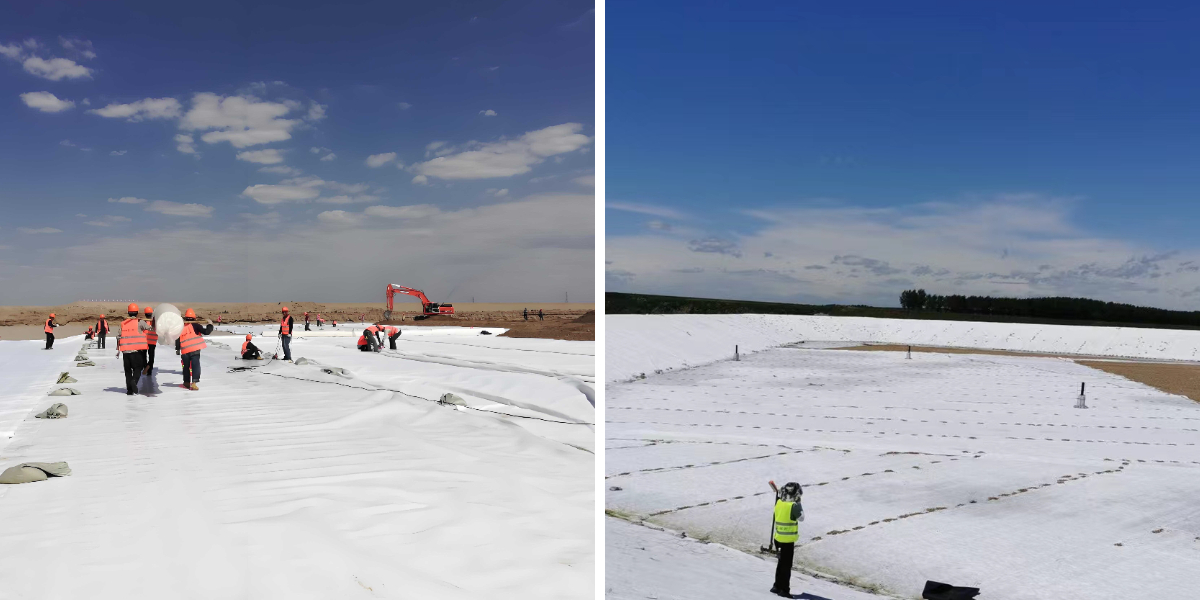
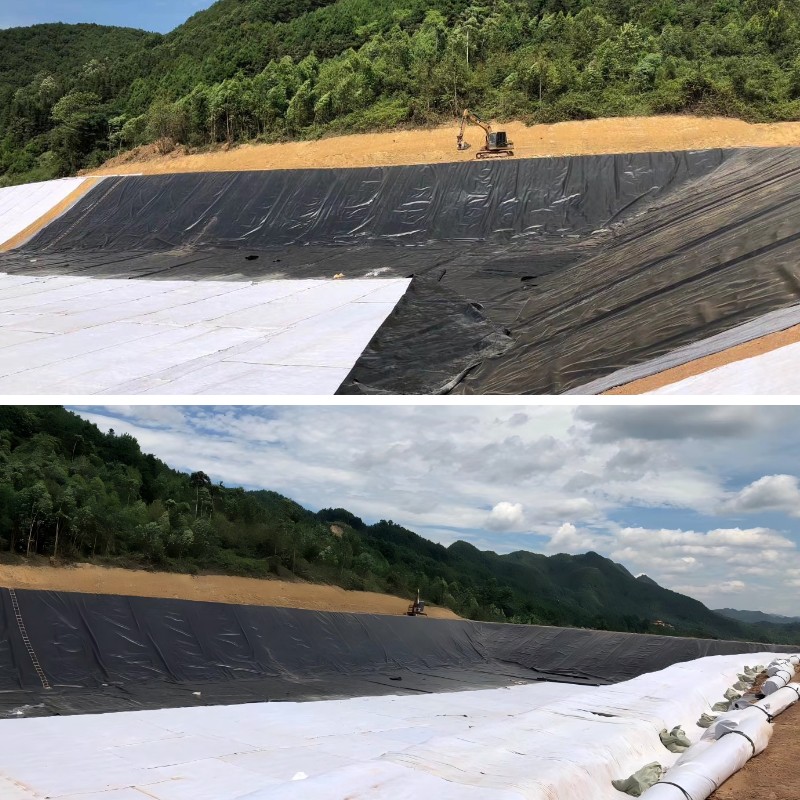
Geotextile Felt Fabric
1.Anti seepage isolation: The dense structure blocks the infiltration of water and soil particles, separates different media, and ensures structural stability.
2.Mechanical enhancement: Improve the shear strength and integrity of soil, disperse loads, and reduce settlement and landslide risks.
3.Drainage and Breathability: Pores allow for smooth drainage of water, avoiding water pressure and maintaining soil permeability.
4.Weather resistant and easy to construct: UV resistant, corrosion-resistant, lightweight and flexible material, convenient cutting and laying, reducing costs.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Geotextile Felt Fabric is a permeable geosynthetic material made from polymer materials such as polypropylene and polyester through processes such as needle punching, weaving, and hot melting. Its basic forms include non-woven fabrics (needle punched, water punched) and woven fabrics, which have physical and chemical properties such as lightweight texture, controllable thickness, and strong chemical stability. They can adapt to different engineering environments with temperature, humidity, and load conditions.
2、 Core functions
Anti seepage and isolation: By using a dense fiber structure to block the migration of moisture, soil particles, or pollutants, physical separation of different media (such as soil and sand, water and foundation) is achieved to prevent damage to engineering structures due to seepage deformation.
Enhancement and reinforcement: With the tensile strength of fiber materials, it combines with soil to form a composite structure, enhancing the shear resistance and integrity of the foundation and slope, and reducing the risk of disasters such as settlement and landslides.
Drainage and filtration: Using a porous structure to allow water to penetrate and be discharged, while intercepting soil particles, avoiding blockage of drainage channels, and maintaining smooth water flow inside the project.
Protection and buffering: When laying on the surface of structures such as roadbeds and dams, it can disperse external load impacts and protect the underlying soil or anti-seepage layer from mechanical damage.
3、 Main features
Strong performance adaptability: parameters such as thickness, tensile strength, and permeability can be adjusted according to engineering requirements, and are suitable for various fields such as water conservancy, transportation, and municipal engineering (such as dam seepage prevention and highway subgrade reinforcement).
High weather resistance and durability: It has characteristics such as UV aging resistance, acid and alkali corrosion resistance, and resistance to biodegradation. Its service life can reach decades in complex outdoor environments, reducing maintenance costs in the later stage.
Convenient and efficient construction: The material is lightweight, flexible, and can be directly cut, spliced, and laid without the need for complex mechanical assistance, shortening the project cycle.
Outstanding economy: Compared with traditional anti-seepage reinforcement materials such as concrete and asphalt, it has lower cost and less construction loss, while also reducing long-term operation and maintenance costs of the project.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1、 Water conservancy engineering field
In hydraulic engineering, geotextile fabric plays a crucial role. In dam construction, it can serve as an impermeable layer, effectively blocking water infiltration between the dam body and foundation using a dense fiber structure, preventing problems such as piping and leakage, and ensuring the stability and safety of the dam. At the same time, in river regulation projects, geotextiles can be used for the protection of river slopes, by enhancing the shear strength of the slope soil, reducing slope collapse caused by water flow erosion, and achieving soil and water isolation to prevent the soil at the bottom of the river from being carried away by water flow. In addition, during reservoir construction, it can be laid on the bottom of the reservoir and the surface of the dam body, playing multiple roles in seepage prevention, filtration, and reinforcement, extending the service life of the reservoir.
2、 Transportation engineering field
Transportation engineering is an important application scenario for geotextile fabrics. In highway construction, geotextile is widely used for roadbed treatment. When laid in the roadbed soil, it can enhance the overall integrity and bearing capacity of the roadbed, disperse the stress generated by vehicle loads, reduce roadbed settlement and deformation, and effectively prevent pavement cracking, collapse and other diseases. In railway engineering, it can be used for isolation and reinforcement of railway track base, isolating fillers of different particle sizes to prevent mixing and affecting the stability of track structure, while improving the shear strength of the base and ensuring the safety of train operation. In addition, in the construction of airport runways, geotextiles can play a filtering and drainage role, timely draining the accumulated water in the runway base, and avoiding damage to the runway structure caused by accumulated water.
3、 Municipal construction field
Municipal construction cannot do without the support of geotextile fabrics. In urban road renovation and expansion projects, geotextile can be used for base treatment during the renovation of old roads, reducing differential settlement between new and old road surfaces and improving the overall strength of the road surface. In underground pipeline laying projects, it can wrap around the pipeline, playing a buffering and protective role, avoiding damage to the pipeline from soil pressure and external construction machinery, while also preventing soil particles from entering the backfill material around the pipeline, ensuring the quality of backfilling. In addition, in the slope greening of urban greening projects, geotextiles can fix the soil, prevent soil erosion, and provide a stable environment for vegetation growth.
4、 Environmental engineering field
Geotextile fabrics also have important applications in environmental engineering. In the construction of landfill sites, it is one of the key anti-seepage materials, which can be laid at the bottom and periphery of the landfill site to effectively prevent the infiltration of leachate into the soil and groundwater, and prevent environmental pollution. In sewage treatment engineering, geotextile can be used as a filtering material for primary filtration of sewage, intercepting suspended particles and impurities in sewage, and improving sewage treatment efficiency. At the same time, in ecological restoration projects such as wetland restoration, geotextiles can help restore the soil structure of wetlands, maintain water and soil, and provide a good foundation for the reconstruction of wetland ecosystems.
In summary, geotextile fabrics have extensive and important applications in various engineering fields such as water conservancy, transportation, municipal engineering, and environmental protection due to their excellent properties of anti-seepage, isolation, reinforcement, drainage, and filtration. It can not only improve the stability and safety of engineering structures, extend the service life of engineering, but also reduce the difficulty and cost of engineering construction, playing an irreplaceable role in ensuring engineering quality and promoting the development of engineering construction. With the continuous advancement of engineering technology, the application fields of geotextile fabrics will further expand, providing more reliable material support for various engineering constructions.