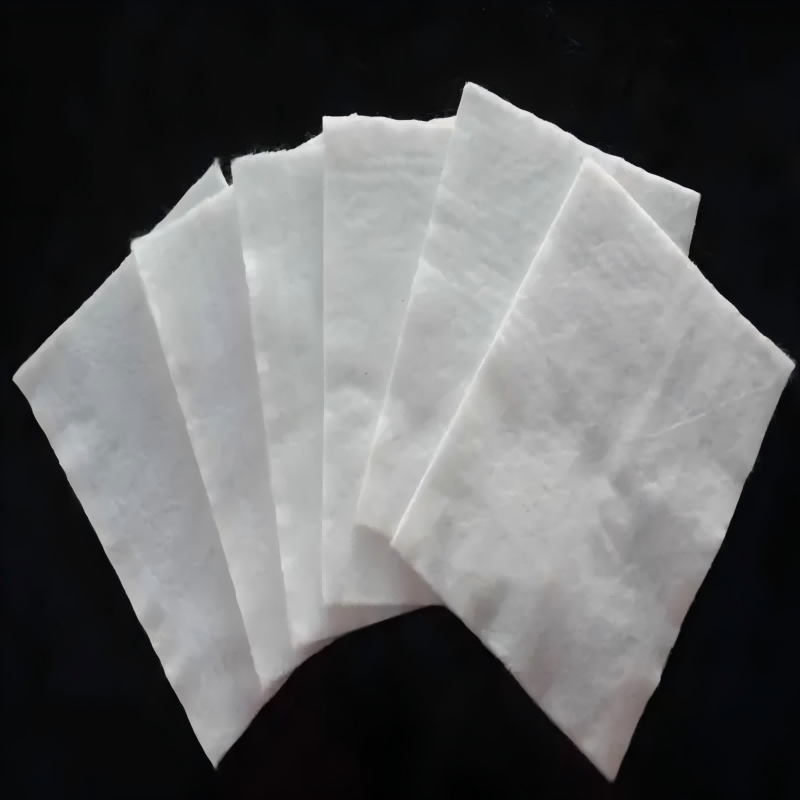
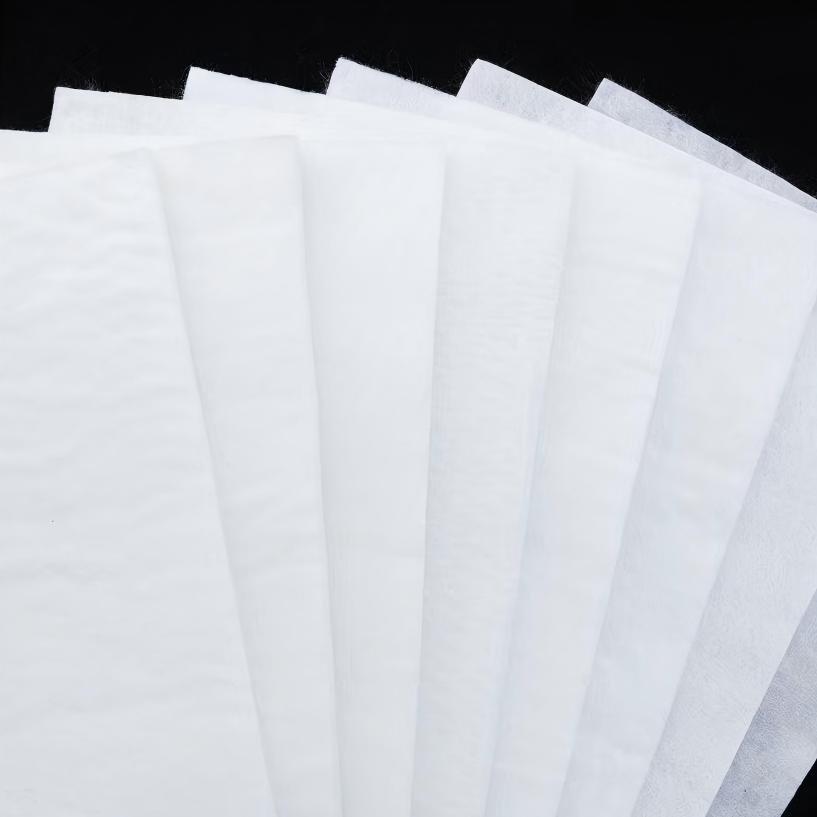
Geotextile Pavers
1.Good filtration: Micro porous solid fast water seepage, no blockage and stable effect;
2.High strength: Polymer material with tensile and tear resistance, compression and impact resistance, not easily broken;
3.Wide adaptability: The pore thickness can be customized, which is compatible with various types of sludge and can resist aging and corrosion;
4.Cost saving: Controllable cost, long lifespan, lightweight and easy to operate, no need for frequent replacement.
Product Introduction
1、 Basic attributes
Material: Geotextile Pavers are mainly made of polypropylene, polyester and other high molecular polymers, some of which contain anti-aging and anti-corrosion composite coatings;
Form: mostly in the form of sheet or tubular fabrics, customizable thickness and aperture, lightweight texture, easy to transport and store in an empty state;
Positioning: Special geotextile materials for environmental protection and infrastructure fields, serving as the core substrate for geotextile bags, anti-seepage engineering, and more.
2、 Core functions
Filtration and separation: solid particles (such as sludge impurities) are intercepted through a microporous structure, while liquids (such as sludge moisture) are quickly released to achieve solid-liquid separation;
Structural support: With its tensile and tear resistance, it can withstand external compression and impact, providing stable structural support for the load-bearing material (such as sludge inside the bag) to avoid deformation and damage;
Environment adaptation: anti-aging and anti-corrosion materials can adapt to outdoor, high pollution and other complex environments, and extend the service life.
3、 Main features
Efficient and practical: fast filtration speed and not easily clogged, strong support, can quickly meet the needs of solid-liquid separation and structural protection;
Flexible adaptation: The aperture and thickness can be customized according to needs, compatible with different treatment objects such as sludge, mud, water, etc., with a wide range of scene adaptability;
Economic durability: controllable raw material costs, long service life (able to support a single complete processing cycle), no need for frequent replacement, reducing application costs.
Product Parameters
project | metric | ||||||||||
Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Application
1、 Environmental protection treatment field
Sludge dewatering carrier: As the core substrate of wastewater sludge dewatering bags (geotextile bags), it is used for sludge treatment in municipal sewage plants and industrial enterprises. Through a microporous structure, it intercepts sludge solids and seeps out water, helping to reduce sludge volume (such as converting dilute sludge with a moisture content of over 90% into sludge cake with a solid content of 30% -60%), and reducing subsequent disposal costs.
Wastewater filtration treatment: used for small-scale wastewater treatment equipment and river water purification projects, it can intercept suspended impurities and particulate pollutants in water, improve water quality transparency, and allow clear water to permeate, avoiding secondary pollution.
2、 In the field of water conservancy and infrastructure engineering
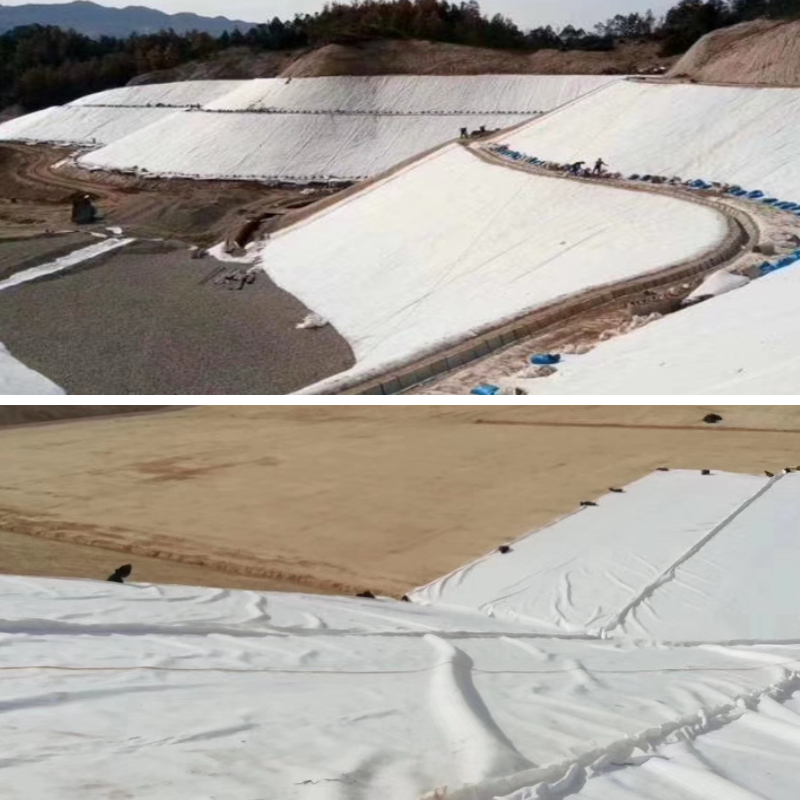
Embankment/roadbed anti-seepage: laid on the inner side of the embankment and below the roadbed, using its anti-seepage properties (partially composite anti-seepage coating geotextile) to block water infiltration, prevent embankment leakage and roadbed settlement, and improve the stability of the engineering structure; At the same time, it can filter soil particles to avoid soil erosion and blockage of the anti-seepage layer.
Dredging and land reclamation projects: In port channel dredging and land reclamation projects, it is used to treat dredging mud. After dehydration, the dry mud can be directly used for land reclamation, roadbed filling, filtered water recycling and reuse, reducing the occupation of engineering waste soil on the environment.
Road/Slope Protection: Installed between the base and surface layers of the road, or on the surface of the slope soil, it can disperse road loads, prevent soil cracking, filter rainwater, maintain soil moisture, avoid soil erosion on the slope, and extend the service life of the road and slope.
3、 Agriculture and Ecology
Irrigation filtration in farmland: used in irrigation channels and drainage systems to filter sediment and impurities in water, prevent blockages in irrigation pipelines, protect soil structure in farmland, and reduce soil nutrient loss.
Ecological restoration engineering: In mining greening and wetland restoration projects, it is laid on the soil surface or under vegetation to fix the soil, filter precipitation, provide a stable environment for plant growth, and prevent the spread of soil pollution in the restoration area.
Geotextiles, with their core capabilities of filtration, anti-seepage, support, and protection, have been deeply integrated into three major fields: environmental protection treatment, water conservancy infrastructure, and agricultural ecology. They have become key materials for solving problems such as solid-liquid separation, structural stability, and ecological protection. It can not only meet the environmental protection needs of sludge dewatering and sewage purification, but also ensure the safety of dam embankments, reduce engineering soil pollution, and assist in the efficient operation and ecological restoration of agricultural water conservancy. It has practicality and multifunctionality, adapts to the differentiated needs of different scenarios, and plays an irreplaceable role in green development and engineering construction.