Fabric Geotextile
•High strength and good mechanical properties
•Excellent filtration and drainage functions
•Chemical corrosion resistance and anti-aging
•Convenient construction and dimensional stability
•Environmental protection and economy
Product Introduction:
Fabric Geotextile is geosynthetic materials made from synthetic fibers (such as polyester, polypropylene, etc.) through a weaving process. They are widely used in engineering fields such as water conservancy, transportation, and environmental protection.Woven geotextiles are commonly used in scenarios such as highway and railway subgrade reinforcement, river embankment seepage control and drainage, and landfill isolation layers. Their versatility makes them one of the indispensable materials in modern civil engineering.
Product Parameters:
| project | metric | |||||||||||||
| Nominal strength/(kN/m) | ||||||||||||||
| 35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | ||||
| 1 Tensile strength per (kN/m) ≥ | 35 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 | |||
| 2. Weft tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | After tensile strength is multiplied by 0.7 | |||||||||||||
| 3 | Maximum elongation at maximum load/% | warp direction ≤ | 35 | |||||||||||
| broadwise ≤ | 30 | |||||||||||||
| 4 | Top penetration force /kN is greater than or equal to | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10.5 | 13 | 15.5 | 18 | 20.5 | 23 | 28 | ||
| 5 | Equivalent aperture O90 (O95)/mm | 0.05~0.50 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10⁵~102) where: K=1.0~9.9 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -1 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | Tear strength in both directions /kN ≥ | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.7 | ||
| 9 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | ||||||||||||
| 10 | Length and width deviation rate/% | ±2 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | Joint/seam strength a/(kN/m) ≥ | Nominal strength x 0.5 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | Anti-acid and alkali properties (strong retention of warp and weft Rate) a /% ≥ | Polypropylene: 90; other fibers: 80 | ||||||||||||
| 13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) b | The strength retention rate in both directions is /%≥ | 90 | |||||||||||
| 14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescencePhotometric ultraviolet lamp method) | The strength retention rate in both directions is /%≥ | 90 | |||||||||||
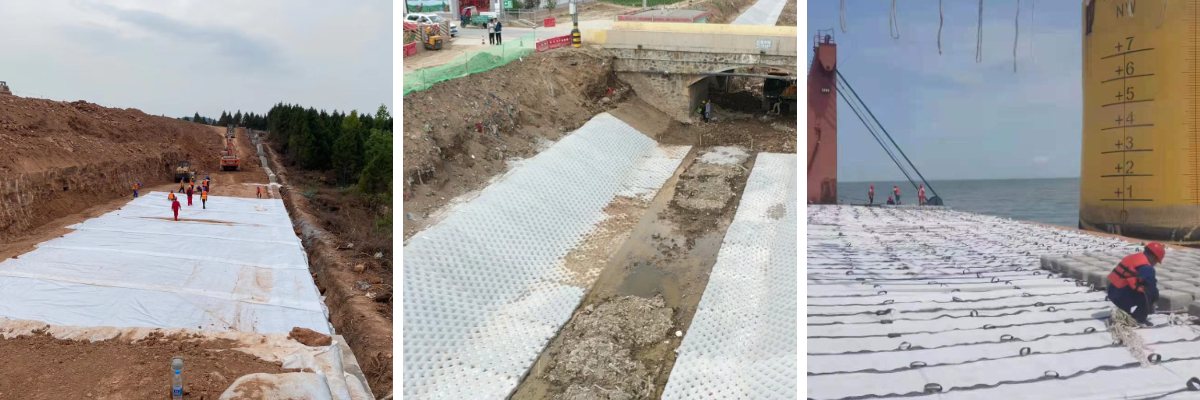
Product Applications:
1.Field of Traffic Engineering
Airport runway infrastructure construction
Enhance the bearing capacity of the runway foundation to prevent foundation deformation caused by aircraft loads.
Sports field foundation treatment
In the drainage systems of golf courses, football fields, etc., it serves as a filter layer or drainage layer to keep the field dry.
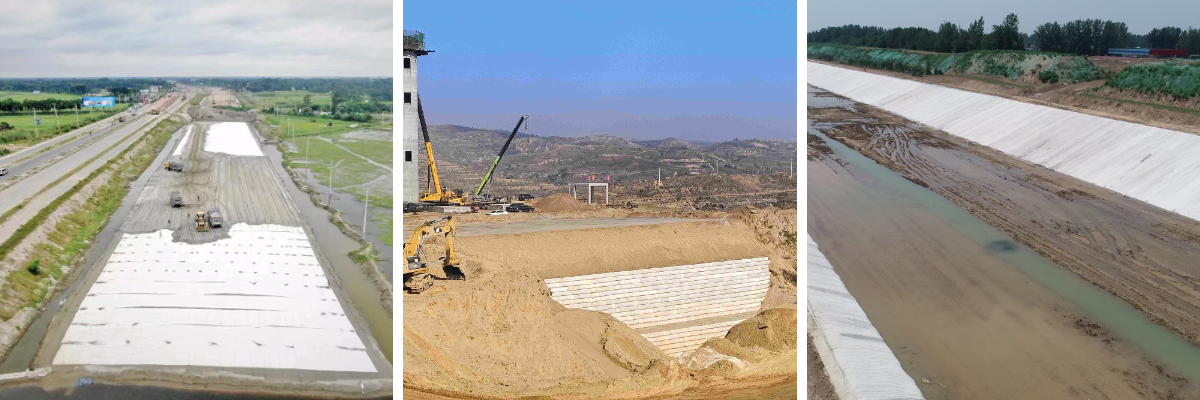
Reinforcement of Highway and Railway Subgrades
Laid between the subgrade and the foundation, it disperses the load pressure, prevents subgrade settlement or cracking, and improves road stability (such as in high-fill sections and soft soil foundation treatment).
Anti-crack Treatment of Road Surfaces
As a reinforcing layer under the asphalt pavement, it inhibits the generation of reflective cracks and extends the service life of the road surface.
Covers the surface of the slope, prevents soil erosion caused by rainwater scouring, and cooperates with structures such as anchor rods to enhance the anti-sliding ability of the slope.
2.Field of Hydraulic Engineering
Seepage Control and Drainage of Dams and Rivers
Used on the upstream or downstream side of dams, serving as a filter layer to prevent the loss of soil particles and discharge seepage water simultaneously, avoiding piping or seepage failure of dams.
Reservoir and Canal Lining
Laid at the bottom of reservoirs or inside irrigation canals to reduce water seepage and improve the efficiency of hydraulic engineering.
Coastal Protection Engineering
In coastal beaches or seawall projects, it resists the erosion of ocean waves and protects the stability of the bank slope (such as breakwaters and revetment projects).
3.Environmental Engineering Field
Landfill Construction
As the isolation layer and drainage layer at the bottom of the landfill, it prevents leachate from polluting groundwater, quickly drains liquids, and reduces the settlement risk of the landfill.
Sewage Treatment Project
In sewage treatment ponds or oxidation ponds, it is used to filter sludge or separate water quality to assist the water treatment process.
Mine Ecological Restoration
Covers the abandoned mine area, prevents soil erosion, and provides basic support for vegetation restoration
4.Construction Engineering Field
Foundation Treatment and Basement Waterproofing
Used as a reinforcing material in soft foundations to improve the bearing capacity of the foundation; applied to the basement floor or side walls to enhance the waterproofing performance.
Retaining Walls and Foundation Pit Support
Serves as a reinforcing layer behind the retaining wall to reduce the effect of soil pressure on the wall, or aids in slope stability during foundation pit excavation.
5. Agricultural and Ecological Engineering Field
Irrigated Farmland and Water Conservancy and Soil and Water Conservation
Used for seepage prevention treatment of farmland drainage ditches and reservoirs, or to prevent soil erosion during terraced field construction and protect cultivated land resources.
Saline-alkali Land Improvement
Laid on the surface or deep layer of the soil to isolate the saline-alkali layer and cooperate with the drainage system to reduce the soil salt content.
Eco-slope Greening
Used in combination with vegetation seeds to provide a carrier for the growth of slope plants and stabilize the soil mass at the same time (such as highway slope greening, river ecological restoration).