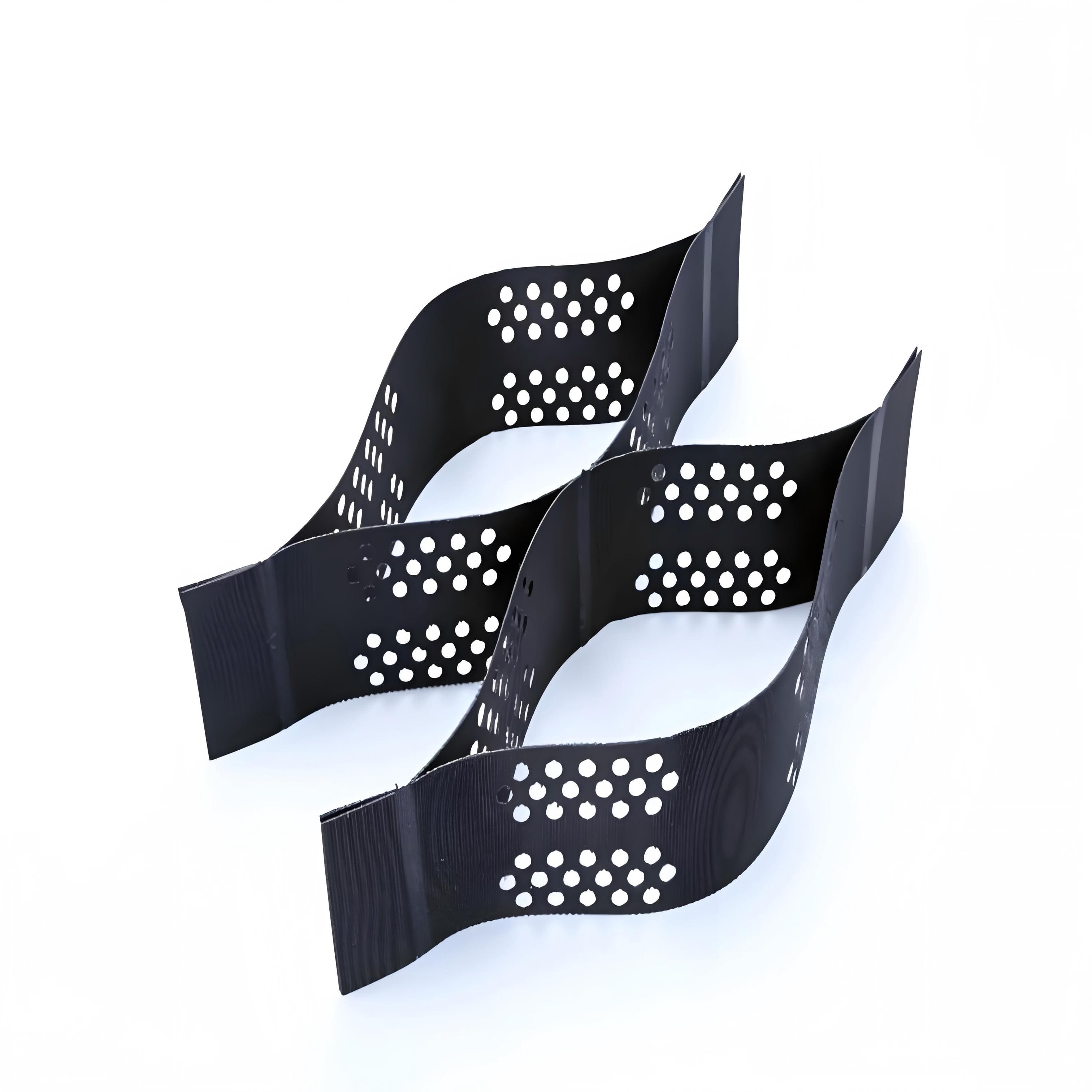
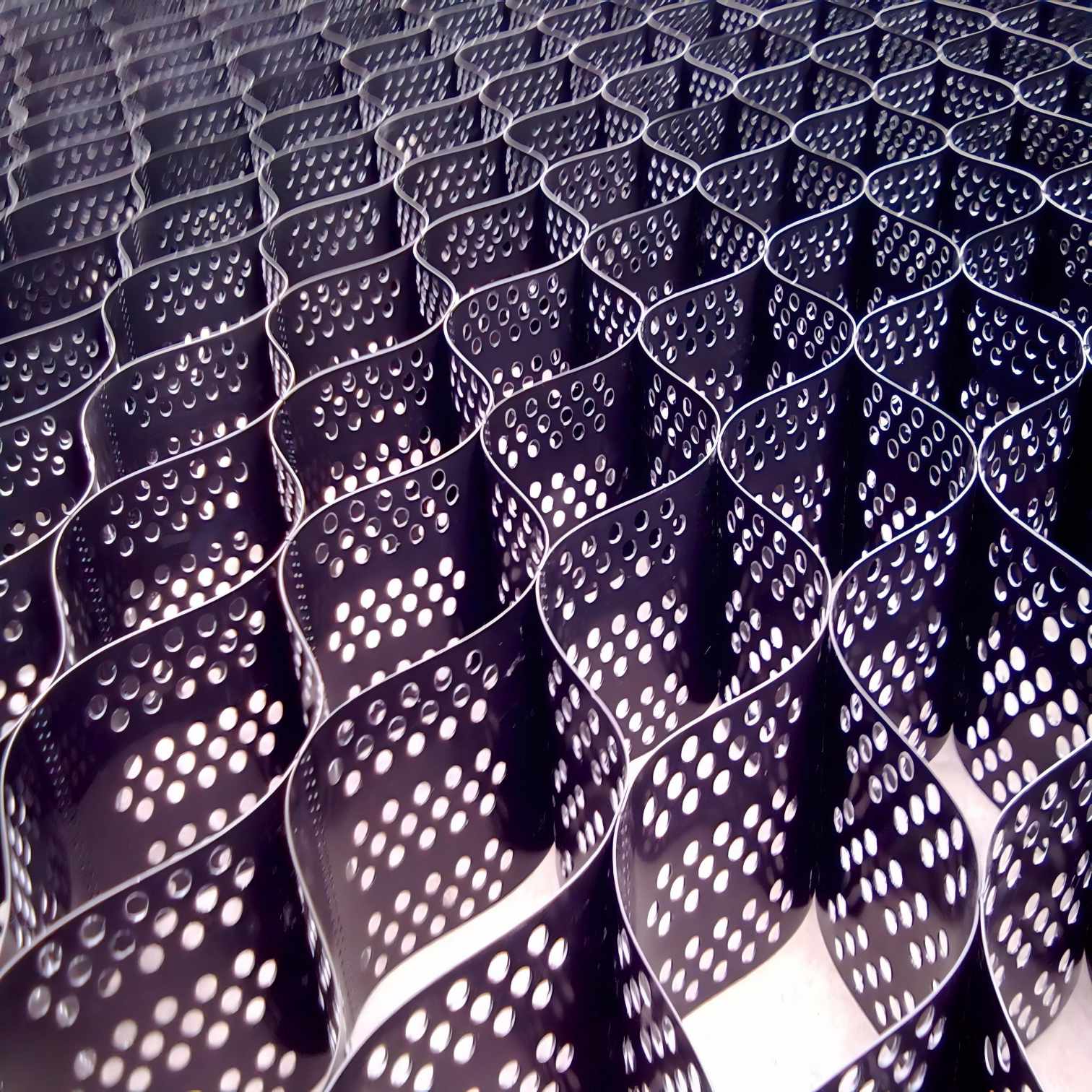
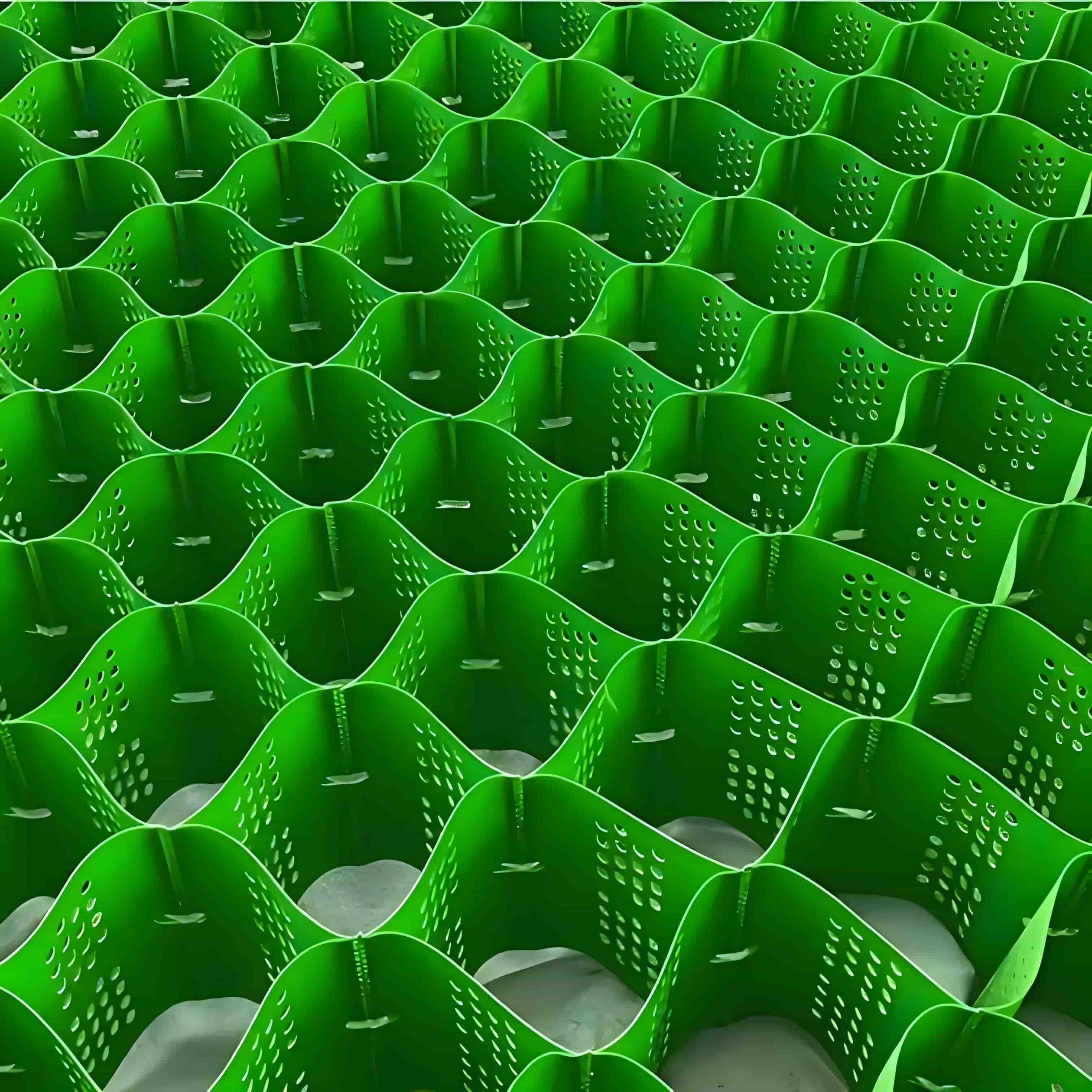
Geocellular Confinement Systems
1.Mechanical properties: The compressive strength is 3 - 5 times higher than that of the traditional crushed stone layer, enabling it to bear the load of heavy - duty vehicles. It has a strong ability to disperse loads and reduces local damage.
2.Construction Efficiency: Modular installation, no need for large machinery, the construction speed is more than 50% faster than that of the traditional concrete base; it can be constructed in harsh environments.
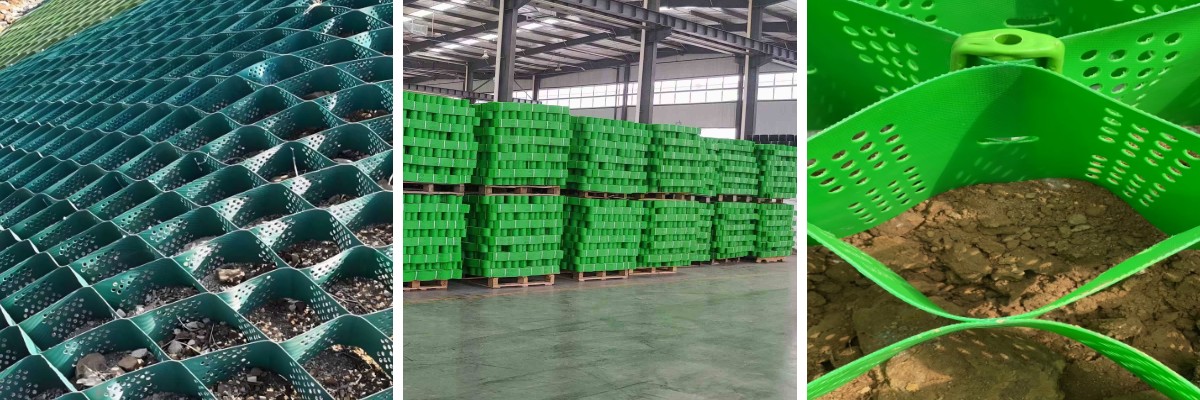
3.Ecological benefits: Allow plants to grow, combining engineering protection with ecological restoration; the materials are recyclable and meet environmental protection requirements.
4.Adaptability: It can adapt to uneven settlement and has stable performance under special geological conditions such as frozen soil and expansive soil.
5.Economy: The comprehensive cost is reduced by 20%-40% compared with the concrete base. The service life is more than 50 years, and the maintenance cost is low.
Product Introduction:
Geocellular Confinement Systems are usually made of high - molecular polymers (such as high - density polyethylene HDPE) through a thermoforming process to form a honeycomb - shaped grid structure that can be expanded into a three - dimensional framework. After materials such as soil and crushed stone are filled in the framework, the honeycomb walls exert lateral confinement on the filled materials, enabling them to form an overall compressive structure similar to "concrete", significantly enhancing the deformation resistance.
Material Properties:
Commonly used materials: HDPE, PP (polypropylene), which have the characteristics of aging resistance, UV resistance, and chemical corrosion resistance;
Physical properties: Tensile strength ≥ 20MPa, elongation at break ≥ 300%, and the applicable temperature ranges from - 50℃ to +80℃.
Core Principle
Utilize the geometric stability and material constraint effect of the honeycomb structure:
The honeycomb walls restrict the lateral displacement of the filling material and disperse the local load to the entire structure;
The three - dimensional grid and the filling material form a "composite" with the characteristics of both flexibility (adapting to foundation deformation) and rigidity (resisting loads).
Product Parameters:
order number | raw and processed material | |||||||
test item | unit | polytene | sulan | polyester | ||||
Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | |||
1 | tensile strength | kN/m | ≥20 | ≥100 | ≥23 | ≥100 | ≥30 | ≥120 |
2 | Tensile yield strain | % | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | - |
3 | Tensile fracture strain | % | — | 8~ 20 | — | 6~ 15 | — | 8~ 20 |
4 | Carbon black content a | % | 2. 0~ 3. 0 | |||||
5 | Carbon black dispersion a | — | There should be no more than one level 3 data item in ten data items and no level 4 or 5 data items | |||||
6 | 200℃ oxidation induction time | min | ≥20 | ≥20 | — | |||
7 | Tensile load stress cracking | h | ≥300 | — | ||||
8 | B. Resistance to artificial climate aging retention rateb | % | ≥80 | |||||
9 | Chemical resistance performance retention rate c | % | — | ≥80 | ||||
Product Applications:
Civil Engineering and Road Construction
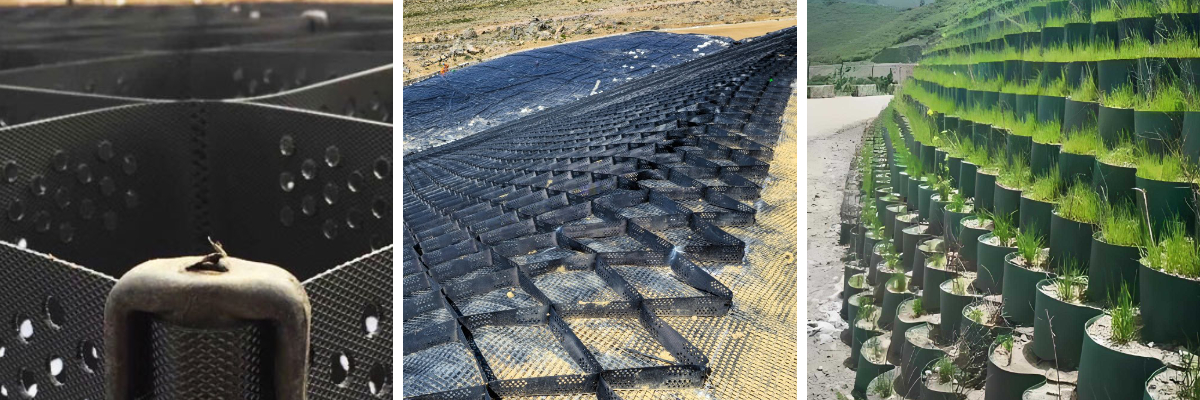
Subgrade Reinforcement: Used for soft soil foundation treatment, reducing subgrade settlement and improving bearing capacity;
Slope Protection: Prevent slope soil erosion and achieve ecological protection by combining with vegetation planting;
Pavement Base: Replace the traditional crushed stone base, reducing the pavement thickness and construction cost.
Ecological Engineering and Environmental Governance
River/Stream Bank Protection: Restrain the scouring of water flow and provide growth space for plant roots at the same time;
Desert Control: Fix sand dunes and create growth conditions for vegetation;
Greening Project: Used as the planting base for rooftop gardens and vertical greening.
Applications in Special Scenarios
Temporary construction access roads, parking lots (can be quickly built and reused);
Temporary road surfaces and bunker reinforcement in military projects;
Slope stability in mine reclamation and landfill sites.
Geocellular Confinement Systems, through the innovative combination of "structure + material", not only solves the problem of engineering stability but also takes into account ecological protection and economy. It is a new material system with both technical advantages and social value in modern infrastructure construction.