Geo Woven Fabric
1. Efficient drainage:Porous structure for quick drainage of accumulated water, reducing pore water pressure and preventing instability.
2. Reinforcing and stabilizing:Transmitting force constraints and deformation, and resisting settlement and sliding of strong foundation slopes.
3. Isolation and energy protection:Separate materials to prevent mixing and ensure stable drainage and load-bearing capacity of the structural layer.
4. Adapt to provincial capital:Lightweight, tough, easy to construct, corrosion-resistant, low maintenance, and cost-effective.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Geo Woven Fabric are permeable geosynthetic materials made from synthetic fibers such as polyester and polypropylene, processed through industrial processes such as needle punching, weaving, and thermal bonding. According to the process form, it can be divided into three categories: non-woven geotextile (such as short fiber/long fiber needle punched fabric), woven geotextile (such as woven fabric), and composite geotextile (multi-layer functional structure combination), which are commonly used functional materials in civil engineering.
2、 Core functions
Isolation: Separate building materials with different physical properties (such as soil, sand, and stone) to prevent material mixing and loss, and maintain structural layering stability.
Filtering: allowing water flow to pass through while effectively intercepting impurities such as soil particles and fine sand, avoiding structural failure caused by the loss of fine materials in water and soil engineering.
Drainage: By using fiber gaps to form internal water channels, excess liquids or gases in the soil can be quickly discharged, reducing the static water pressure of the structure.
Reinforcement: By enhancing the tensile strength and deformation resistance of soil through its own high strength characteristics, it improves the bearing stability of structures such as roadbeds and dams.
Protection: Disperse concentrated stresses such as water flow erosion and external impact, and protect soil or structures from erosion and damage.
3、 Main features
Stable performance: lightweight (unit area mass 100-1000g/m ²), high strength, able to maintain good mechanical properties in both dry and wet environments, suitable for complex working conditions.
Strong weather resistance: resistant to acid and alkali corrosion, resistant to microbial erosion, can be used for a long time in soil, water and other environments, and has a certain ability to resist UV aging.
Good functional adaptability: with controllable permeability, it can efficiently guide water and accurately filter, and different types of products can be selected according to engineering needs.
Convenient construction: The width is usually 4-9 meters, and the laying is flexible. It can be connected by overlapping, sewing or welding to meet the rapid construction needs of various engineering scenarios.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
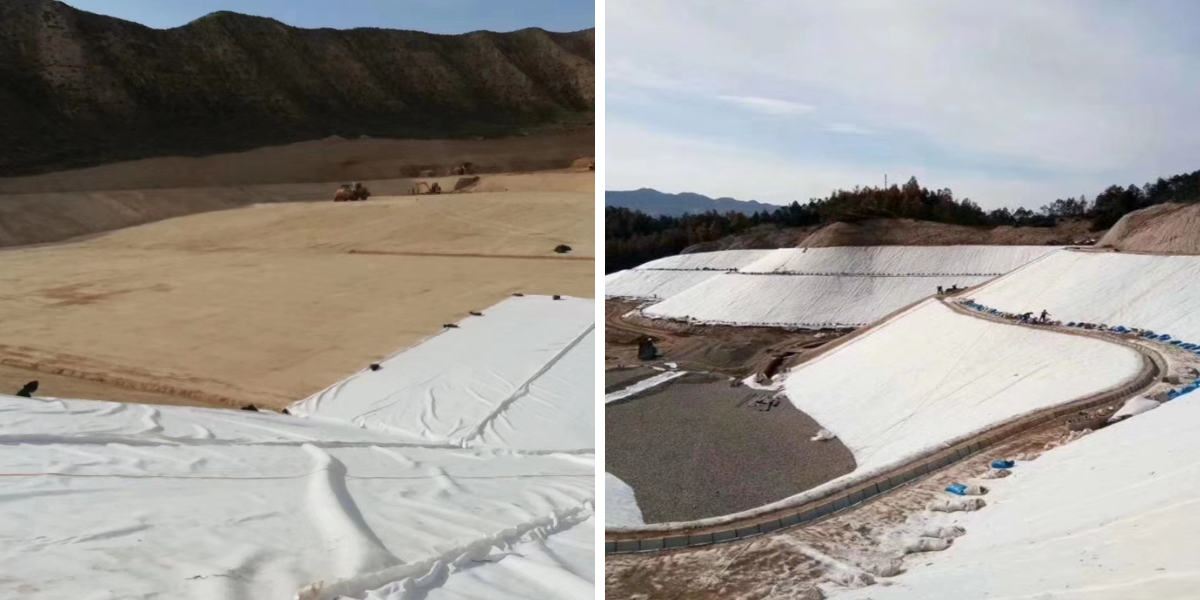
1、 Traffic engineering: Strengthening the stability of the roadbed
(1)Laying geotextile on railway subgrade to isolate fill soil from foundation soil and reduce uneven settlement.
(2)In highway pavement maintenance, enhancing the stability of the base layer and delaying pavement cracking problems.
(3)The foundation of the airport runway is reinforced with geotextile to enhance its bearing capacity and cope with the impact of aircraft takeoff and landing.
2、 Water conservancy engineering: strengthening protection and drainage efficiency
(1)Laying geotextile on the slope protection of river embankments to resist water erosion and prevent embankment collapse.
(2)In reservoir dam body and channel engineering, it serves as a filtering layer to guide the discharge of seepage and avoid pipe surges.
(3)In the mining beneficiation drainage system, slag impurities are filtered to ensure smooth drainage channels.
3、 Environmental engineering: Building anti-seepage and safety barriers
(1)In landfills, a composite layer of geomembrane is used to form an anti-seepage layer, preventing leachate from contaminating soil and groundwater.
(2)Geotextile is laid in the sewage treatment tank to enhance the stability of the anti-seepage structure, while intercepting sludge particles to improve treatment efficiency.
4、 Municipal engineering: adapting to diverse scene requirements
(1)The drainage layer of the underground garage roof uses geotextile to divert accumulated water and protect the structure from immersion.
(2)Laying geotextile in green belts can suppress weed growth while maintaining soil permeability.
(3)During the renovation and expansion of urban roads, it is used to isolate and reinforce the connection between new and old road surfaces, reducing the difference in settlement.
5、 Agricultural Engineering: Supporting Efficient Production and Operation
(1)Laying geotextile in farmland drainage ditches to filter sediment, prevent clogging, and improve drainage efficiency.
(2)The foundation of the greenhouse is reinforced with geotextile to prevent soil deformation from causing the greenhouse to tilt.
(3)In irrigation channels, reducing the erosion of water flow on the channel walls and extending the service life of the channel.
Geotextiles play an irreplaceable role in transportation, water conservancy, environmental protection, municipal administration, agriculture, and other fields due to their multifunctional characteristics of isolation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement, and protection. It can not only improve the stability and durability of engineering structures, reduce maintenance costs, but also contribute to sustainable engineering construction through its eco-friendly characteristics, becoming a key material for ensuring safety and improving efficiency in modern civil engineering.