Geotextile Fabric for Waterproofing
Highly effective waterproofing and anti-seepage: It adheres tightly to the base surface, forming a continuous waterproof barrier that effectively blocks water penetration while allowing moisture from within the soil to escape, preventing damage to the base surface caused by accumulated moisture.
Durable and wear-resistant: The material is UV-resistant, acid- and alkali-resistant, and has high tensile strength, resisting construction friction, soil compression, and environmental degradation, extending the service life of the waterproofing system.
Easy and flexible installation: Its lightweight construction allows for easy cutting and adaptability to various terrains (such as slopes and curved surfaces). It can be laid without complex tools, significantly shortening the construction cycle.
Eco-friendly and economical: Most products are made from recyclable or environmentally friendly materials, leaving no soil or water pollution. They also provide drainage and filtration functions, eliminating the need for additional geotechnical materials and reducing overall costs.
Product Introduction:
Geotextile Fabric for Waterproofing is an engineered textile material designed to block water penetration while maintaining environmental adaptability. It's primarily made from high-molecular-weight synthetic fibers such as polypropylene and polyester, and is produced through needle-punching, knitting, or thermal bonding processes. It forms a two-layer structure consisting of a fiber base and a waterproof membrane. The fiber layer enhances tensile strength and tear resistance, while the waterproof membrane enhances seepage control, achieving a balance of functionality and durability.
Unlike ordinary geotextiles, its core advantage lies in its ability to balance waterproofness with breathability. Its dense structure blocks liquid water penetration while allowing vapor from the soil or substrate to escape, preventing cracking, mold, or structural damage caused by trapped water vapor. It also offers environmental adaptability, including resistance to UV rays, acid and alkali corrosion, and biological attack (such as root penetration). Furthermore, the product offers a variety of specifications, offering varying thicknesses, widths, and tensile strengths tailored to the application. Some special models can also be customized with additional features such as flame retardancy and antistatic properties, making it suitable for a wide range of waterproofing needs, from civil buildings to large-scale engineering projects.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
| Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
| 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
| 1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
| 2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
| 3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
| 4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
| 5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
| 7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
| 8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
| 9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
| 10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
| 11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
| 12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
| 13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
| 14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
Construction Engineering:
Underground waterproofing: This waterproofing layer is used as an anti-seepage layer between the basement side walls, floor slab, and foundation. It adheres to the soil surface to prevent groundwater infiltration while simultaneously dissipating moisture from the foundation soil, preventing moisture buildup and mold on the basement walls. Compared to traditional membranes, its lightweight construction reduces disturbance to the foundation structure.
Roof and Terrace Waterproofing: This waterproofing underlayment is suitable for flat roofs and roof gardens. Installed between the insulation layer and the protective layer, it prevents rainwater from penetrating the building interior while allowing moisture from within the insulation layer to escape, extending the lifespan of the roof waterproofing layer. It is particularly suitable for curved roofs, as its easy-to-cut and easy-to-fit properties reduce the risk of leakage caused by joints.
Wall Moisture-Proofing: This waterproofing layer is used as a moisture-proof layer on the exterior or interior walls. In rainy and humid areas (such as the plum rain season in southern China), it prevents rainwater from penetrating the wall while preventing moisture accumulation within the wall, which can cause peeling and alkalinity. Municipal and Transportation Engineering
Road and Bridge Waterproofing: Installed between the road base and surface layers, and between the bridge deck and pavement, it prevents rainwater from penetrating the roadbed or bridge structure. Water seepage in the roadbed can easily lead to pavement settlement and cracking, while water seepage in bridges can corrode steel reinforcement. Waterproof geotextiles form an anti-seepage barrier while also adapting to the slight deformations of roads and bridges caused by vehicle loads (due to their high tensile strength).
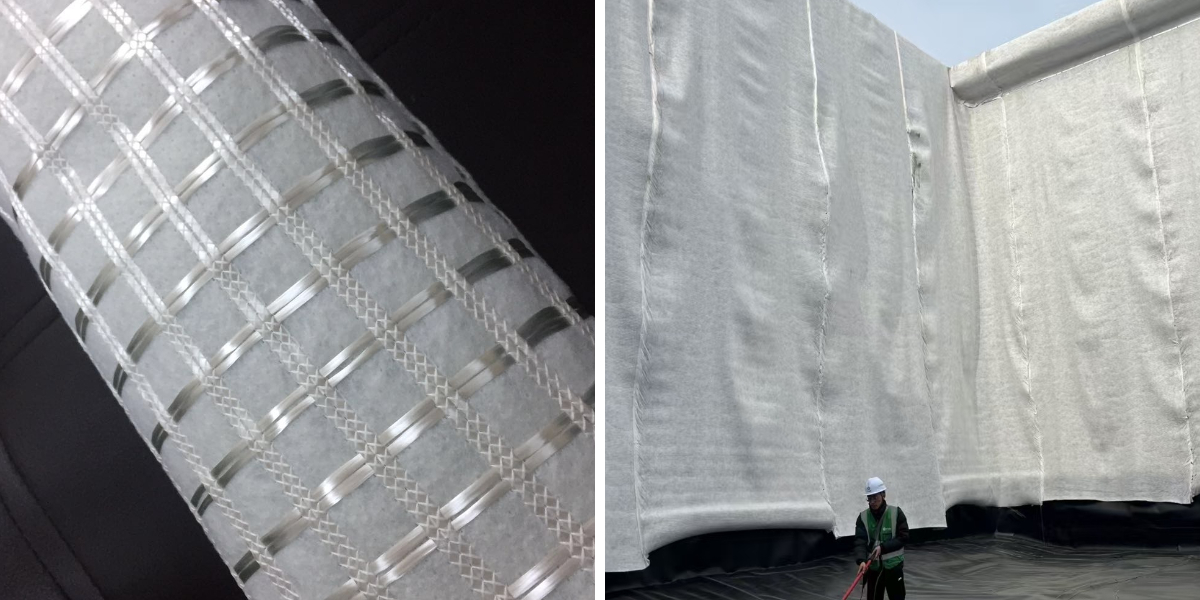
Underground Pipeline Corridor/Tunnel Waterproofing: Serving as a secondary anti-seepage layer for underground utility corridors and subway tunnels, it is installed on the outer walls of the corridor or the outside of the tunnel lining to supplement the waterproofing weaknesses of concrete structures, prevent groundwater from penetrating the corridor, and protect pipeline equipment. Its tear resistance allows it to withstand surrounding rock compression or settlement during tunnel construction. Water Conservancy and Environmental Engineering
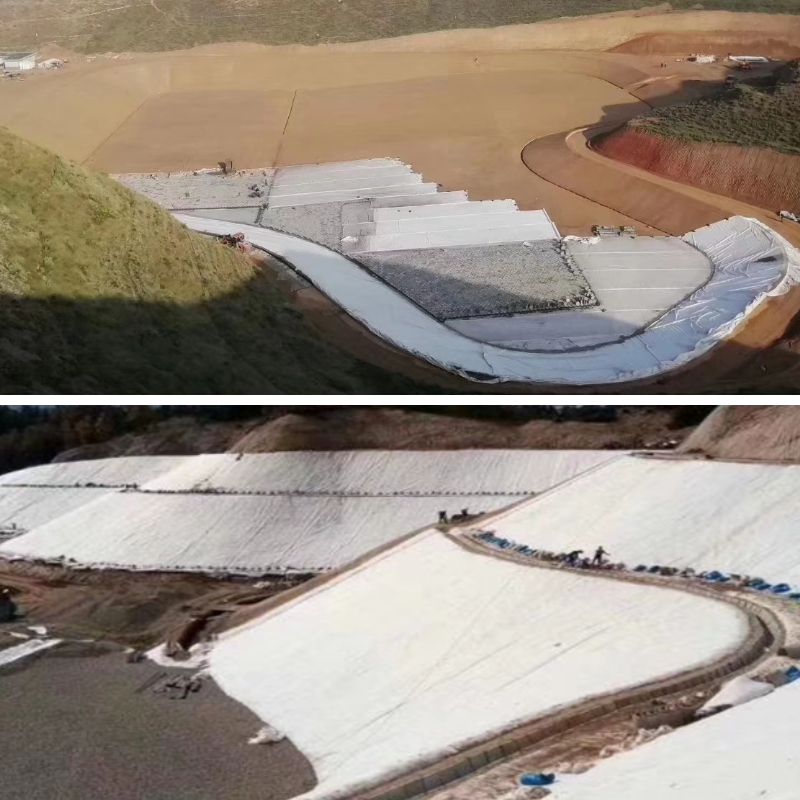
Artificial Lake/Reservoir Anti-seepage: Used as an anti-seepage lining for the bottom of artificial lakes and small reservoir embankments, it replaces traditional clay anti-seepage layers (which require a thick soil layer and are prone to cracking due to settlement). Through continuous laying, it forms a comprehensive waterproof barrier, reducing water leakage. Its acid- and alkali-resistant properties allow it to withstand long-term immersion in lake and reservoir water.
Landfill Anti-seepage: Serving as a "secondary anti-seepage system" for landfills, it is laid beneath or around the primary anti-seepage membrane (such as HDPE membrane) to prevent landfill leachate from seeping into the subsoil and groundwater system. Its anti-bioerosion properties protect against corrosive substances produced during waste degradation, reducing the risk of environmental pollution.
Agriculture and Landscape Engineering
Greenhouse Waterproofing: Used as a moisture-proof layer on the floor or side walls of greenhouses, it prevents underground moisture from rising into the greenhouse, maintaining a suitable humidity level and preventing crop root rot. Its lightweight and easy-to-lay properties make it suitable for temporary greenhouse construction and renovation. Landscape river / wetland park anti-seepage: Used as the riverbed lining of landscape rivers or the aquatic plant planting area of wetland parks, it prevents river water and wetland moisture from penetrating into the surrounding soil, maintaining a stable river water level. At the same time, the environmentally friendly material will not cause pollution to water bodies, soil, flora and fauna, and meets the environmental protection requirements of ecological landscapes.
Geotextile Fabric for Waterproofing is an engineering textile material designed to block water penetration while taking into account environmental adaptability. It is mostly made of high-molecular synthetic fibers such as polypropylene and polyester, and some are composite waterproof coatings to form a "fiber substrate + waterproof membrane" structure. Its core advantage lies in balancing "waterproofness" and "breathability", and it can block liquid water and discharge gaseous water vapor. It also has properties such as UV resistance and corrosion resistance, and can provide specifications with different thicknesses, widths, and tensile strengths, supporting customized additional functions. It has a wide range of applications. In construction projects, it is used for waterproofing and moisture-proofing of basements, roofs, and walls. In the municipal transportation field, it is suitable for anti-seepage of roads, bridges, underground pipelines and tunnels. In water conservancy and environmental protection projects, it can be used as an anti-seepage layer for artificial lakes, reservoirs, and landfills. In agriculture and landscape projects, it can also meet the needs of moisture-proofing of greenhouses and stabilizing the water level of landscape rivers and wetlands. The adaptation logic revolves around its waterproof, durable, and flexible construction characteristics.