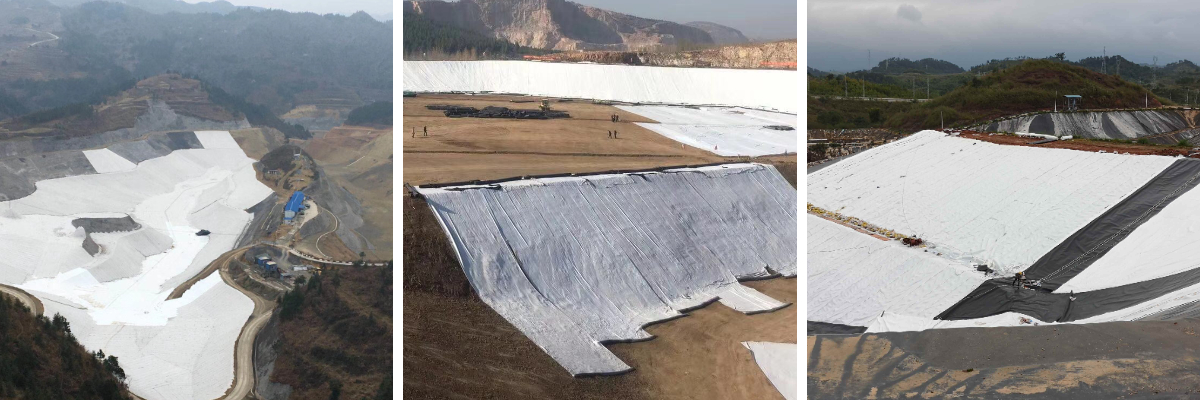
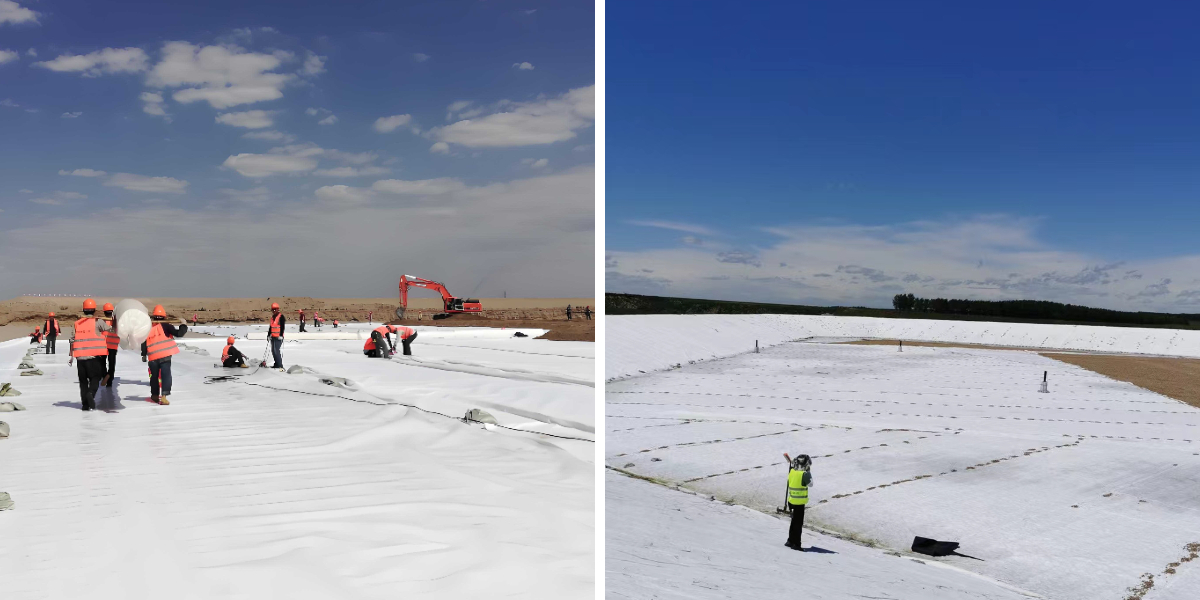
Geotextiles for Erosion Control
1. Anti damage and durable: weather resistant and corrosion-resistant, able to provide long-term stable protection in both dry and wet environments.
2. Eco friendly: Degradable material, naturally decomposes after use, with no environmental residue.
3. Control seepage and prevent loss: Permeable design takes into account both drainage and soil retention to reduce soil erosion.
4. Time saving and cost saving: easy to construct with high quality, long service life, and reduced labor and replacement costs.
5. Strong adaptability: adaptable to diverse terrains, resistant to microbial and pest infestations.
Products Introduction:
Geotextiles for Erosion Control is a high-performance engineering material designed specifically to address soil erosion issues. It is made of polymer fibers (such as polyester, polypropylene) or naturally degradable materials (such as coconut shell fiber, straw fiber) as raw materials, and formed into sheet materials with specific mechanical properties and permeability characteristics through special processes such as weaving, non-woven or needle punching. This material can not only provide a physical barrier for surface soil to resist external forces such as rainwater erosion and wind erosion, but also coordinate the dynamic balance between water and soil by regulating water infiltration and discharge, avoiding soil structure damage caused by water flow accumulation or excessive leakage.
As a key material in the field of ecological protection and engineering stability, it has completely changed the "hard protection" mode of traditional erosion prevention methods (such as concrete hardening and stone stacking), and instead adopted the concept of "flexible protection" - achieving soil stability without damaging the surface ecological chain. Compared to traditional solutions, it is more targeted in terms of protection effect (parameters can be customized according to erosion intensity), reduces ecological intervention in terms of environmental protection, and reduces comprehensive costs by extending service life in terms of economy. It has become the preferred solution for controlling soil erosion in fields such as water conservancy, transportation, agriculture, and mining. At present, this type of product has formed a complete series from light (used for agricultural gardens) to heavy (used for river embankments), which can meet the protection needs of different scenarios.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
1. Water conservancy engineering:
In the protection of river slopes, geotextiles are laid layer by layer along the slope and fixed with anchor nails to form a composite system of "surface protection+internal drainage" - which can resist the scouring force of river water fluctuations (measured to withstand the impact of 3m/s flow velocity), and can also discharge the internal seepage of the slope through pores, reducing the risk of landslides. In the application of reservoir embankments, laying them on the upstream face or shoulder of the dam can prevent wind and waves from scouring the soil material of the dam body. At the same time, with the design of the anti filter layer, it can avoid the phenomenon of pipe surge caused by water seepage in the dam body. In addition, replacing traditional concrete in channel lining engineering can reduce cracks caused by temperature changes and extend the service life of channels by 3-5 times.
2. Transportation construction:
The combination scheme of "geotextile+vegetation" is adopted for the slopes on both sides of the highway and railway subgrade: firstly, geotextile is laid to stabilize the topsoil of the subgrade, and then grass or shrub seeds are sprayed. Geotextile can provide temporary protection in the early stage of vegetation growth (1-3 months), and after the vegetation roots are formed, it forms a synergistic protection system with the plants, which improves the anti erosion ability by more than 40% compared to simple vegetation protection. In high fill sections, burying geotextiles in layers into the fill can disperse soil pressure through fiber tension, reduce roadbed settlement (measured settlement rate reduced by 20% -30%), and avoid pavement cracking. In the drainage system around the airport runway, geotextile is used as a filter layer to wrap the gravel blind ditch, which can effectively block sediment from entering the drainage channel and ensure smooth drainage.
3. Agriculture and ecological restoration:
In the application of farmland terraced fields, laying geotextiles along the inner side of the field embankment can prevent irrigation water or rainwater from washing away the soil on the embankment, reduce the loss of cultivated land area, and supplement groundwater sources through infiltration. Experimental data shows that it can increase the soil water retention rate of terraced fields by 15%. In the restoration project of barren mountains, geotextile is laid on the bare rock slope, and then covered with improved soil and grass seeds. Geotextile can fix the improved soil and prevent it from being washed away by rainwater, providing a stable environment for vegetation germination. The survival rate of vegetation can be increased to over 85%. In the scenario of mine reclamation, special anti-seepage geotextiles are selected for heavy metal polluted soil, which can prevent the exchange of polluted soil with the surrounding environment, while allowing plant roots to penetrate and grow, achieving the dual goals of ecological restoration and pollution isolation.
4. Municipal engineering:
In the protection of urban green belts, covering landscape gravel with geotextile can suppress weed growth (reduce 70% of weeding workload), while allowing rainwater to penetrate into the soil of the green belt to avoid water accumulation. In the application of artificial lakeshore, the use of ecological geotextile combined with aquatic plant planting can not only prevent the soil on the lakeshore from being carried into the lake by wind and waves, causing turbidity in the water body, but also provide a habitat microenvironment for aquatic organisms, improving the ecological stability of landscape water bodies. In the greening project at the top of the underground parking lot, geotextile is laid as an isolation layer above the waterproof layer, which can protect the waterproof layer from being pierced by sharp particles of planting soil and extend its service life.
Geotextiles for Erosion Control geotextiles are designed with the core concept of "flexible protection and ecological synergy". Through the combination of material science and engineering technology, they achieve an organic unity of erosion prevention effect, ecological compatibility, and engineering economy. Its porous structure solves the contradiction between soil interception and drainage, its durability meets long-term protection needs, its environmentally friendly design conforms to the concept of sustainable development, and its construction convenience improves engineering efficiency - these four core advantages upgrade it from a simple "protective material" to an "ecological engineering system component".
From practical applications, whether it is the anti erosion requirements in water conservancy engineering, the stability requirements of roadbeds in transportation construction, or the soil protection goals in ecological restoration, this product can accurately match the scene requirements through parameter customization (such as material thickness, porosity, degradation cycle). With the deepening of the concept of "green mountains and clear waters are as valuable as mountains of gold and silver", this material that balances engineering safety and ecological protection will replace traditional hard protection solutions in more fields, becoming a key support for balancing human engineering activities and natural ecology, and providing efficient and sustainable solutions for global soil erosion control and ecological protection.