
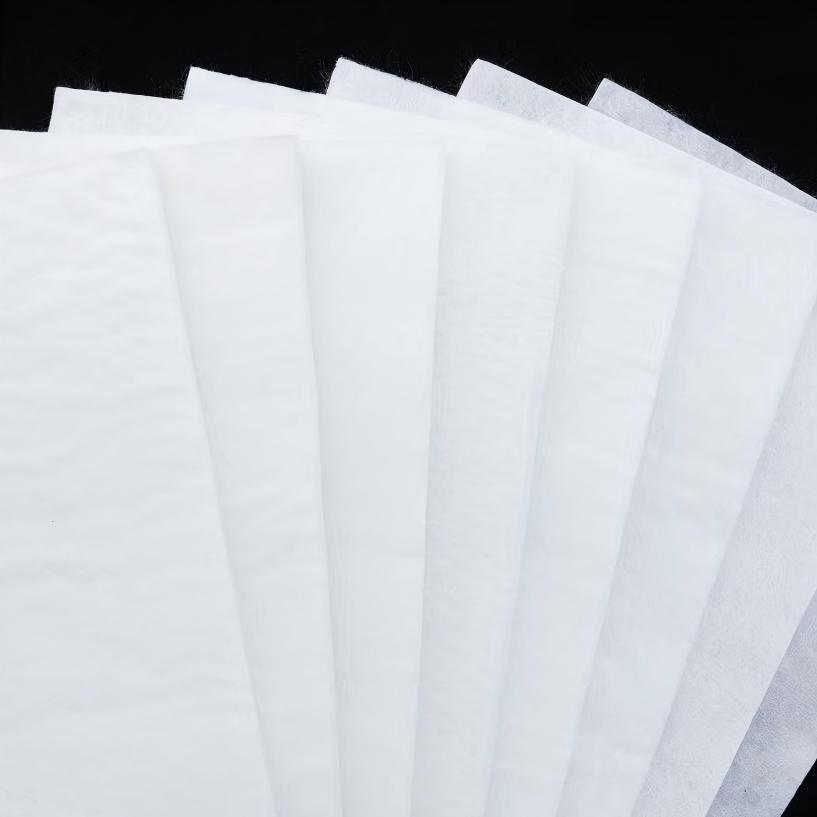
Non Woven Filter Fabric is mainly made of synthetic fibers such as polypropylene and polyester, and is processed through needle punching, weaving, or hot melt techniques. It is a permeable geosynthetic material, and some products use natural fibers, but its application is limited. Its physical form is mostly a cloth like roll or sheet, with a thickness ranging from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters, a width of usually 1-6 meters, and a length that can be customized. It has a certain pore structure that allows water or gas to pass through while blocking soil particles. It also has mechanical properties such as tensile strength, tearing, and bursting. The performance of products varies greatly depending on different processes and raw materials.
Core functions
Filtering function: When water flows through, it intercepts soil particles to prevent their loss, while ensuring water infiltration and avoiding instability of foundations or slopes, such as used as a filter layer for dams and drainage ditches.
Drainage function: By using porous structures to collect and discharge excess water from the soil, the pore water pressure of the soil is reduced, and the stability of the foundation is improved. For example, laying behind roadbeds and retaining walls can accelerate drainage.
Isolation function: Separate materials with different physical properties to prevent mixing and maintain their functional and structural integrity, such as isolating between roadbed and foundation, gravel layer and clay layer.
Reinforcement effect: Utilizing its own tensile strength to enhance the mechanical properties of soil, transmit stress, limit soil deformation, and improve the bearing capacity and stability of structures such as slopes and embankments, such as for soft foundation reinforcement and steep slope protection.
Protective function: Protect soil or other materials from external environmental erosion such as water flow erosion and wind erosion, reduce mechanical damage during construction, such as protecting embankments in river regulation.
Main features
Geotextiles have strong durability, and synthetic fiber materials are resistant to corrosion and aging. They can work stably in complex environments for a long time, with a service life of 10-50 years. Convenient construction, lightweight texture, easy transportation and laying, simple splicing process, suitable for large-scale and rapid construction, can greatly shorten the construction period. Good economy, lower unit area cost than traditional materials, can reduce material usage and construction labor costs, and long-term maintenance costs are also lower. Wide adaptability, can customize different specifications according to engineering needs, suitable for multiple fields such as water conservancy, highways, railways, municipal engineering, environmental protection, etc. In addition, some products are environmentally friendly, made of biodegradable materials or recycled fibers, and can reduce soil excavation and sand and gravel mining, thereby reducing ecological damage.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
Application in Water Conservancy Engineering
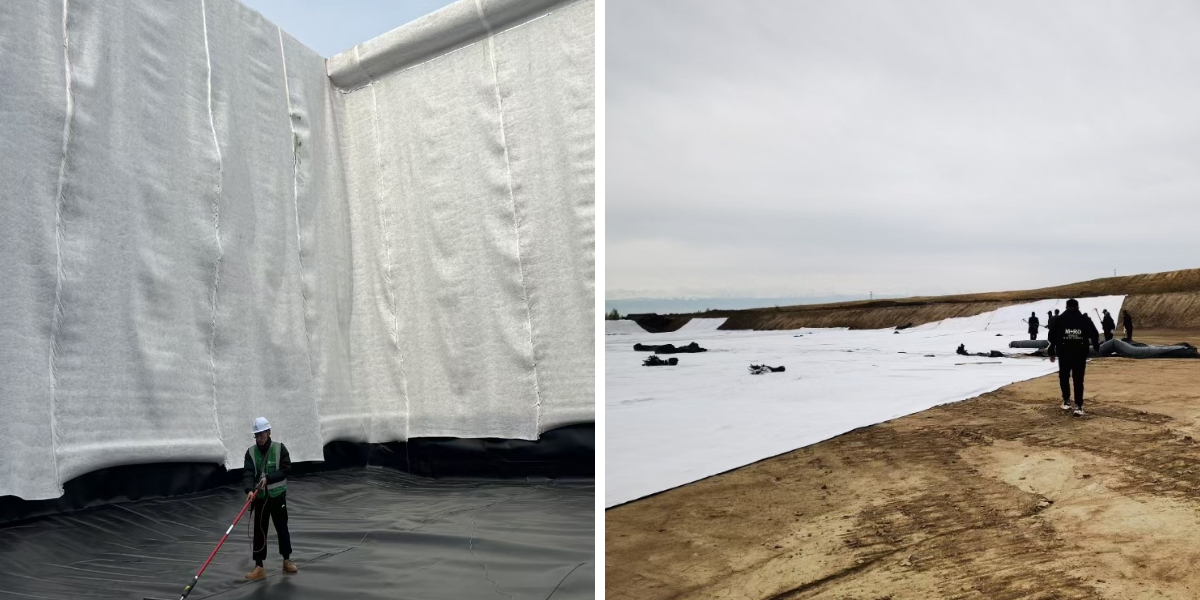
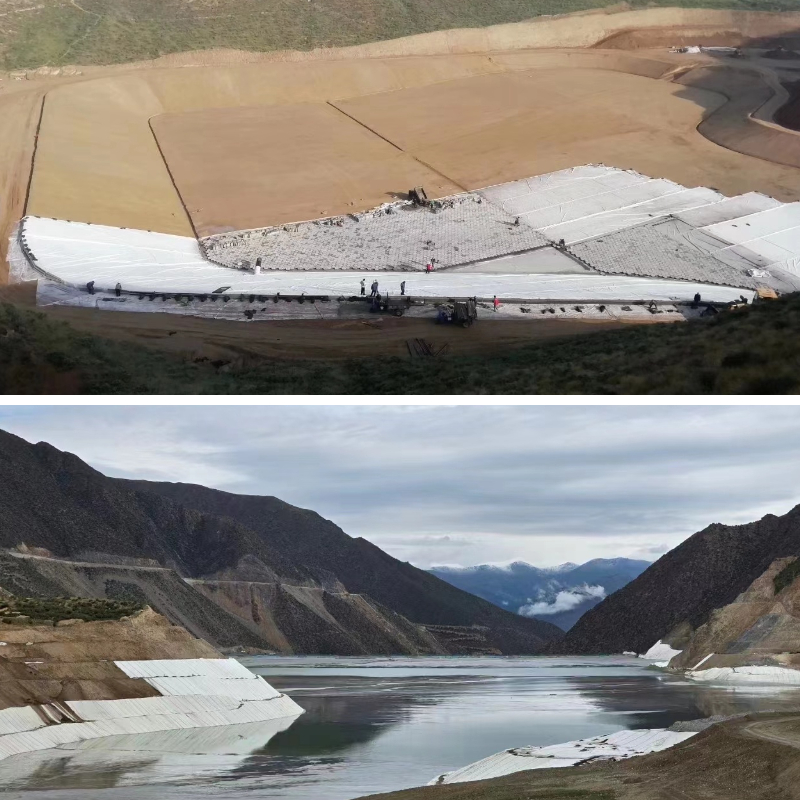
In hydraulic engineering, geotextile is an indispensable material. During the construction of dams, it is often used as an anti filter layer, which can effectively prevent soil particles in the dam from flowing away with water, while ensuring the normal discharge of seepage and ensuring the stability of the dam; When renovating the river, laying it on the surface of the embankment can resist the erosion of water flow, protect the embankment structure, and reduce soil erosion; In the construction of water conservancy facilities such as reservoirs and canals, geotextiles can also play a filtering and drainage role, extending the service life of the facilities.
Application in Transportation Engineering
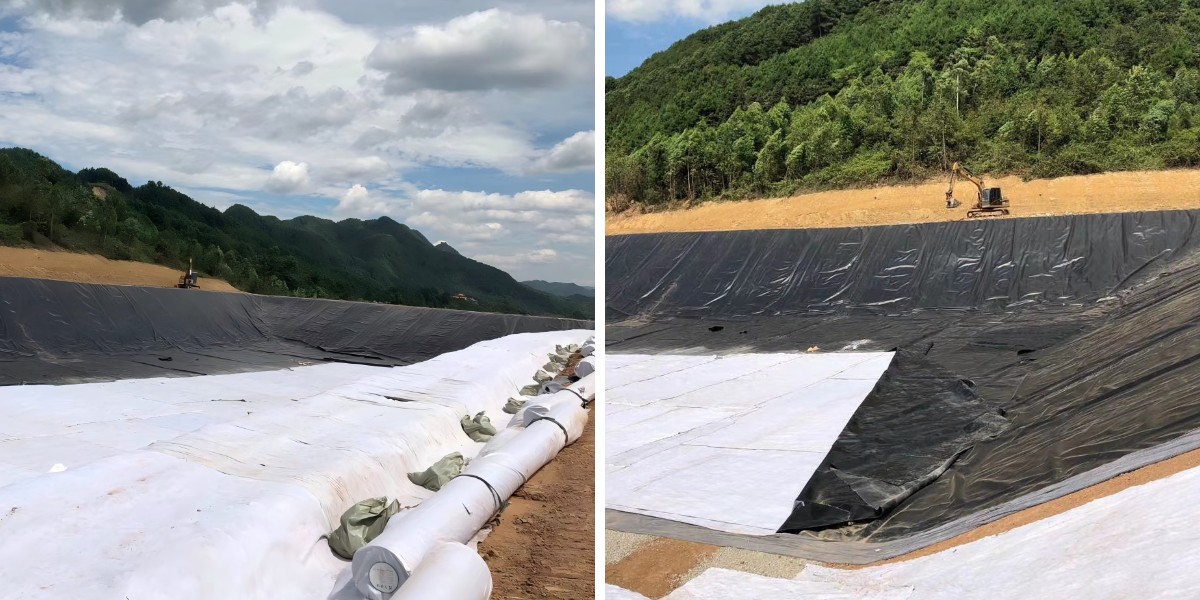
The application of geotextiles in transportation engineering can significantly improve the quality of the project. During the roadbed construction phase of highways and railways, laying geotextiles can isolate different soil layers between the roadbed and the foundation, prevent them from mixing, and avoid problems such as roadbed settlement; At the same time, the reinforcement effect of geotextile can enhance the overall strength of the roadbed and improve the bearing capacity of the road. Laying geotextile between the base and surface layers of the road can reduce the wear and tear of vehicles on the base and extend the service life of the road surface; The use of geotextile in the filling areas at both ends of the bridge can alleviate uneven settlement of the filling and reduce the probability of vehicle jumping at the bridgehead.
Application in Environmental Protection Engineering
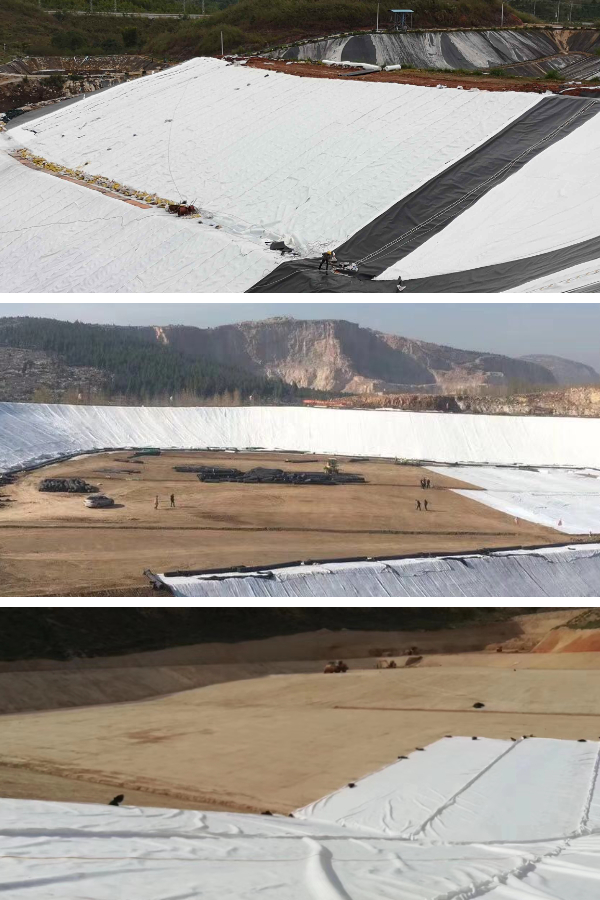
In environmental engineering, geotextiles play a prominent role in pollution prevention and control. In the construction of landfill sites, geotextile serves as an isolation and filtration layer, which can prevent the infiltration of leachate into underground soil and water bodies, prevent groundwater pollution, and facilitate the collection and treatment of leachate; When constructing artificial wetlands, geotextiles can fix the matrix materials in the wetland, such as soil, sand and gravel, and can also filter impurities in the water, providing a guarantee for the stable operation of wetland ecosystems; In some treatment facilities of sewage treatment plants, geotextiles can also assist in water purification and improve sewage treatment efficiency.
Application in Municipal Engineering
Geotextile can be seen in multiple aspects of municipal engineering. When renovating and expanding urban roads, using geotextiles to reinforce the original roadbed can improve the overall bearing capacity of the road and adapt to the increasing traffic flow; In urban underground drainage systems, geotextiles are laid around drainage ditches and rainwater pipes to filter out impurities such as sediment and prevent pipe blockages, ensuring smooth drainage; In the paving engineering of parks, squares and other venues, geotextiles can isolate the paving materials from the base soil, avoid soil pollution of the paving materials, and ensure the stability of the paving structure.
Geotextile, with its diverse functions, has a wide and important application in many engineering fields such as water conservancy, transportation, environmental protection, and municipal engineering. It can not only improve the stability and durability of engineering, but also reduce construction costs and shorten the construction period. It plays a key role in promoting the high-quality development of various engineering constructions and is an indispensable important material in modern engineering construction.