Smooth vs. Textured Geomembrane: A Comprehensive Comparison for Modern Engineering Projects
Geomembranes are key parts in all sorts of engineering and environmental work. You’ll find them in landfill liners, mining sites, water storage areas, and farm projects. When it comes to the types used most often, smooth geomembranes and textured geomembranes top the list. Each has its own set of pluses, depending on what the project needs.
This piece takes a shut look at how smooth and textured geomembranes stack up. It dives into their features, what makes them good, where they fall short, and the conditions they work best in. By getting a clear picture of their differences, engineers, project heads, and environmental professionals can pick the right one for their work.
What Are Geomembranes?
Geomembranes are man-made sheets. They’re made from stuff like HDPE, LLDPE, PVC, and EPDM. Their job is to stop fluids from moving around in construction and environmental projects.
Smooth Geomembranes
(https://www.cggeosynthetics.com/hdpe-geomembrane/smooth-geomembrane.html)
1.Have a flat, non-textured surface.
2.Provide excellent chemical resistance and durability.
3.Typically used in applications where friction is not a critical factor.
Textured Geomembranes
(https://www.cggeosynthetics.com/hdpe-geomembrane/textured-geomembrane.html)
1.Feature a rough or patterned surface to increase friction.
2.Enhance stability on slopes and improve interface shear strength.
3.Commonly used in applications requiring anti-slip properties.
Key Differences Between Smooth and Textured Geomembranes
1. Surface Characteristics
Smooth Geomembranes:
Flat and even surface.
Lower frictional resistance, making them easier to install in flat applications.
Ideal for projects where liner movement is minimal.
Textured Geomembranes:
Embossed, rough, or dimpled surface.
Higher friction coefficient, preventing slippage between layers.
Suitable for steep slopes and applications requiring soil or geotextile reinforcement.
2. Friction and Stability
Smooth Geomembranes:
Can be slippery when wet, making them less suitable for sloped installations.
Require additional anchoring or ballast in high-wind or sloped conditions.
Textured Geomembranes:
Provide superior grip between the geomembrane and adjacent materials (soil, geotextiles, or other liners).
Reduce the risk of liner slippage in landfill caps, pond liners, and embankments.
3. Installation and Handling
Smooth Geomembranes:
Easier to weld due to uniform surface.
Faster installation in flat applications like tank linings and canal liners.
Textured Geomembranes:
Require more careful welding techniques due to surface irregularities.
May need specialized welding equipment to ensure proper seam integrity.
4. Hydraulic Performance
Smooth Geomembranes:
Offer slightly better hydraulic performance due to minimal surface disruptions.
Preferred in applications where fluid flow efficiency is critical.
Textured Geomembranes:
Surface texture may slightly reduce flow efficiency but improves stability in dynamic water conditions.
Often used in reservoirs, wave-impacted liners, and erosion control.
5. Cost Considerations
Smooth Geomembranes:
Generally more cost-effective due to simpler manufacturing processes.
Lower installation costs in flat applications.
Textured Geomembranes:
Typically 10-30% more expensive due to additional manufacturing steps.
Higher installation costs but provide long-term stability benefits.
Best Applications for Each Type
1.When to Use Smooth Geomembranes
Landfill Base Liners – Where chemical resistance is critical.
Secondary Containment – For tanks and industrial facilities.
Flat Canal Liners – Where minimal friction is needed.
Wastewater Ponds – For uniform fluid containment.
2.When to Use Textured Geomembranes
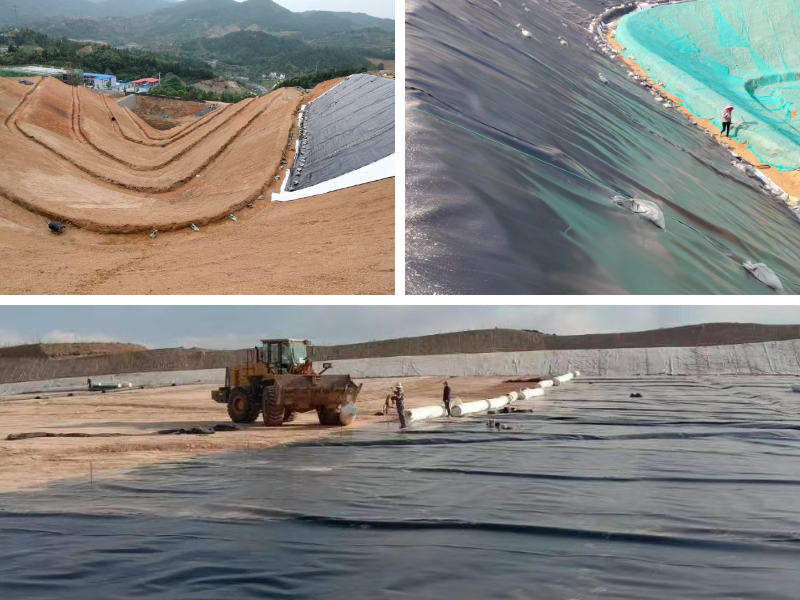
Landfill Caps – To prevent slippage on slopes.
Reservoirs & Dams – For enhanced stability under water pressure.
Mining Heap Leach Pads – Where steep slopes and heavy loads are present.
Erosion Control – In areas with high water flow or wave action.
Durability and Longevity
Both smooth and textured geomembranes are designed for long-term performance, but their durability can vary based on environmental conditions:
1.Smooth Geomembranes:
Less prone to dirt accumulation, making them easier to clean.
Better UV resistance in some cases due to uniform material distribution.
2.Textured Geomembranes:
Surface texture can trap debris, requiring occasional maintenance.
Superior resistance to wind uplift and mechanical stresses.
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between smooth and textured geomembranes depends on project-specific needs:
Opt for smooth geomembranes if your project involves flat surfaces, chemical containment, or cost-sensitive applications.
Choose textured geomembranes for sloped installations, high-friction requirements, and projects where stability is a priority.
By evaluating factors such as friction needs, slope requirements, installation conditions, and budget, engineers can select the most suitable geomembrane(https://www.cggeosynthetics.com/hdpe-geomembrane/hdpe-membrane-sheet.html) for optimal performance and longevity.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person : Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number : +86 19305485668
WhatsApp: +86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province