Geotextile Fabric Pavers
1.Wide adaptability: Choose the type as needed, suitable for soft foundation, rainy and other scenarios;
2.Fully functional: Reinforced anti settlement, drainage anti softening, isolation and anti mixing;
3.Cost saving: Durable and easy to maintain, with high long-term cost-effectiveness;
4.Fast construction: Lightweight and easy to lay, no need for complex equipment, short construction period.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Material: Geotextile Fabric Pavers are mainly polypropylene, polyester and other polymer materials, which are divided into two categories: woven (warp and weft interwoven, high tensile strength) and nonwoven (fiber bonding, good water permeability), some of which have undergone anti-aging and anti-corrosion treatment to adapt to the outdoor environment;
Form: mostly roll material, thickness 0.5-5mm, unit mass 100-600g/㎡, lightweight and easy to cut and transport;
Physical characteristics: It has certain tensile and tear strength and porosity, can withstand construction and use stresses, and achieve soil water separation.
2、 Core functions
Reinforcement: dispersing vehicle loads, enhancing the deformation resistance of roadbeds and base layers, reducing soft foundation settlement and cracking of heavy-duty roads;
Filtering and drainage: intercepting soil particles to prevent blockage, exporting accumulated water from the road, and avoiding softening of the road due to high moisture content;
Isolation: Separate different structural layers of the road (such as subgrade and base, new and old subgrade) to prevent material mixing and ensure the performance of each layer.
3、 Main features
Strong adaptability: can select corresponding types according to road conditions (soft foundation, rainy, saline alkali land, etc.) to meet diverse needs;
Excellent economy: With a service life of 10-20 years, it extends the lifespan of roads, reduces maintenance, and offers high long-term cost-effectiveness;
Convenient construction: No need for complex equipment, simple and fast laying, can shorten the construction or renovation period of roads.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
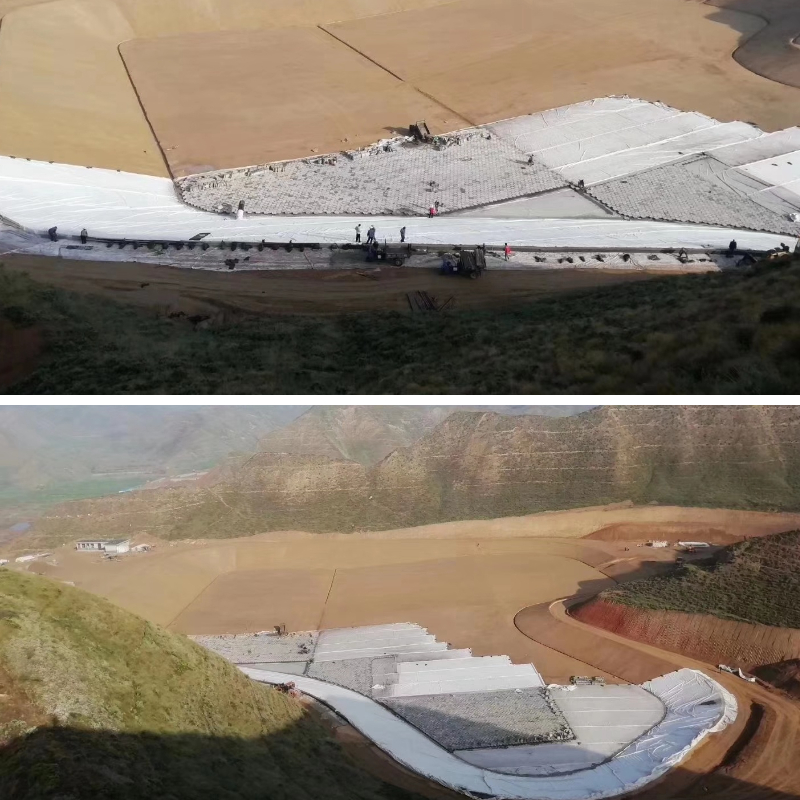
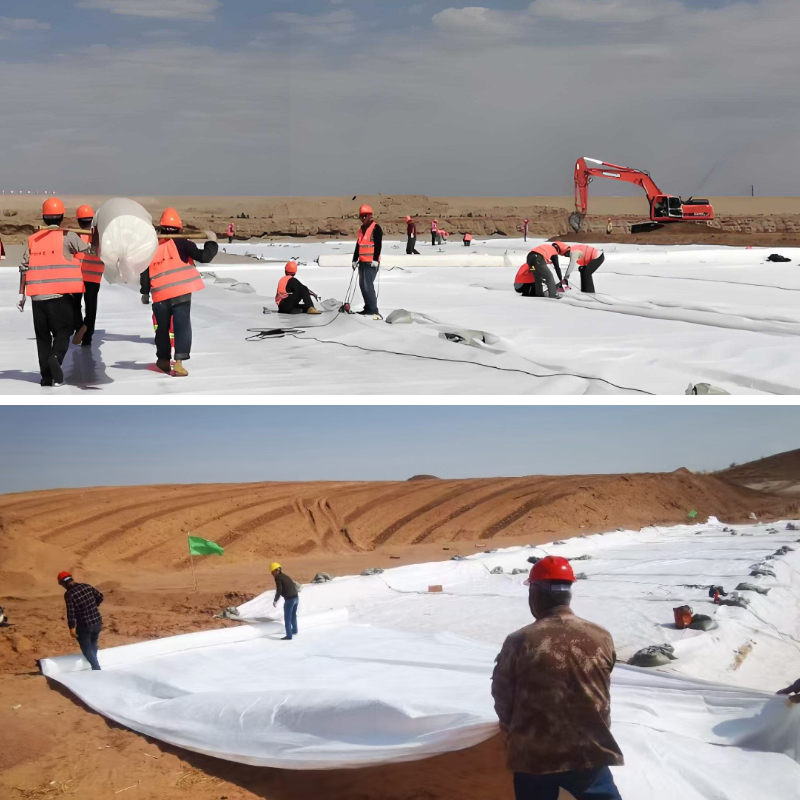
1、 Roadbed treatment: laying the "foundation" of the road
Isolation: Separate the soil and rock filling materials used for paving from the soft soil and expansive soil below, to prevent the filling materials from sinking into the soft soil and to prevent the expansive soil from affecting the roadbed when it comes into contact with water.
Drainage: In areas with frequent rainfall or high groundwater levels, geotextile can allow accumulated water in the roadbed to seep out, avoiding the problem of "slurry boiling" caused by water soaking in the roadbed.
Reinforcement: disperses vehicle loads above the road surface, reduces uneven settlement of the foundation, especially suitable for soft soil foundations of new highways and municipal roads.
2、 Grassroots construction: enhancing the stability of the "load-bearing layer"
Anti mixing: It is laid between the base layer and the roadbed to prevent the crushed stones of the base layer from seeping into the roadbed soil, and to prevent the fine soil of the roadbed soil from running into the base layer, ensuring the thickness and strength of the base layer.
Crack resistance: In response to the problem of shrinkage and cracking of cement-based base due to temperature and drying, geotextile (mixed with asphalt) is laid on the surface of the base to disperse the stress of cracks and reduce the propagation of cracks onto asphalt pavement (commonly used on highways and heavy-duty roads).
Connection: When widening or repairing roads, laying geotextile at the junction of new and old base layers can enhance the bonding strength of the connection and avoid the occurrence of joint seams.
3、 Surface layer assistance: protecting the "surface layer" of the road surface
Waterproof scouring: Laying geotextile between the asphalt surface layer and the base layer, combined with asphalt sealing layer, can not only prevent the fine materials of the surface layer from infiltrating into the base layer, but also guide the rainwater in the surface layer to the roadside, avoiding damage to the surface layer caused by rainwater bubbles, resulting in peeling and loosening.
Joint protection: The gaps (shrinkage joints, expansion joints) in cement pavement are prone to water ingress, which can wash away the underlying base layer. Laying geotextile under the gap can filter rainwater, prevent the base soil from being washed away, and avoid "mud splashing" (mud splashing from vehicles passing through the gap) at the gap.
4、 Special section reinforcement: dealing with complex situations
High fill slope: The slope of high fill subgrade is prone to collapse. Layered laying of geotextile can "reinforce" the slope together with filling materials, improve stability, and reduce deformation.
Permafrost subgrade: The melting of permafrost can cause settlement of the subgrade. Laying geotextile on top of permafrost can reduce heat transfer, delay permafrost melting, and discharge melted ice water to avoid subgrade softening.
Bridgehead/Culvert Back: The junction between the bridgehead, culvert, and roadbed is prone to "jumping" due to different compaction degrees of the filling material. Laying geotextile can enhance the overall integrity of the filling material, reduce settlement differences, and make driving smoother.
In summary, geotextile is not an optional auxiliary material in paving engineering, but a functional key material that runs through the roadbed, base layer, surface layer, and special road sections. It solves common problems such as settlement, cracking, and water damage in road construction from the source through core functions such as isolation, drainage, reinforcement, and crack resistance. It can not only improve the bearing capacity and stability of roads, but also significantly reduce maintenance costs in the later stage, making roads more durable and driving safer. It is a highly cost-effective practical solution in modern road construction