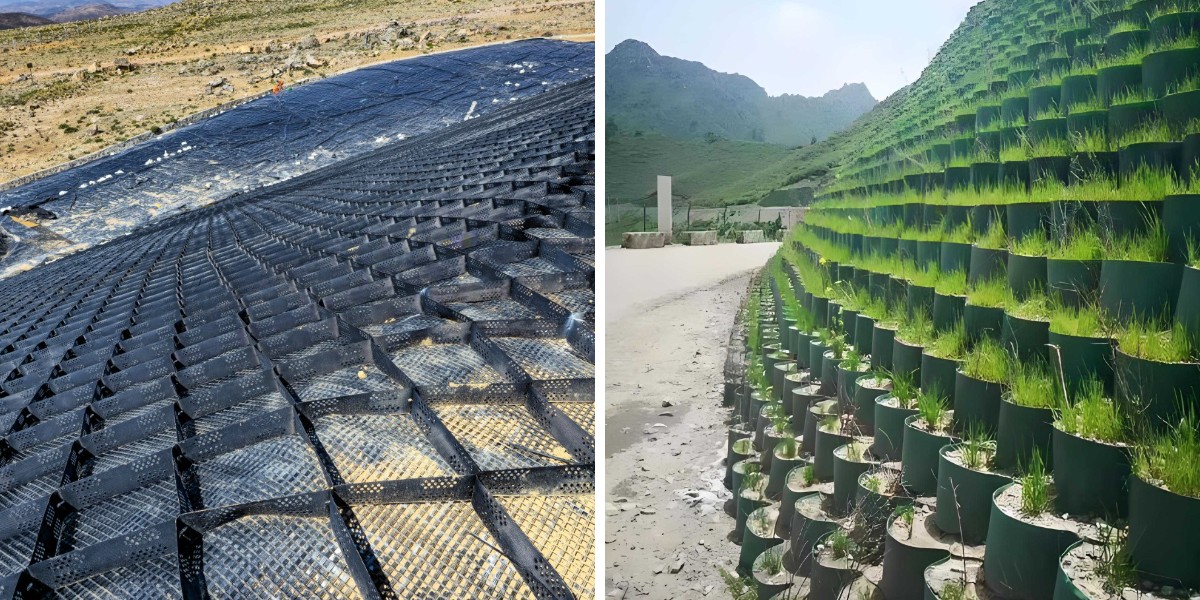
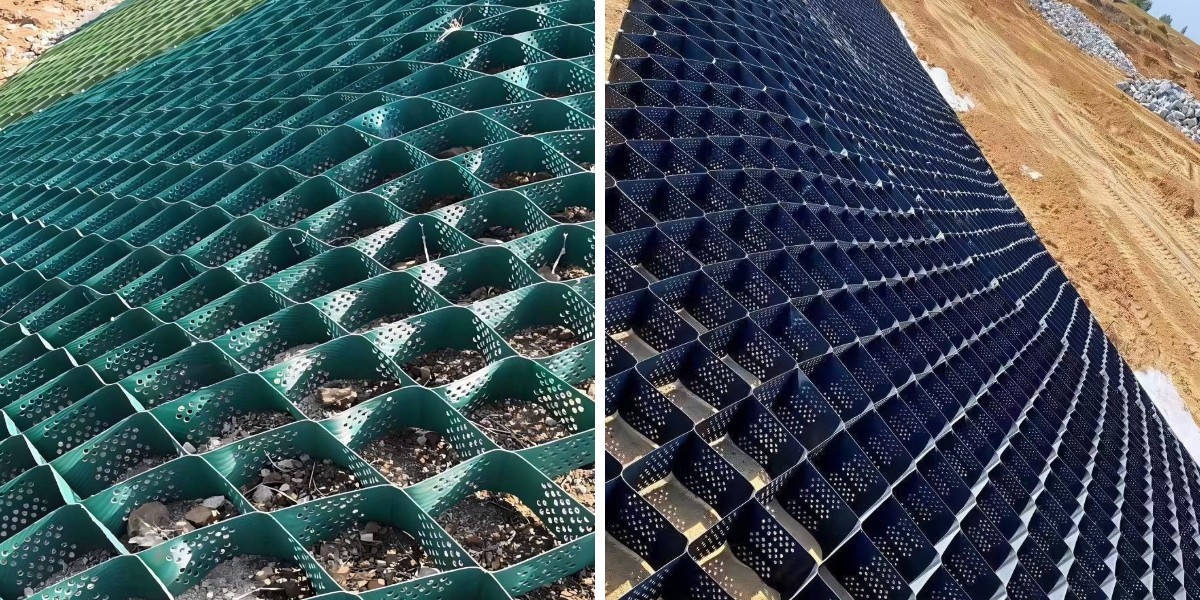
Geocell for Gravel Driveway
1. High strength and stability: The three-dimensional structure can effectively disperse loads and improve the bearing capacity of the foundation.
2. Convenient construction: lightweight, foldable for transportation, fast installation, saving labor and time costs.
3. Strong adaptability: Suitable for complex geological conditions such as soft soil, steep slopes, and uneven foundations.
4. Environmental protection and energy conservation: reduce the use of traditional stone and concrete, and lower carbon emissions.
5. Permeable drainage: Honeycomb structure facilitates water infiltration and reduces the damage of accumulated water to the project.
Product Introduction:
Geocell for Gravel Driveway is a three-dimensional mesh structure material formed by ultrasonic welding, needle welding, or riveting of high-strength polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP) sheets. The core principle is to significantly improve the bearing capacity and deformation resistance of filling materials (such as soil, sand, gravel, etc.) through the lateral confinement effect of three-dimensional mesh. After unfolding, it forms a honeycomb shape and can be folded and expanded. During construction, it is filled with loose materials to form a high stiffness structure, which belongs to special geosynthetic materials.
characteristic
1. Three dimensional reinforcement
Compared to the planar reinforcement of geogrids, geogrid cells provide upward support in the vertical direction, forming a "honeycomb" three-dimensional structure that significantly improves overall stability.
2. Flexibility and adjustability
Variable grid size: Adjust the welding distance according to the slope, using small grids when the slope is steep and large grids when the slope is gentle.
Modular design: The units are independent and formed as a whole through welding, with strong resistance to erosion, especially suitable for high flow areas such as rivers and coasts.
3. Lightweight and durability
The material has low density and light weight, making it easy to handle and install manually. It is also resistant to ultraviolet radiation, acid and alkali, and suitable for extreme weather conditions.
4. Multi functional combination application
It can be combined with geotextile (filtering and retaining sand) and three-dimensional vegetation mesh (stabilizing vegetation) to form a composite protective system, improving the overall performance of the project.
Product Parameters:
order number | raw and processed material | |||||||
test item | unit | polytene | sulan | polyester | ||||
Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | |||
1 | tensile strength | kN/m | ≥20 | ≥100 | ≥23 | ≥100 | ≥30 | ≥120 |
2 | Tensile yield strain | % | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | - |
3 | Tensile fracture strain | % | — | 8~ 20 | — | 6~ 15 | — | 8~ 20 |
4 | Carbon black content a | % | 2. 0~ 3. 0 | |||||
5 | Carbon black dispersion a | — | There should be no more than one level 3 data item in ten data items and no level 4 or 5 data items | |||||
6 | 200℃ oxidation induction time | min | ≥20 | ≥20 | — | |||
7 | Tensile load stress cracking | h | ≥300 | — | ||||
8 | B. Resistance to artificial climate aging retention rateb | % | ≥80 | |||||
9 | Chemical resistance performance retention rate c | % | — | ≥80 | ||||
Product Applications:
1. Transportation Engineering
Roadbed reinforcement: Treatment of semi filled and semi excavated roadbeds, roadbeds in windy and sandy areas, to prevent uneven settlement. For example, geogrids are used in frozen soil sections of the Qinghai Tibet Railway to ensure the minimum filling height.
Reinforcement at the back of the bridge: reduces the settlement difference between the bridge abutment and the roadbed, alleviates the phenomenon of "bridge head jumping", and has been applied significantly in the Shanghai Nanjing Expressway expansion project.
2. Water conservancy and flood control
Riverbank protection: In the management of rivers such as the Yellow River and the Yangtze River, geogrid protection can resist water erosion, promote vegetation growth, and achieve ecological slope protection.
Embankment reinforcement: used for reinforcing flood control embankments and reservoir bodies to enhance anti sliding stability, such as the use of geogrids to strengthen the dam body in the Three Gorges Project.
3. Environmental Engineering
Desert greening: In areas such as the Taklamakan Desert, geogrids fix sand dunes and fill them with soil to provide a growth foundation for vegetation and help prevent and fix sand.
Saline soil improvement: In the northwest saline soil area, geogrids isolate salt and improve soil structure to support highway construction.
4. Special geological treatment
Loess collapsibility control: In areas with collapsible loess, geogrids limit soil expansion and prevent roadbed collapse, such as the application case of the loess section of the Lanzhou Xinjiang high-speed railway.
Expansive soil restoration: In expansive soil areas, geogrids resist soil expansion and contraction deformation, ensuring long-term stability of the project.
5. Agriculture and Landscape
Greenhouse construction: used for greenhouse foundation reinforcement, improving bearing capacity and preventing settlement.
Landscape design: In parks, golf courses, and other settings, geogrids are used to construct stepped slopes or flower beds that combine functionality and aesthetics.
Geogrids, with their unique structural advantages and engineering applicability, have become an indispensable material in modern geotechnical engineering, especially suitable for scenarios that require rapid construction, long-term stability, and ecological friendliness.