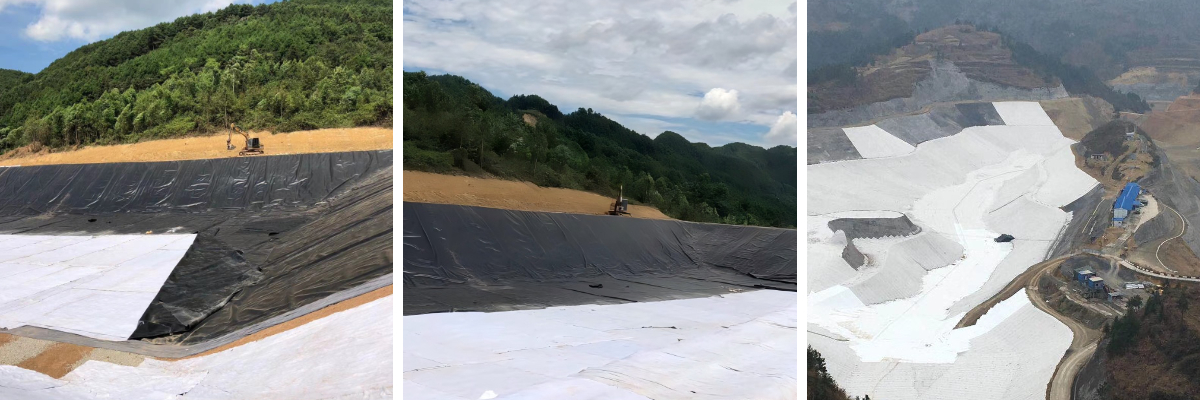
Best Geotextile Fabric
1.Good filtering performance:Accurate pore size, capable of blocking impurities, allowing water to flow, and avoiding engineering blockages.
2.Efficient drainage:Fiber structure forms channels to quickly drain excess water and reduce structural settlement.
3.Reliable isolation:Can separate different materials to prevent mixing and ensure the integrity of the engineering structure layering.
4.Strong reinforcement effect:High strength materials enhance soil tensile strength, improve structural load-bearing capacity, and reduce landslides.
5.Comprehensive protection:It can resist erosion from water flow, ultraviolet radiation, wear and tear, and extend the service life of the project.
Product Introduction
Basic attributes
The raw materials for Best Geotextile Fabric are mostly high molecular weight polymers with strong weather resistance and good chemical stability. Polypropylene has excellent corrosion resistance, while polyester has excellent tensile strength. After processing through spinning, needle punching, weaving and other techniques, permeable geosynthetic materials with uniform pores are formed. It is usually in the shape of a cloth, with a thickness that can be adjusted according to engineering needs, ranging from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters. It has good flexibility and can adapt to the laying needs of different terrains. The texture is lightweight, with a weight of between 100-600 grams per square meter, making it easy to transport, cut, and lay, greatly reducing labor costs during construction.
Core functions
Filtering: Its pore size is precisely designed to effectively prevent soil particles around the dam from infiltrating with water flow in the anti-seepage system of hydraulic engineering, while ensuring smooth passage of seepage and avoiding safety hazards such as pipe surges caused by dam blockage; In road construction, it can prevent roadbed soil from entering the graded gravel layer and maintain the stability of the roadbed structure.
Drainage: A continuous channel formed between fibers that can quickly drain accumulated water in slope engineering, reducing the damage to the slope caused by static water pressure; In underground engineering, the groundwater around the structure can be diverted to the drainage system to reduce the erosion of the structure by groundwater.
Reinforcement: High strength materials can disperse the load on soft soil foundation treatment, enhance the shear strength and overall stability of the foundation soil, and reduce foundation settlement; In retaining wall engineering, it works together with the wall to resist the lateral thrust of the soil and prevent the overturning of the retaining wall.
Main features
Reliable isolation: In railway subgrade construction, the crushed stones of the roadbed can be completely separated from the subgrade soil, avoiding the crushed stones from sinking into the subgrade soil or mixing with the crushed stones, ensuring the drainage and bearing capacity of the roadbed; In landfill engineering, different levels of anti-seepage materials and landfill materials can be separated to prevent harmful substances from infiltrating and contaminating each other.
Comprehensive protection: In river regulation projects, it can resist the erosion of water flow on the riverbank and protect the riverbank structure; In outdoor engineering, it can resist the aging damage of itself and the underlying materials caused by ultraviolet radiation, while reducing the wear and tear during mechanical construction, significantly extending the service life of the project, and generally extending the maintenance cycle of the project by 3-5 years.
Convenient construction: Due to its lightweight texture, the weight of a single roll is usually 50-100 kilograms, which can be easily transported manually. Cutting can be quickly completed with simple tools, and there is no need for complex splicing processes during the laying process, which can greatly improve the construction efficiency of the project. Compared with traditional materials, it can shorten the construction period by 20% -30%.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
Water conservancy engineering field
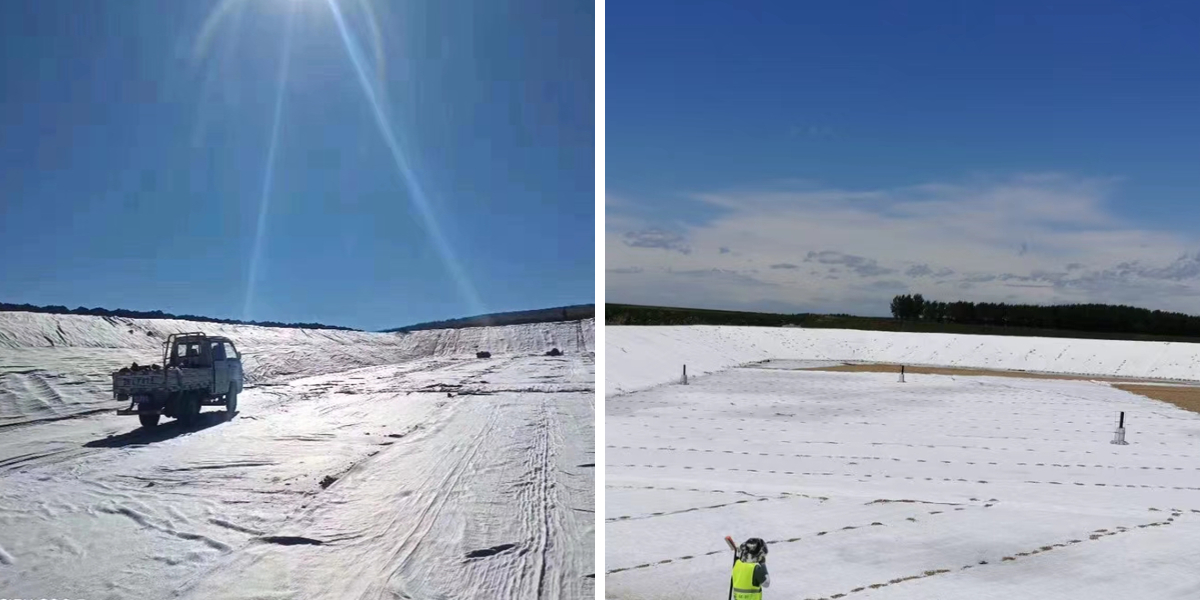
Geotextiles play a crucial role in hydraulic engineering. When constructing a dam, laying it inside and on the surface of the dam can utilize its filtering and isolation properties to prevent the mixing of dam soil and foundation soil, while also draining seepage from the dam, enhancing the stability of the dam, and effectively resisting the impact of natural disasters such as floods. In addition, in river regulation projects, geotextiles can protect riverbanks from water erosion, reduce soil erosion, and maintain the normal shape and function of the river.
Transportation construction field
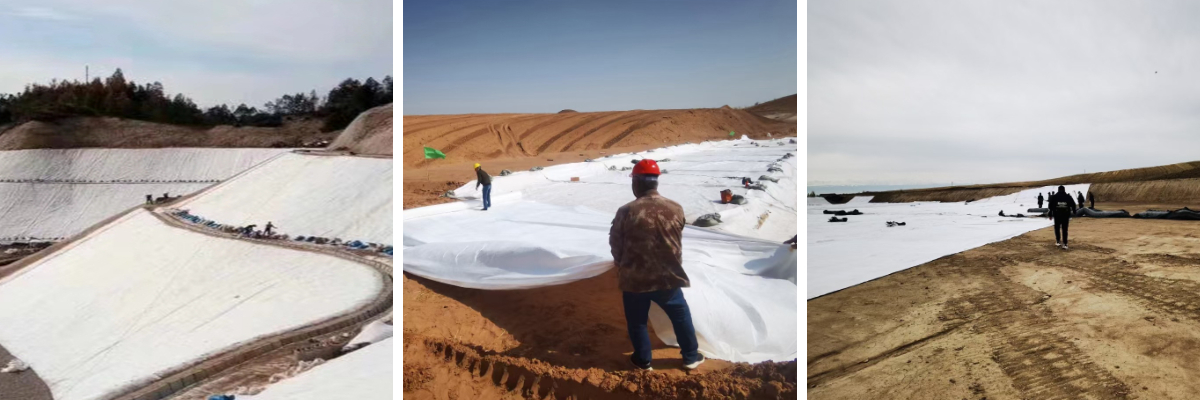
Transportation construction cannot do without the support of geotextiles. In highway construction, geotextiles are laid between the roadbed and the pavement to serve as isolation and reinforcement, avoiding mixing of roadbed soil and pavement materials, improving the bearing capacity of the roadbed, and reducing pavement settlement and cracking. In railway track laying, it can be used to isolate the track bed from the roadbed, prevent track bed particles from entering the roadbed, and ensure the stability and safety of the track. In airport runway construction, geotextiles can also enhance the strength and durability of runway foundations through drainage and reinforcement functions.
Municipal engineering field
Geotextiles are widely used in municipal engineering. In underground pipeline laying projects, laying geotextile around the pipeline can reduce the pressure of soil on the pipeline, prevent soil erosion around the pipeline, and protect pipeline safety. In the construction of landfill sites, geotextiles, as part of the anti-seepage system, can effectively isolate garbage from surrounding soil and groundwater, prevent environmental pollution caused by garbage leachate, and also play a drainage role in timely exporting and treating leachate.
Environmental protection field
In the field of environmental protection, geotextiles also have important applications. In the construction of artificial wetlands, it can serve as a cushioning material to prevent sewage from seeping into the ground, while providing a stable environment for the growth of wetland plants, helping to build wetland ecosystems and purify water quality. In soil remediation engineering, geotextiles can isolate contaminated soil from uncontaminated soil, prevent the spread of pollutants, and create favorable conditions for soil remediation work.
In summary, geotextiles, with their multiple characteristics such as filtration, drainage, reinforcement, isolation, and protection, are used to safeguard the stability of dams and rivers in hydraulic engineering, ensure the safety and durability of roads, railways, and airports in transportation construction, facilitate the smooth progress of various infrastructure in municipal engineering, and contribute to ecological protection and pollution control in the field of environmental protection. Its wide application not only effectively improves the quality and stability of various projects, but also extends the service life of projects, making it an indispensable and important material in modern engineering construction.