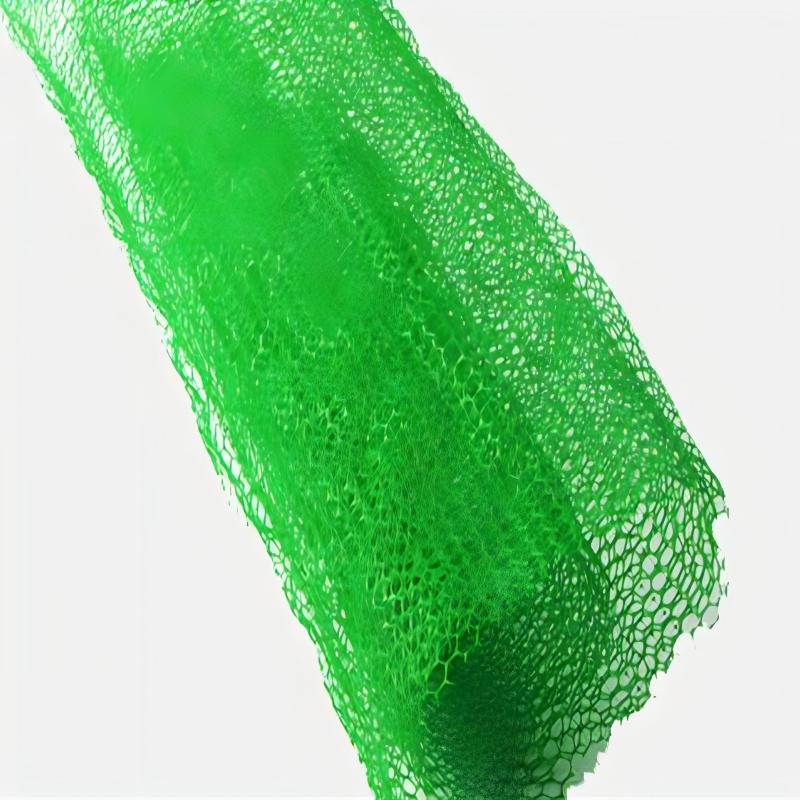
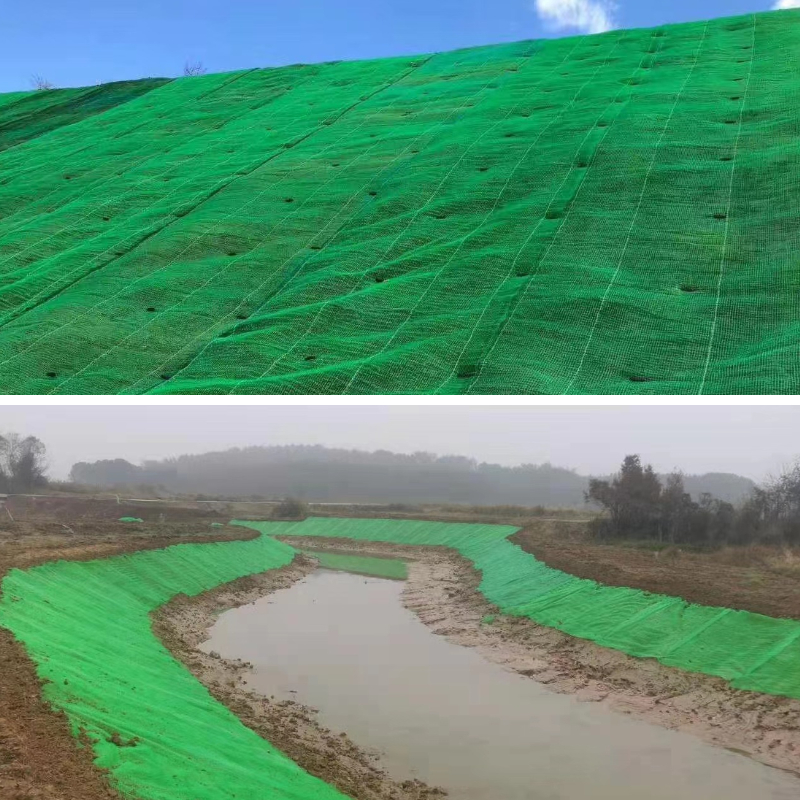
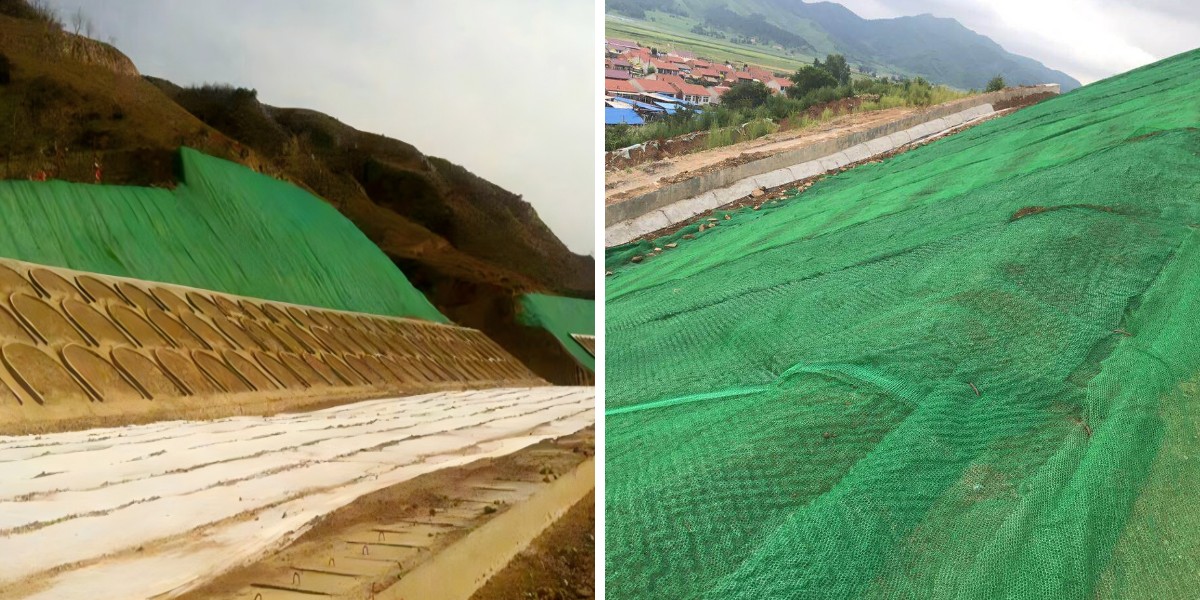
Erosion Control Matting
1. Rapid greening: providing plant growth substrate, accelerating vegetation coverage, and shortening the ecological restoration cycle.
2. Low cost maintenance: Compared to traditional concrete slope protection, vegetation net slope protection has lower maintenance costs in the later stage.
3. Eco friendly: Promote natural vegetation growth and enhance biodiversity.
4. High strength durability: UV resistance, corrosion resistance, long service life.
5. Convenient construction: It can be mechanically laid and is suitable for large-scale projects.
Product Introduction:
Erosion Control Matting is a three-dimensional mesh structure made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and other materials, usually composed of a surface foaming layer, internal fluffy mesh bags, and a bottom flat mesh. Its design simulates the natural vegetation growth environment, with a loose and flexible surface, leaving over 90% of the space filled with soil, gravel, or plant roots, forming a "net soil vegetation" composite system. This structure can both fix the soil and provide a growth support for plants, ultimately forming a sturdy green protective layer.
Core Features
1. High strength and flexibility
The bottom plane mesh has low elongation and high tensile strength, which can withstand large shear forces and effectively prevent slope landslides; The surface mesh bag has strong flexibility and can adapt to complex terrains such as curved surfaces and cracks, avoiding the problem of traditional materials being prone to breakage.
2. Permeability and water retention
The mesh structure promotes water infiltration while reducing surface runoff velocity and decreasing erosion energy. Black polyethylene material absorbs heat and provides insulation, which can raise the ground temperature by 2-3 ℃ and prolong the growth period of plants.
3. Ecological compatibility
Completely replace hard materials such as concrete and asphalt to avoid the ecological fragmentation caused by "grey protection". The interweaving of plant roots and mesh reinforcement forms a "reinforced plate", enhancing the shear strength of the soil and reducing pore water pressure.
Product Parameters:
Item | EM2 | EM3 | EM4 | EM5 |
Unit mass per area / (g/m2) | ≥220 | ≥260 | ≥350 | ≥430 |
thickness /mm | ≥1O | ≥12 | ≥14 | ≥16 |
Width deviation /m | ±1.0 | |||
length variation /m | ±1 | |||
Longitudinal tensile strength/(KN/m) | ≥O. 8O | ≥1.4 | ≥2. O | ≥3. 2 |
Tensile strength in the transverse direction / (KN/m) | ≥O. 8O | ≥1.4 | ≥2. O | ≥3. 2 |
Product Applications:
1. Protection of transportation infrastructure
Highway/Railway Slope: In projects such as the Beijing Zhangjiakou High speed Railway and the Hong Kong Zhuhai Macao Bridge, the combination of three-dimensional vegetation networks and spraying technology forms a dual effect system of "flexible protection+ecological restoration", reducing maintenance costs in the later stage.
Tunnel entrance: solves the problem of traditional stone masonry cracking, improves safety and aesthetics.
2. Water conservancy and river management
River embankments: In the Yellow River, Yangtze River and other river basin management, the three-dimensional vegetation network fixes the mudflat soil to prevent the water flow from hollowing out, while providing habitat for aquatic organisms.
Reservoir slope: Replace concrete slope protection, reduce sedimentation in the reservoir area, and extend the life of the reservoir.
3. Mining and Desertification Restoration
Open pit mines: In mining areas such as Shanxi and Inner Mongolia, three-dimensional vegetation networks combined with soil spraying can quickly restore vegetation and reduce dust pollution.
Desert greening: On the edge of the Taklamakan Desert, three-dimensional vegetation networks are laid to fix quicksand and and create conditions for plant growth.
4. Urban ecological construction
Roof greening: Lightweight 3D vegetation mesh reduces building load while achieving thermal insulation.
Vertical greening: laying on three-dimensional walls to form a "green curtain wall" and improve the urban heat island effect.
The three-dimensional vegetation network uses "small mesh bags" to carry the "big ecology", and through the coordination of physical structure and biological effects, achieves a leap from "passive resistance" to "active restoration" in slope protection. Its low cost, high efficiency, and strong compatibility make it an indispensable "green guardian" in modern ecological engineering, providing innovative solutions for sustainable development.