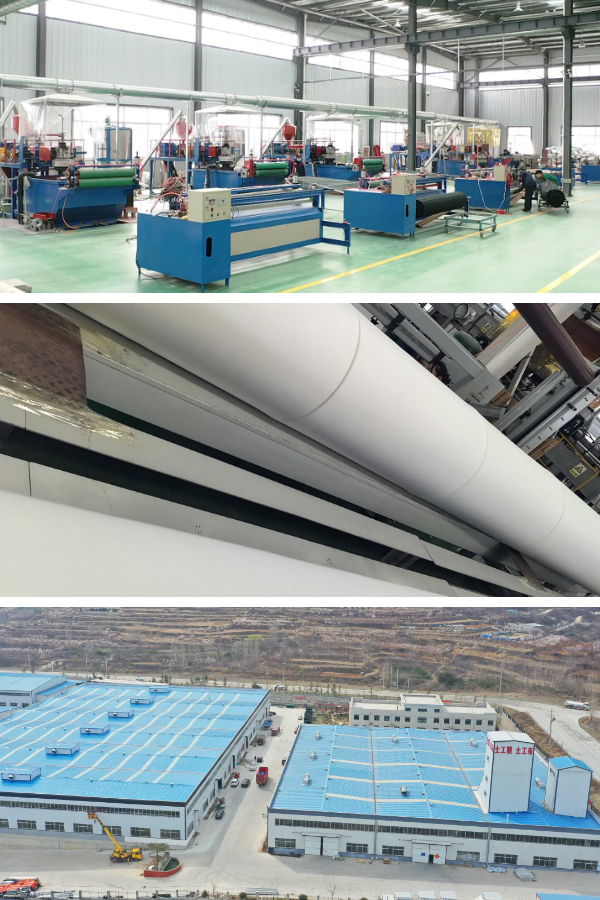
Geotextile 160g
1. Extend the service life of the project: Through functions such as isolation and reinforcement, uneven settlement and reflection cracks are effectively reduced, significantly extending the service life of structures such as roads and dams.
2. Improve engineering quality: Provides continuous and consistent filtration and drainage layers, ensuring the long-term stability and reliability of the project.
3. Reduce engineering costs:Save materials, easy installation, fast construction speed, and shorten the construction period.
4. Beneficial for environmental protection:Reduced the exploitation of natural sand and gravel materials, protecting the natural environment. In slope protection engineering, it can prevent soil erosion, promote vegetation growth, and play a role in ecological restoration.
Product Introduction:
Geotextile 160g is a synthetic fiber textile or non-woven material specifically used in civil engineering. It is essentially a permeable and flexible "fabric" widely used in soil, rock, or other geotechnical materials as a component for isolation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement, protection, or anti-seepage purposes.
Simply put, it is the "multifunctional fabric" in engineering, although not conspicuous, it is an indispensable basic material in modern civil engineering.
Feature
The reason why geotextiles can be widely used is due to their excellent engineering properties:
1. High permeability: With numerous pores, it allows water to pass smoothly while effectively preventing excessive loss of soil particles, playing a filtering role.
2. Good mechanical properties: It has high tensile strength, tear resistance, puncture resistance, and burst resistance, and can withstand various loads during construction and use.
3. Flexibility and adaptability: The texture is soft and can fit well with different shapes of foundations and irregular surfaces, adapting to the settlement and deformation of foundations.
4. Corrosion and Microbial Resistance: Made from chemically synthesized fibers such as polyester (PET) and polypropylene (PP), it is resistant to acid, alkali, insect infestation, and mold, and has good durability.
5. Easy construction: The finished product is a roll material, which is lightweight, easy to transport and lay, and can greatly improve construction efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications
1. Transportation Engineering
Core function: isolation, reinforcement, drainage
Specific application:
Laying geotextile between the roadbed and cushion layer to isolate the roadbed soil (fine particles) from the cushion layer sand and gravel (coarse particles), avoiding blockage of the cushion layer, and reducing roadbed settlement through the tensile strength of geotextile;
Laying geotextile underneath the pavement base to drain accumulated water inside the base and prevent pavement cracking caused by winter frost heave.
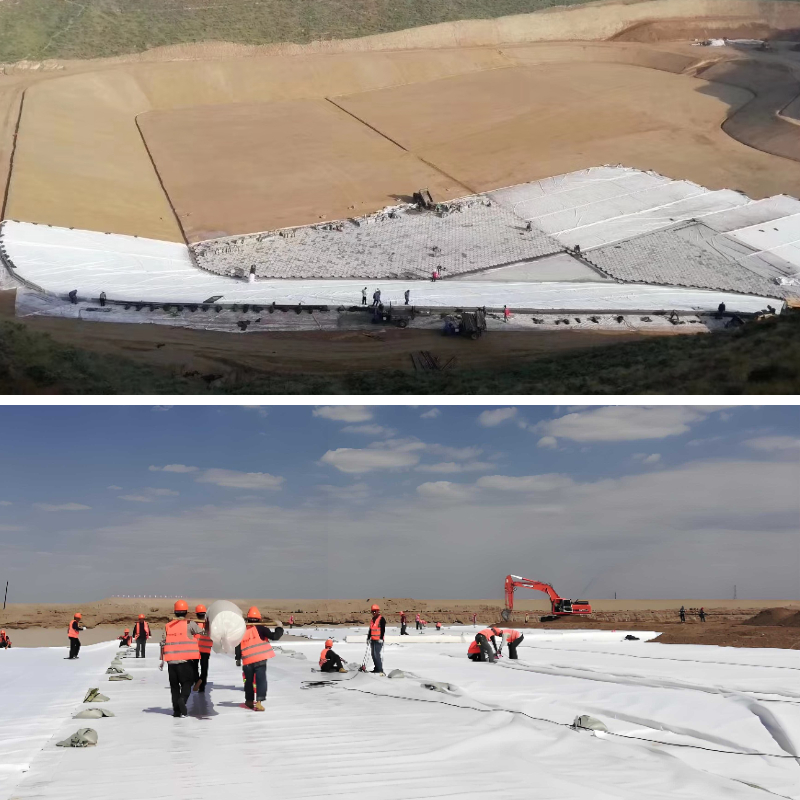
2. Water conservancy engineering
Core function: filtration, drainage, anti-seepage assistance
Specific application:
Laying geotextile (in conjunction with anti-seepage membrane) on the upstream slope of the dam to intercept sediment in the water, prevent the anti-seepage membrane from being punctured by sharp particles, and discharge the seepage inside the dam to prevent landslides;
In river bank protection projects, geotextiles wrap crushed stones to form "geotextile bags", which resist water flow erosion while allowing water infiltration to protect the ecology of the bank slope.
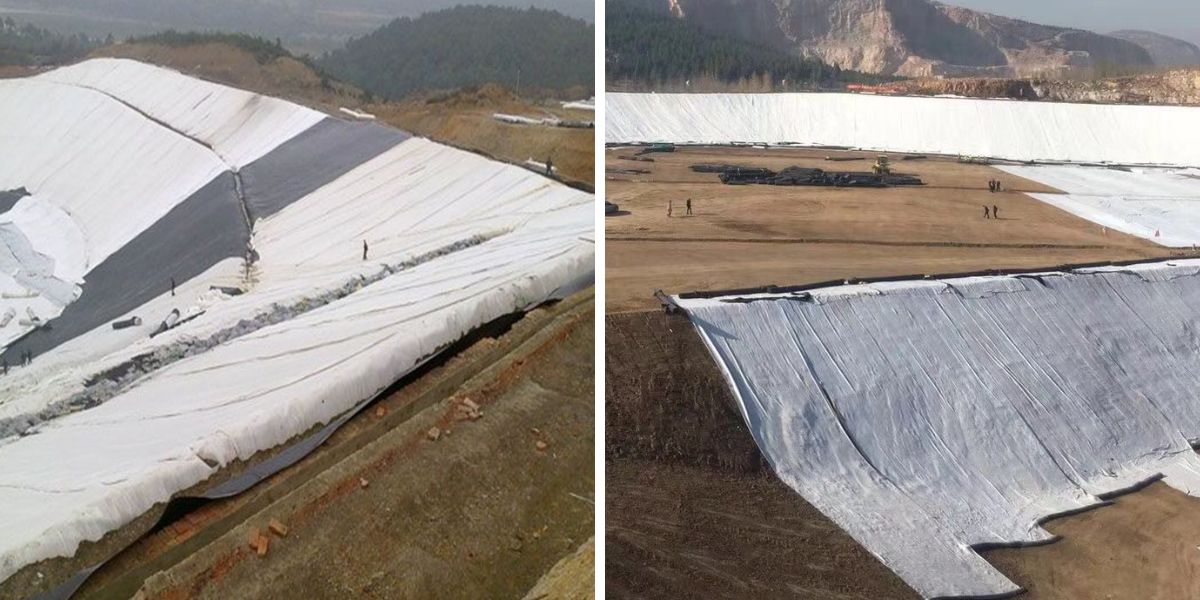
3. Geotechnical Engineering
Core function: Reinforcement and protection
Specific application:
In slope greening projects, geotextile (or geogrid composite fabric) is laid to fix the surface soil, prevent rainwater erosion and soil erosion, and provide a growth carrier for plant roots;
During excavation of the foundation pit, geotextile is combined with soil nails and anchor rods to form a "reinforced soil retaining wall", enhancing the stability of the side wall of the foundation pit and avoiding collapse.
4. Municipal engineering
Core function: filtration, isolation, and pollution prevention
Specific application:
Lay geotextile around the municipal drainage pipeline to filter soil particles, prevent pipeline joints from being blocked, and discharge accumulated water around the pipeline to reduce pipeline corrosion;
Geotextile is laid under the anti-seepage layer of the landfill site to isolate the leachate from the underlying soil, prevent leachate from contaminating groundwater, and guide the leachate towards the collection system.
5. Agriculture and Environmental Protection Engineering
Core function: Drainage and protection
Specific application:
Laying geotextile in farmland irrigation channels to reduce channel leakage (with anti-seepage film) and prevent soil erosion on channel slopes;
In artificial wetland engineering, geotextile serves as an isolation layer for wetland substrates (such as gravel and soil) to filter suspended solids in wastewater and improve wetland purification efficiency.
In summary, geotextile has become an indispensable material in modern engineering construction due to its advantages of "multifunctionality, low cost, and high durability", and its application scenarios are still expanding into emerging fields such as ecological restoration and sponge cities.