Geosynthetics and Geotextiles
1. Comprehensive functionality: covering multiple functions such as reinforcement, anti-seepage, filtration and drainage, and coordinating multiple categories to meet complex engineering needs.
2. Reliable performance: tensile resistance, corrosion resistance and aging resistance, adaptability to extreme environments, long service life (5-30 years).
3. Strong adaptability: Suitable for various terrains, easy to construct, compatible with various engineering scenarios and processes.
4. Economic and environmental protection: The cost is lower than traditional materials, the construction is efficient and cost-effective, and it is eco-friendly and pollution-free.
Products Introduction:
Geosynthetics and Geotextiles are general term for a class of materials with engineering functions made from high molecular weight polymers (such as polypropylene, polyester, polyethylene, etc.) through processing, covering multiple categories such as geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, geonets, composite geotextiles, etc. Geotextiles are the most widely used basic category in geosynthetic materials, made through processes such as non-woven, woven, and needle punched, with the core functions of "reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and isolation".
Overall, Geosynthetics and Geotextiles together form the "multifunctional protection system" of modern civil engineering: geosynthetic materials complement each other's performance through different categories, covering the full range of needs from structural reinforcement to ecological protection; As a fundamental material, geotextile plays an irreplaceable role in core processes such as filtration and isolation, and the two work together to promote the development of civil engineering towards high efficiency, environmental protection, and low cost.
Product Features:
(1) Common characteristics of geosynthetics
Functional diversification: Different categories have clear division of labor - geogrids focus on high-strength reinforcement, geomembranes emphasize anti-seepage isolation, geonets excel in three-dimensional protection, and composite materials have multiple functions (such as "geotextile+geomembrane" to achieve the combination of filtration and anti-seepage), which can meet the single or composite needs in engineering.
High performance of materials: generally with tensile resistance, tear resistance and anti-aging characteristics, the tensile strength of some products (such as filament geotextiles, steel plastic grids) can reach more than 100kN/m; Acid and alkali resistant, resistant to biological corrosion, capable of stable use in complex environments such as underground moisture and soil erosion, with a service life of 5-30 years (depending on the product type).
Wide adaptability: from extreme temperatures ranging from -40 ℃ to 80 ℃, to special environments such as high altitude and high salinity, all have corresponding category adaptability; Flexible cutting and splicing can be carried out according to the engineering terrain (flat ground, slope, river channel), adapting to irregular structures, and construction can be carried out without the need for large equipment, manual or small machinery.
(2) Core features of Geotextiles
Outstanding basic functions: As the "basic model" of geosynthetic materials, non-woven geotextiles have excellent permeability (permeability coefficient ≥ 1 × 10 ⁻ cm/s) and high filtration accuracy (intercepting fine soil particles of 0.05-0.3mm); Woven geotextiles have high tensile strength (20-80kN/m) and are suitable for mild reinforcement scenarios. The two together cover the core requirements of "filtering, isolation, and auxiliary reinforcement".
Strong ecological compatibility: using environmentally friendly polymer materials, non-toxic and harmless, with good breathability, can be directly used as vegetation growth carriers (such as in conjunction with spray seeding greening); When in contact with soil and water, it does not produce pollution and is suitable for high environmental protection scenarios such as ecological restoration and river management.
Significant economic benefits: The unit price is lower than traditional materials such as metal and concrete, and the construction efficiency is high (the laying speed is 2-5 times that of traditional protection). The comprehensive cost is reduced by 10% -30% compared to traditional engineering solutions, especially suitable for large-scale engineering batch applications.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
(1) Typical application scenarios of Geosynthetics
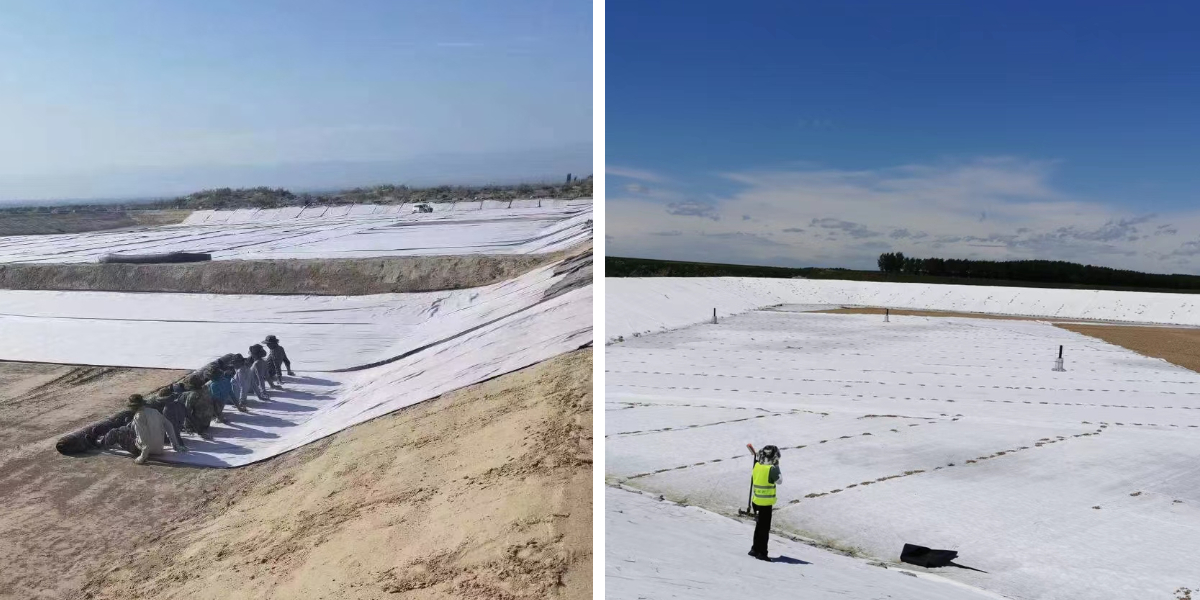
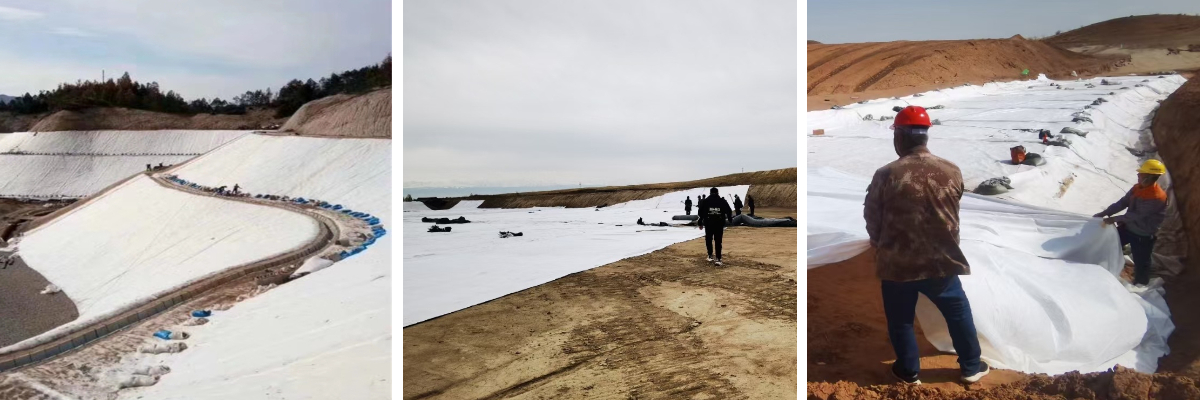
Transportation engineering: Geogrids are used for reinforcing highway and railway roadbeds to reduce settlement; Laying geotextile on the pavement base to achieve filtering and isolation; Composite geomembrane is used for tunnel anti-seepage to ensure structural dryness.
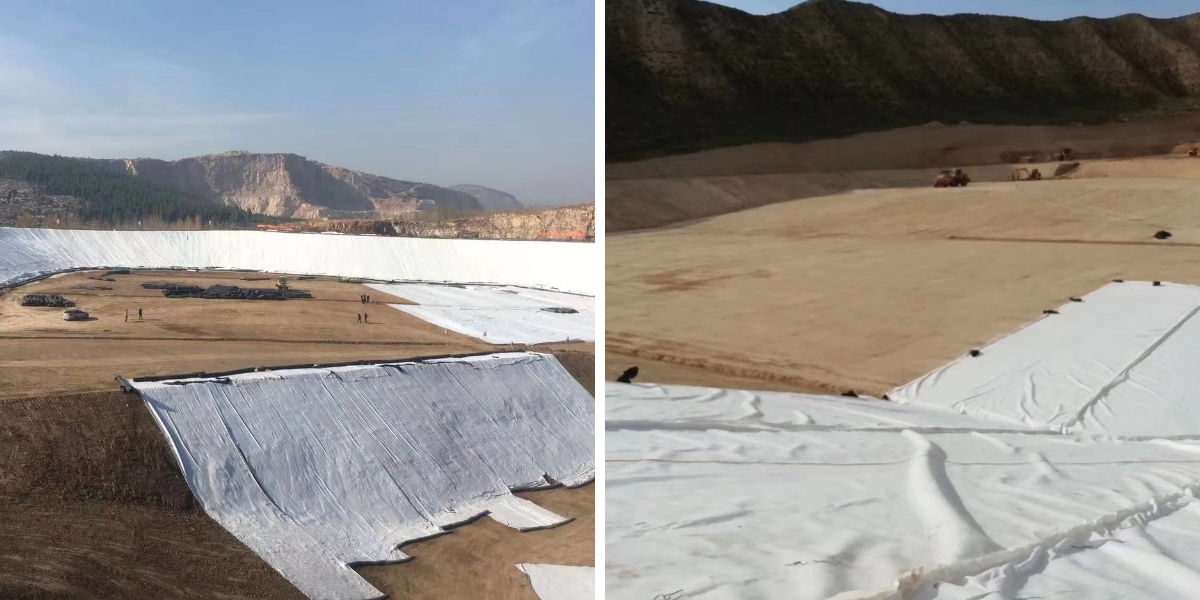
Water conservancy and environmental engineering: Geomembranes are used for anti-seepage in reservoirs and reservoirs to reduce water resource leakage; Geonet cages (stone cage nets) are used for protecting river bank slopes and resisting water erosion; Geotextile serves as a filter layer for landfill sites to prevent the spread of pollutants.
Municipal and mining engineering: Geogrid reinforcement of municipal road slopes to prevent collapse; Composite geotechnical materials are used for underground pipe gallery anti-seepage and pipeline safety protection; In the greening of mines, geonets are combined with vegetation to fix the surface soil and prevent soil erosion.
(2) Key application areas of Geotextiles
Filtering and Drainage: Wrap drainage pipes and infiltration ditches to filter sediment and prevent blockage; Laying in farmland irrigation channels to protect the soil on the canal walls from erosion and to divert excess water.
Roadbed and slope protection: Separate different soil materials in highway roadbeds to avoid mixing; Lay non-woven geotextile on the surface of the slope, cooperate with vegetation planting, intercept soil particles, and resist rainwater erosion.
Temporary engineering and emergency rescue: As the base of temporary construction access roads, it quickly enhances the site's carrying capacity; After the flood disaster, it was laid on muddy roads, isolated from the mud, and temporary traffic was restored.
(3) Collaborative application cases
In high-grade highway engineering, the combination of "geogrid (deep reinforcement)+geotextile (middle filter and drainage)+geomembrane (shallow anti-seepage)" is used: the grid enhances the bearing capacity of the roadbed, the geotextile filters and drains, and the geomembrane prevents surface water infiltration. The three work together to ensure long-term stability of the road surface and greatly extend the service life of the highway.
Geosynthetics and Geotextiles, as the core materials of modern civil engineering, have completely changed the traditional engineering model that relies on hard materials such as concrete and masonry, with the core advantages of "multiple functions, reliable performance, wide adaptability, and economic efficiency". Geosynthetics have built a full chain solution from structural reinforcement to ecological protection through multi category collaboration; As the fundamental support, geotextile plays an irreplaceable role in key processes such as filtration and isolation, jointly promoting the transformation of engineering construction towards "green, efficient, and low-cost".
Whether it is large-scale infrastructure projects such as transportation and water conservancy, or livelihood projects such as ecological restoration and municipal engineering, they can balance engineering safety and ecological protection needs through precise selection and combination application, and are key materials for promoting the sustainable development of civil engineering.