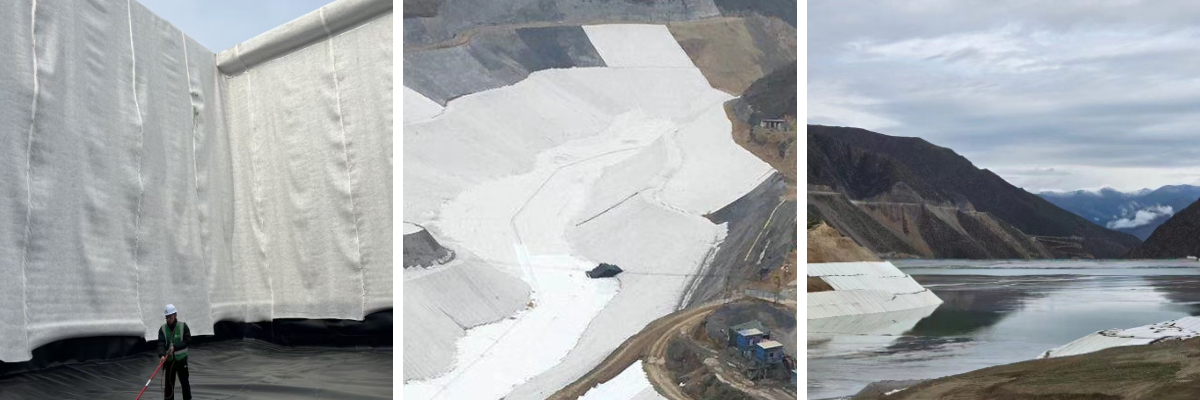
Geo Fabric for Driveway
1. Reduce engineering costs: lightweight, convenient transportation and construction, can reduce labor and machinery investment
2. Improve the service life of the project: anti-aging, anti-corrosion, resistant to the erosion of acid and alkali substances in the soil, and extend the overall service life of the project.
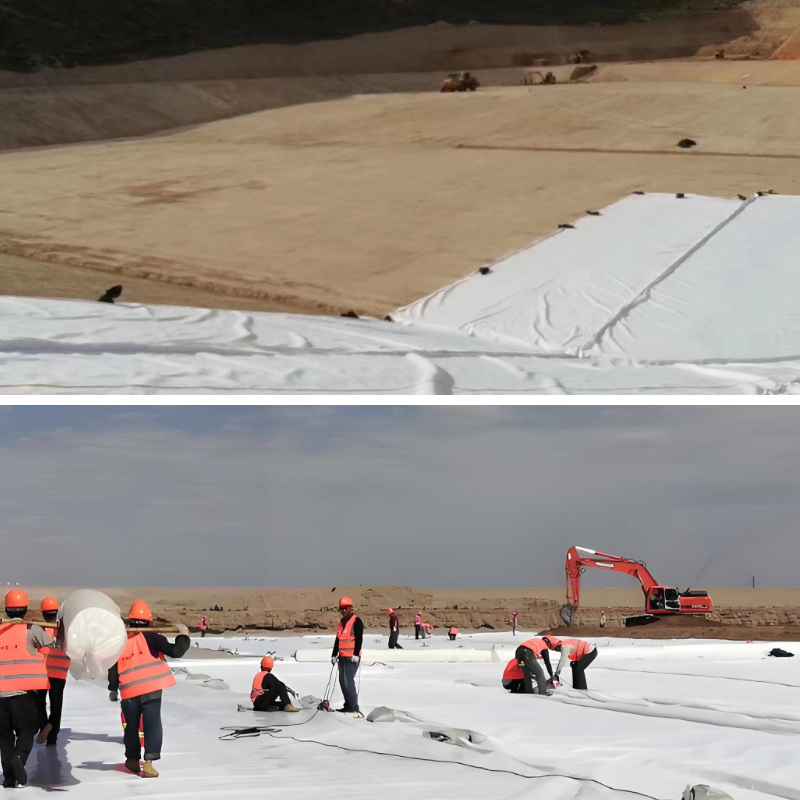
3. Simplify the construction process: With good flexibility, it can be cut and spliced according to the shape of the construction site, reducing construction difficulty.
4. Environmental sustainability: Some geotextiles can be recycled and reused, and the energy consumption during the production process is lower than that of materials such as concrete; At the same time, it can reduce the amount of earthwork excavation and minimize the damage to the surrounding ecological environment.
Product Introduction:
Geo Fabric for Driveway is a functional fabric specifically designed for the field of civil engineering. It processes synthetic fibers such as polypropylene (PP) and polyester (PET) (with a small amount of natural fibers such as cotton and hemp) into a mesh structure, which has five core functions: filtration, drainage, reinforcement, protection, and isolation. It can significantly improve engineering stability and service life, and is one of the key materials in modern geotechnical engineering.
Main Features
The characteristics of geotextile revolve around its "functionality" and "engineering adaptability", which can be specifically divided into four points:
Strong physical stability: resistant to high and low temperatures (can be used in an environment of -40 ℃~120 ℃), resistant to UV aging, and not easily decomposed even when exposed to outdoor or soil for a long time. The service life can usually reach 10~50 years (depending on the material and usage environment).
Controllable permeability: By adjusting the fiber density and process, different permeability rates (ranging from 10 ⁻³~10 ⁻¹ cm/s) can be achieved, which can quickly remove excess water from the soil and prevent soil particles from being lost with water.
Excellent mechanical properties: It has high tensile strength, tear strength, and burst strength, and can withstand the weight of soil, vehicle loads, or rolling of construction machinery. At the same time, it has a certain degree of flexibility and can adapt to small deformations in terrain to avoid cracking.
High construction convenience: light weight (usually 100-800g per square meter), soft texture, can be cut into any size according to engineering needs, no complex equipment is required for laying, and can be tightly adhered to materials such as soil and sand, with high construction efficiency.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
1. Water conservancy and hydropower engineering
Dam/reservoir construction: Laying geotextile (often combined with anti-seepage membrane) on the upstream slope of the dam can prevent water flow from scouring the soil of the dam and prevent particle loss; Simultaneously laying inside the dam body can discharge seepage water, reduce pore water pressure, and prevent landslides or dam breaches.
River/Channel Management: Laying geotextiles on the slopes or bottom of channels on both sides of the river can replace traditional concrete lining, reduce water erosion on slopes, while maintaining soil permeability and protecting the ecology of the river; For irrigation channels, it can also reduce water leakage and improve water resource utilization efficiency.
Hydroelectric power station/pump station project: Laying geotextile at the inlet, dissipation pool and other parts can protect the concrete structure from the wear and tear of sand and gravel carried by high-speed water flow, and extend the service life of equipment and buildings.
2. Transportation Engineering
Highway/railway subgrade: Laying geotextile between the subgrade filling (such as sand layer) and the underlying soil can isolate materials of different particle sizes and prevent soil particles from infiltrating the sand layer and causing deformation of the subgrade; In soft soil foundation sections, geotextiles can be used in conjunction with geogrids to form a "reinforcement layer" that disperses vehicle loads and reduces roadbed settlement.
Pavement base/sub base: Laying geotextile between the base and sub base of asphalt or cement pavement can play a role in "stress absorption", alleviate fatigue stress caused by vehicle driving, and reduce the occurrence and propagation of pavement cracks (commonly known as "crack prevention cloth").
Airport runway/apron: Due to the high load and flatness requirements of the airport, high-strength geotextile will be laid on the runway base to enhance the overall integrity of the base, while filtering rainwater to prevent the base material from softening due to water immersion.
3. Construction and Municipal Engineering
Building basement/underground garage: Lay geotextile on the outside of the basement wall and below the garage roof to filter out moisture in the soil, guide water flow into the drainage blind pipe, prevent moisture from penetrating into the interior of the wall or roof, and prevent mold growth or structural damage; The geotextile under the planting layer of the garage roof can also isolate the planting soil from the waterproof layer, preventing plant roots from piercing through the waterproof layer.
Municipal roads/sidewalks: Geotextile is laid on the green belts and pedestrian base on both sides of the road to isolate the soil and sand and gravel cushion layer, preventing soil erosion from causing pedestrian settlement; At the same time, it can accelerate rainwater infiltration and reduce the risk of urban waterlogging.
Building foundation pit support: In the spray anchor support of the foundation pit slope, laying geotextile can protect the soil of the slope, prevent rainwater erosion from causing slope collapse, and allow water seepage in the soil to be discharged, maintaining slope stability.
4. Environmental Protection Engineering
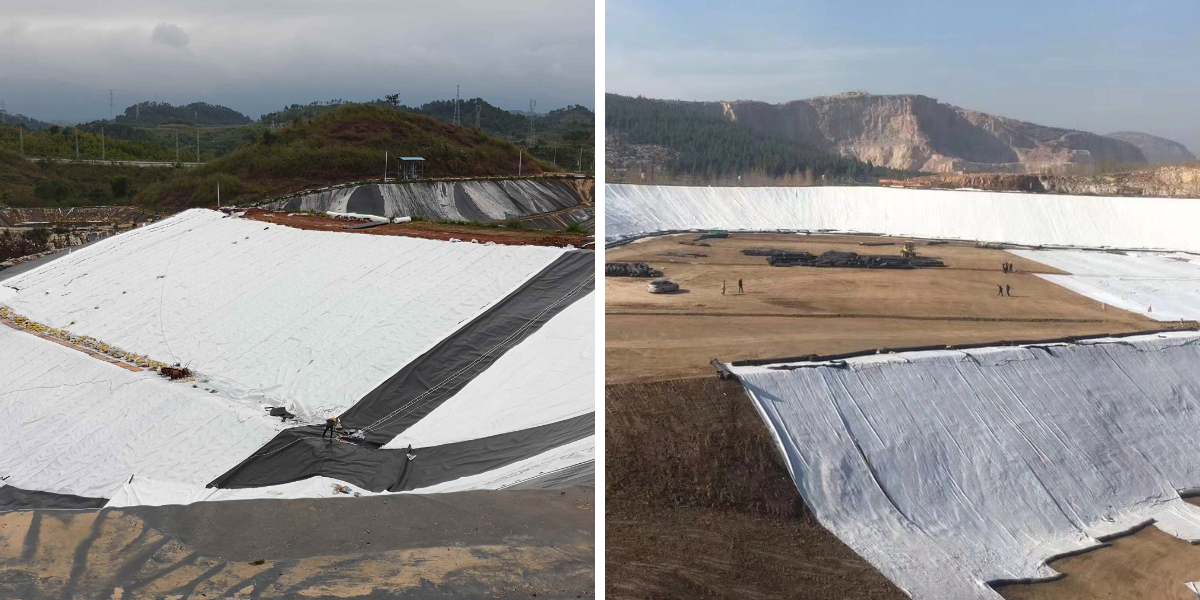
Landfill site: In the "anti-seepage system" at the bottom of the landfill site, geotextile is the key protective layer - laying geotextile above the anti-seepage membrane (HDPE membrane) can prevent sharp objects (such as metal and glass) in the garbage from piercing the anti-seepage membrane; Laying geotextile underneath the anti-seepage membrane can filter groundwater, prevent sediment from blocking the drainage system of the anti-seepage membrane, and prevent the anti-seepage membrane from being worn by stones in the soil.
Sewage treatment plant/artificial wetland: Geotextile is laid between the bottom of the sewage treatment tank and the filling layer of the artificial wetland, which can filter suspended solids, organic matter and other impurities in the sewage and improve the efficiency of sewage treatment; Simultaneously isolate different layers of fillers to prevent mixing of fillers that may lead to a decrease in treatment effectiveness.
Solid waste storage yard/tailings pond: Geotextiles are laid at the bottom and slopes of the solid waste or tailings storage area to isolate harmful substances from the surrounding soil and groundwater, prevent the leakage of heavy metals and other pollutants, and protect the surrounding ecological environment.
5. Agriculture and Ecological Engineering
Irrigation of farmland/water-saving agriculture: Laying geotextiles around irrigation channels and drip irrigation systems in farmland can reduce water leakage and improve water resource utilization efficiency; In the improvement of saline alkali land, geotextiles can isolate saline alkali soil from improved soil, prevent the reverse infiltration of saline alkali components, and accelerate soil improvement.
Slope ecological restoration: On exposed slopes on both sides of highways and railways, or slopes in mining reclamation areas, geotextiles (often biodegradable) are laid and then covered with soil and vegetation to fix the soil, prevent rainwater erosion and soil erosion, and provide a stable environment for plant growth, achieving a combination of "engineering protection+ecological restoration".
Aquaculture: Laying geotextiles at the bottom of fish ponds and shrimp ponds can prevent soil leakage at the bottom of the pond from causing a decrease in water level, reduce the accumulation of silt at the bottom of the pond, facilitate cleaning, and prevent aquaculture organisms (such as shrimp and crabs) from drilling into the soil, thereby improving aquaculture efficiency.
The application of geotextiles has covered multiple core engineering fields such as water conservancy, transportation, construction, and environmental protection. The core is to solve key problems such as soil stability, waterproofing, anti-seepage, and structural protection in engineering through its five functions of filtration, drainage, isolation, reinforcement, and protection.