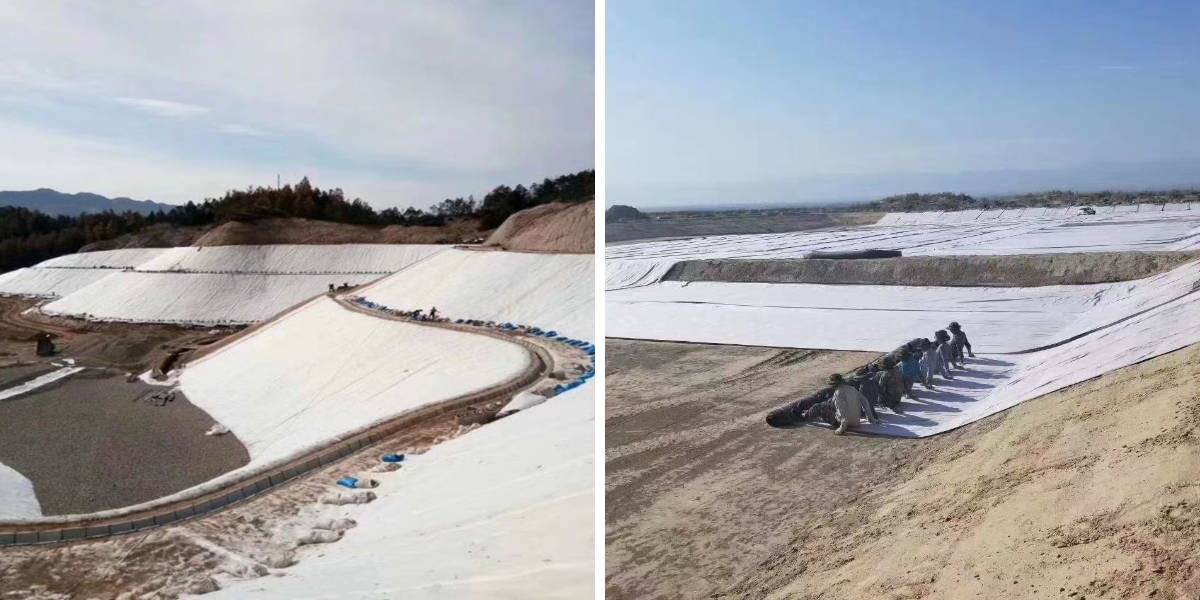
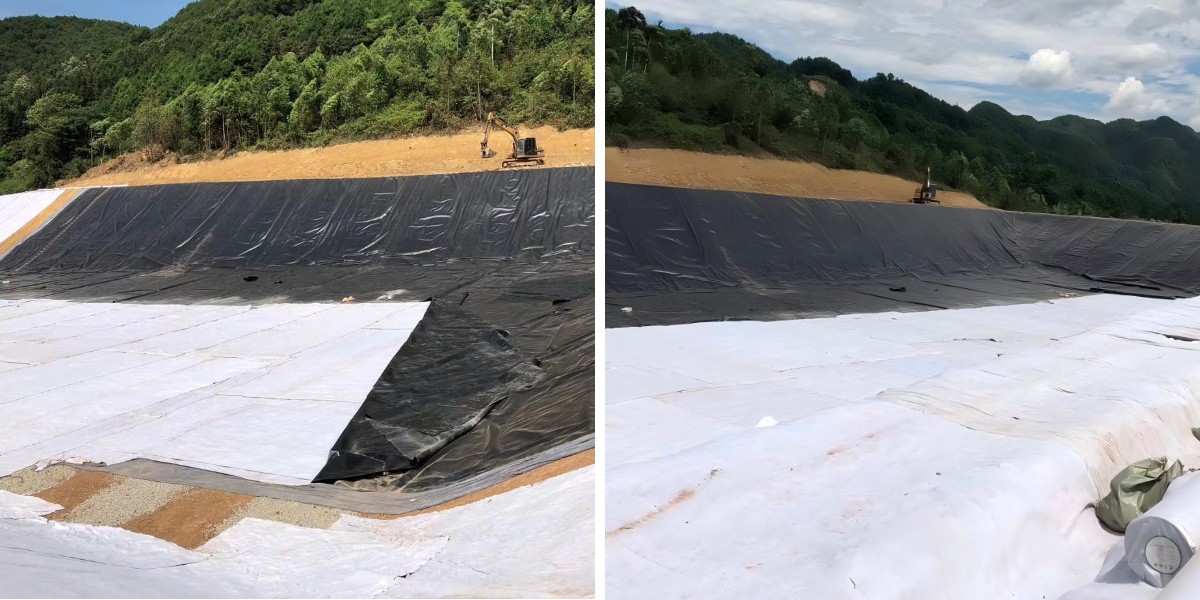
Non Woven Geotextile Drainage Fabric
1.Fast drainage: The three-dimensional structure forms a smooth channel, quickly draining accumulated soil water.
2.Stable foundation: Enhance the soil's ability to resist deformation and improve the stability of the foundation or slope.
3.Long weather resistance: Corrosion-resistant and aging resistant, with a long service life in complex soil environments.
4.Good construction: Easy to lay, reducing processes, saving time and costs.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Non Woven Geotextile Drainage Fabric is a permeable geosynthetic material made from polymer materials such as polypropylene and polyester through non-woven processes such as needle punching, thermal bonding, or chemical bonding. Its structure is mostly in the form of a three-dimensional mesh or interwoven fibers, with a certain thickness and porosity, lightweight texture, and strong integrity, which can adapt to the physical and chemical properties of different soil environments.
2、 Core functions
Drainage and infiltration: Through continuous internal pore channels, excess water (such as rainwater and groundwater) in the soil is quickly discharged, reducing soil pore water pressure and avoiding soil softening or landslides caused by water accumulation.
Soil reinforcement: With its own tensile strength and friction characteristics, it disperses the force on the soil, limits the displacement of soil particles, enhances the stability of the foundation, slope or roadbed, and reduces settlement deformation.
Filtering and isolation: During the drainage process, intercept soil fine particles to prevent them from flowing away with water and causing piping or blockage. At the same time, isolate soil layers of different particle sizes to avoid mixed pollution.
3、 Main features
Efficiency: The three-dimensional pore structure has low drainage resistance, fast water conductivity, and can quickly respond to soil drainage needs.
Durability: The raw materials are resistant to acid and alkali, corrosion, and biodegradation, and have a long service life in underground or outdoor environments, making them less prone to failure due to environmental erosion.
Convenient construction: The texture is soft and curly, lightweight, and does not require complex machinery for laying. It is easy to assemble and can adapt to irregular terrain, shortening the construction period.
Multi functional integration: It has functions such as drainage, filtration, and reinforcement, without the need to lay multiple materials, reducing project costs and complexity.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1. Road and Rail Transit Engineering
Roadbed drainage: It is laid between the roadbed soil and the base layer to discharge rainwater and groundwater from the roadbed, prevent roadbed softening, settlement, or frost heave, and ensure the stability of road structures (such as highways, municipal roads, and rural roads).
Slope protection: It is laid on the surface or inside of road slopes to discharge slope seepage, reduce pore water pressure, and cooperate with vegetation or grid reinforcement to prevent slope landslides and collapses.
Tunnel drainage: used between the surrounding rock and lining of the tunnel to collect water seepage from the surrounding rock and export it, avoiding excessive water pressure that may cause lining cracking and protecting the safety of the tunnel structure.
2. Water conservancy and waterway engineering
River and embankment reinforcement: laid on the upstream face or inside the embankment body, to discharge seepage from the embankment body, reduce the infiltration line, enhance the anti sliding stability of the embankment, and prevent dangerous situations such as pipe surge and embankment collapse (such as river embankments and reservoir embankments).
Channel anti-seepage and drainage: Laying on the slopes or bottoms of irrigation channels and water conveyance channels can not only drain accumulated soil around the channels, but also isolate different soil layers, reducing channel leakage losses.
Port and dock engineering: used for port yard and breakwater foundation, to discharge accumulated water from the foundation, reinforce soft soil foundation, reduce foundation settlement, and ensure the bearing capacity of the yard and the safety of the dock structure.
3. Construction and Municipal Engineering
Building foundation drainage: In the treatment of building foundations (especially soft soil foundations), drainage channels are formed by laying drainage fabrics to accelerate soil consolidation, reduce settlement rate, and improve foundation bearing capacity.
Underground engineering drainage: used for the outside of basements, underground pipe galleries, and civil air defense projects to collect underground seepage and guide it to the drainage system to prevent groundwater from seeping into the interior or structure.
Landfill site: laid at the bottom and slope of the landfill site, on the one hand to discharge leachate from the garbage, and on the other hand to isolate the garbage from the surrounding soil, prevent leachate from polluting groundwater, and enhance the stability of the landfill body.
4. Mining and Environmental Engineering
Mine slope treatment: laying the slope or tailings dam body after mining, discharging slope seepage and tailings dam seepage, reducing landslide risk and environmental pollution risk.
Soil remediation engineering: In the remediation of polluted sites, contaminated groundwater or rainwater is discharged as a drainage layer, which is combined with an anti-seepage layer to prevent the spread of pollutants and assist in soil purification.
5. Agricultural and Landscape Engineering
Farmland drainage: It is laid in low-lying and flood prone farmland and greenhouse foundations to discharge excess soil moisture, improve soil permeability, and enhance crop growth environment.
Landscape greening drainage: an underground drainage system used in parks, green spaces, golf courses, and other venues to discharge surface water and soil seepage, prevent plant root rot, and protect landscape vegetation.
In summary, non-woven geotextile drainage fabrics have effectively solved engineering problems such as water damage, unstable foundations, and pollution dispersion in many fields such as road infrastructure, water conservancy protection, construction and municipal engineering, and ecological restoration through their multiple functions of "drainage, reinforcement, and filtration". Its lightweight, easy to construct, and strong durability characteristics not only simplify the construction process and reduce project costs, but also fundamentally improve the structural safety and long-term stability of various infrastructure, becoming an indispensable key material in modern engineering construction.