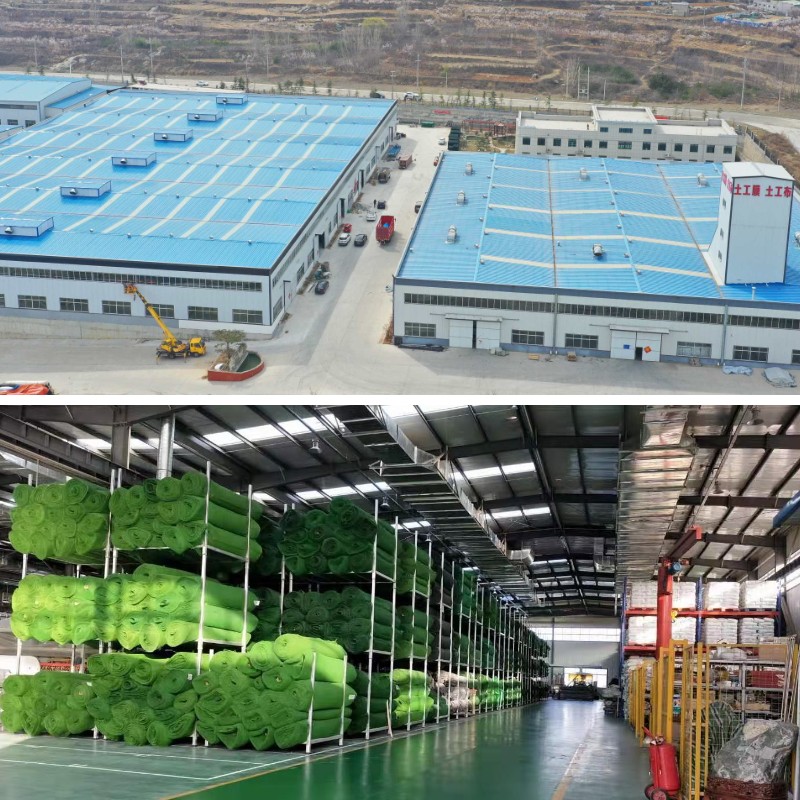
Geotextile Reinforced Retaining Wall
1.Stable structure, anti sliding:The combination of geotextile and fill soil can disperse pressure, prevent wall slippage, and can be used for high fill and soft soil foundations.
2.Easy construction, short construction period:Compared to traditional retaining walls, it is lighter, easier to cut, does not require complex equipment, and can be laid layer by layer, with faster construction and lower difficulty.
3.Durable to the environment, more environmentally friendly:Not afraid of moisture, temperature difference, no need for heavy excavation or stacking of hard materials, minimal damage to terrain and vegetation, suitable for ecological projects.
4.Low cost, high cost-effectiveness:The cost of raw materials, labor, and equipment is low, and there is no need for frequent maintenance in the later stage. It can also save on foundation treatment fees, making it suitable for small and medium-sized projects.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Geotextile Reinforced Retaining Wall use geotextile as the reinforcing material and are combined with fill layers to form a composite structure; Overall lightweight, strong flexibility, and no need to rely on traditional rigid masonry materials; It has the characteristics of moisture resistance and temperature difference resistance, and can adapt to various outdoor construction environments.
2、 Core functions
Stable soil retention: dispersing soil pressure through the tensile strength of geotextile, preventing wall sliding and overturning, and supporting high fill or soft soil foundation scenarios;
Simplified construction: Without the need for complex templates and heavy equipment, the construction can be completed by laying geotextiles and filling soil layer by layer, reducing the difficulty of construction.
3、 Main features
Environmental adaptation: No need for large excavation or stacking of hard materials, reducing damage to terrain and vegetation, suitable for ecological protection projects;
Cost controllable: minimal input of raw materials, labor, and equipment, low frequency of maintenance in the later stage, and can also save on foundation treatment costs, with high cost-effectiveness;
Widely applicable: It is suitable for small and medium-sized retaining projects, as well as special scenarios such as high fill and soft soil foundations, with strong practicality.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1、 Road and Traffic Engineering
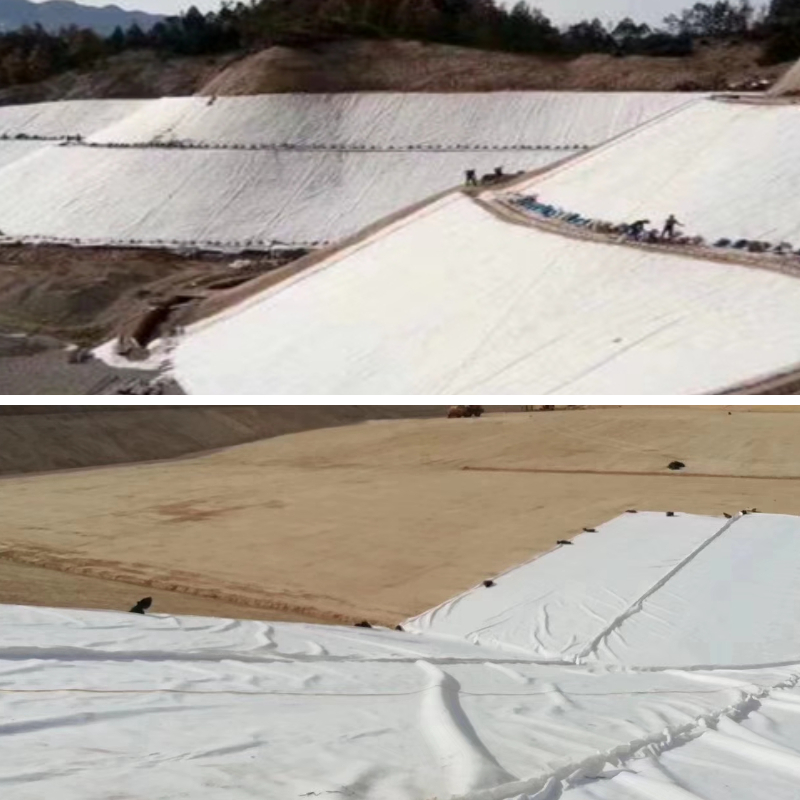
Highway/railway slope protection: Built at the filling or excavation slopes on both sides of the road, it can prevent landslides and collapses of the slope soil, especially suitable for soft soil foundation sections or high filling slopes, ensuring road traffic safety;
Service area/parking lot retaining soil: used for retaining soil at the boundary of service areas and parking lots, separating different functional areas, while avoiding soil loss caused by vehicle driving or rainwater erosion, and flexible construction without occupying too much space.
2、 Municipal and Civil Engineering
Landscape retaining walls in residential areas/parks: used in the undulating terrain of residential areas and parks, they can create layered landscape green spaces, which can not only fix the soil and prevent soil erosion, but also coordinate more with the surrounding green environment because they do not require hard masonry materials;
Municipal drainage/river bank protection: used for protecting the banks of both sides of municipal drainage channels or small rivers, resisting the erosion of water flow on the banks, and adapting to humid environments with moisture resistance to reduce damage to the river ecology.
3、 Water Conservancy and Ecological Engineering
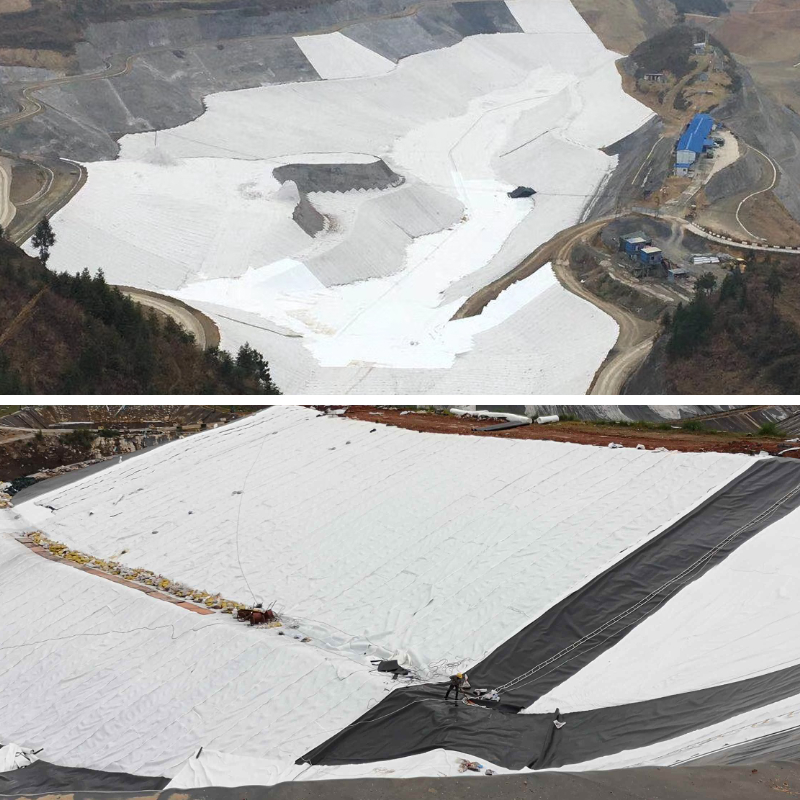
Small reservoir/pond bank slope reinforcement: Built on the bank slope of small reservoirs or artificial ponds to prevent bank slope collapse caused by water level changes or rainwater erosion, and protect the soil structure around the water body;
Ecological restoration slope protection: Used for slope soil protection in ecological projects such as mine restoration and barren mountain greening, combined with vegetation planting, it can not only stabilize the slope but also reduce damage to the native terrain vegetation, helping ecological restoration.
4、 Industrial and Storage Engineering
Boundary soil blocking of factory/storage areas: used for the boundary of factory areas and storage logistics parks, separating different areas or blocking the intrusion of surrounding soil, adapting to the bearing needs of industrial sites, and construction is fast without affecting the operation of the factory area;
Reinforcement of filling site: Used in industrial filling sites (such as site leveling before factory construction) to solve the problem of soil instability caused by soft soil foundation or high filling, and provide a stable foundation for subsequent factory construction.
Geotextile reinforced retaining walls, with their core advantages of strong stability, flexible construction, and environmental adaptability, widely cover four core areas: road transportation, municipal and civil use, water conservancy ecology, and industrial warehousing. Whether it is ensuring traffic engineering safety, improving municipal landscape coordination, assisting ecological restoration, or addressing industrial site reinforcement needs, it can combine the characteristics of different scenarios to provide practical solutions for "preventing collapse, reducing damage, and saving costs", becoming an efficient choice in various types of retaining and slope protection projects.