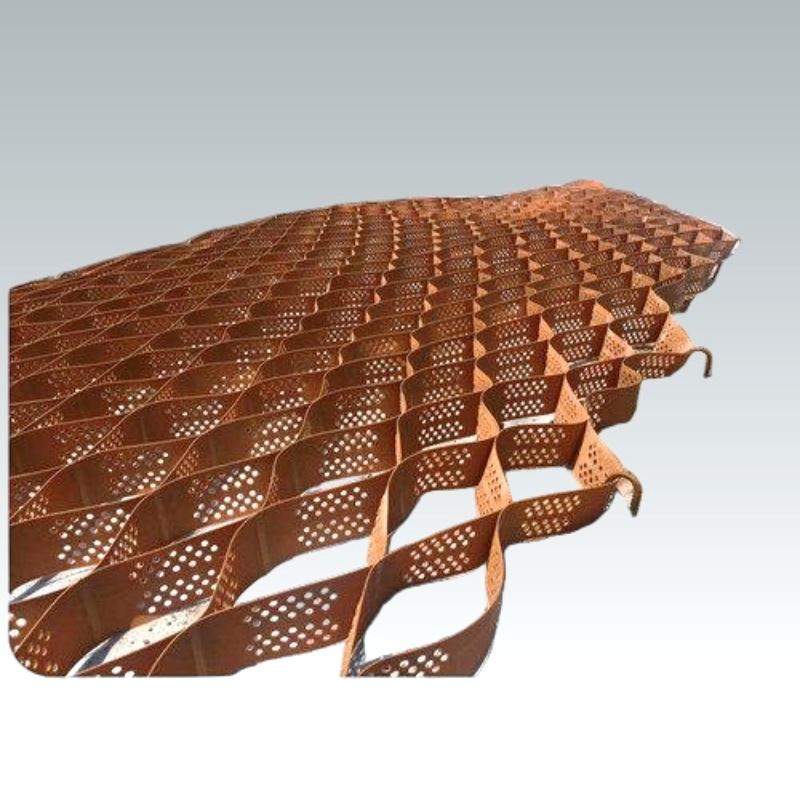
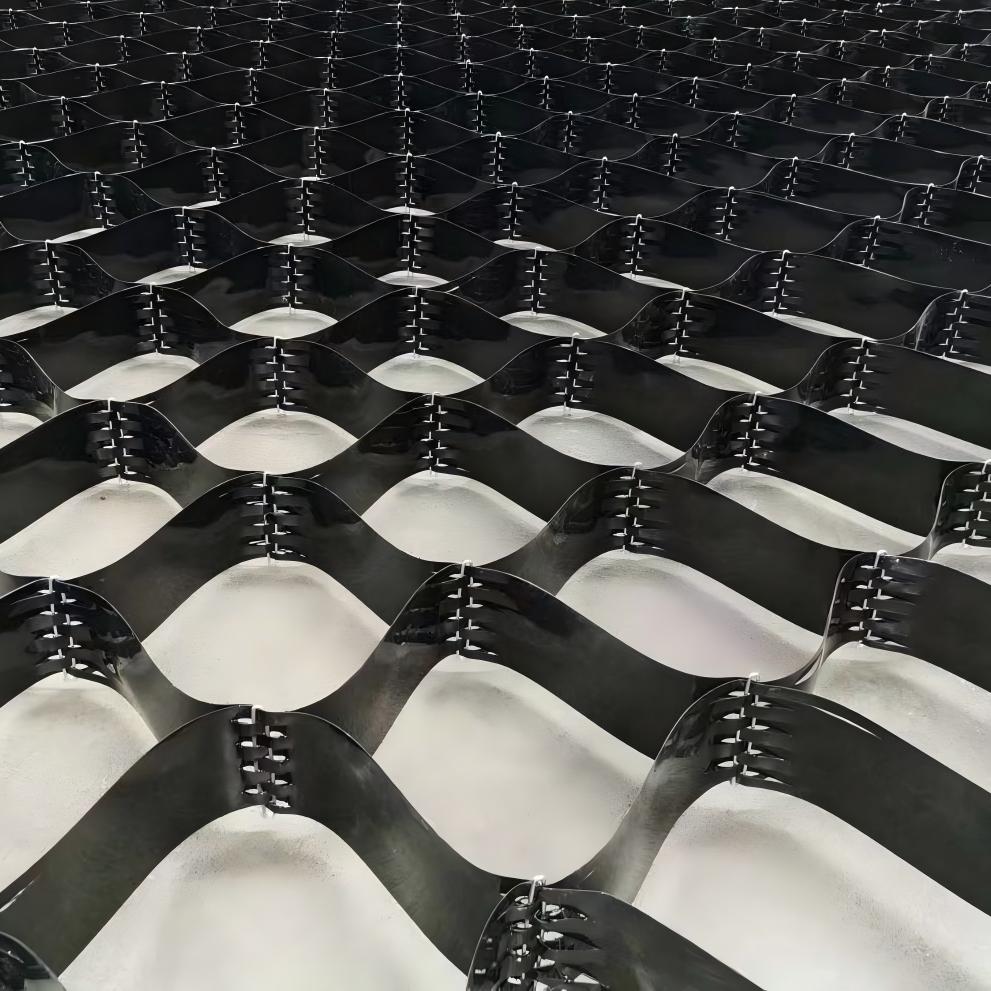
Cellular Confinement Systems
1.High-Efficiency Reinforcement
The three-dimensional honeycomb structure distributes loads effectively, significantly enhancing the bearing capacity and stability of foundations, slopes, and other engineering projects
2.Excellent Drainage and Flow Guidance
The grid space facilitates lateral drainage, reducing water pressure erosion on structures and effectively preventing soil erosion.
3.Convenient and Efficient Construction
Modular design allows for quick deployment and filling, greatly shortening construction time and reducing labor costs.
4.Strong Adaptability
Flexible structure accommodates complex terrains, resists frost heave and corrosion, ensuring long-term stability and durability.
Product Introduction:
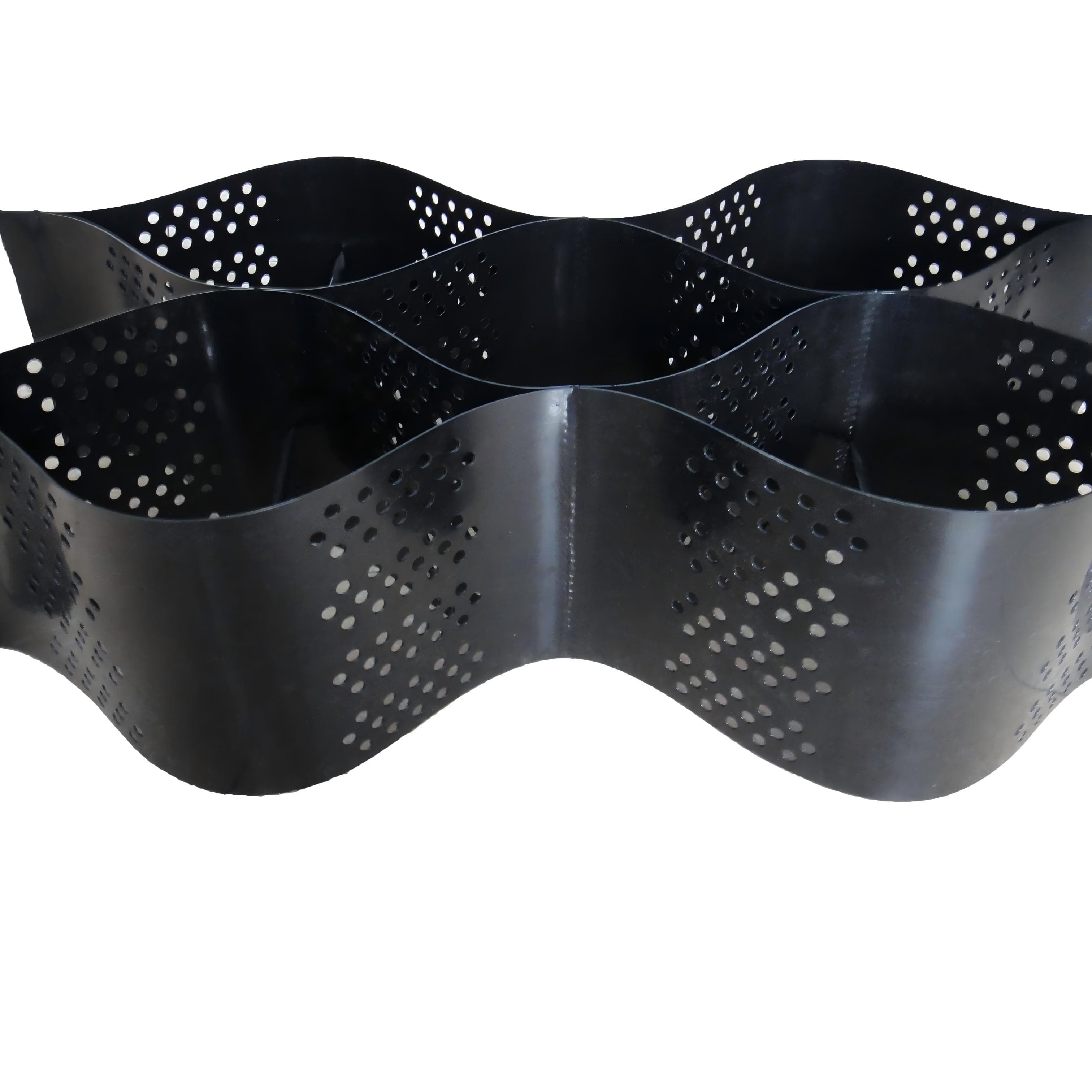
Cellular Confinement Systems are three-dimensional honeycomb-structured geosynthetic material made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), or other polymer materials through welding or riveting. When expanded, it forms a rigid, three-dimensional cellular network that can be filled with sand, soil, or other materials, making it widely applicable in civil engineering projects.
Structural Form:
High-strength sheets are connected into a honeycomb - like grid through welding or injection molding processes. The cell height is usually 50 - 500mm, and the grid size (side length) is 300 - 1000mm. The specifications can be adjusted according to engineering requirements. When unfolded, it presents a three - dimensional honeycomb shape. After filling with soil, stone, or concrete, it can form a rigid whole.
Material composition:
The main raw materials are HDPE or PP, which have the characteristics of chemical corrosion resistance, UV resistance (improved by additives), and aging resistance. The service life can reach 10 - 15 years (outdoor environment).
Biodegradable materials (such as PLA) or anti - aging additives can be added to optimize environmental friendliness or weather resistance.
Technical Advantages
Convenient Construction: It can be folded for transportation. After being unfolded on-site, filling materials can be formed, reducing the reliance on machinery and construction period.
Economical Cost: Compared with concrete slope protection or traditional retaining structures, it requires less material usage and is lightweight, reducing the comprehensive cost by 30% - 50%.
Eco - friendly: After filling with soil, plants can be planted, achieving the dual goals of engineering protection and ecological restoration.
Product Parameters:
order number | raw and processed material | |||||||
test item | unit | polytene | sulan | polyester | ||||
Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | Extruded type | Stretch type | |||
1 | tensile strength | kN/m | ≥20 | ≥100 | ≥23 | ≥100 | ≥30 | ≥120 |
2 | Tensile yield strain | % | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | — | ≤15 | - |
3 | Tensile fracture strain | % | — | 8~ 20 | — | 6~ 15 | — | 8~ 20 |
4 | Carbon black content a | % | 2. 0~ 3. 0 | |||||
5 | Carbon black dispersion a | — | There should be no more than one level 3 data item in ten data items and no level 4 or 5 data items | |||||
6 | 200℃ oxidation induction time | min | ≥20 | ≥20 | — | |||
7 | Tensile load stress cracking | h | ≥300 | — | ||||
8 | B. Resistance to artificial climate aging retention rateb | % | ≥80 | |||||
9 | Chemical resistance performance retention rate c | % | — | ≥80 | ||||
Product Applications:
1.Transportation Engineering
Subgrade reinforcement for highways/railways, foundation treatment for desert sections.
2.Water Conservancy Engineering
Riverbank slope protection, anti-scour protection for dams.
3.Slope Governance
Ecological protection for highway slopes, reinforcement of filler behind retaining walls.
4.Ecological Engineering
Sand fixation in deserts, construction of vegetation planting bases.
In conclusion, with its unique three - dimensional structure and versatility, the Cellular Confinement Systems has become a key material for enhancing soil performance in modern geotechnical engineering. It demonstrates significant advantages, especially in complex geological conditions and ecological engineering.