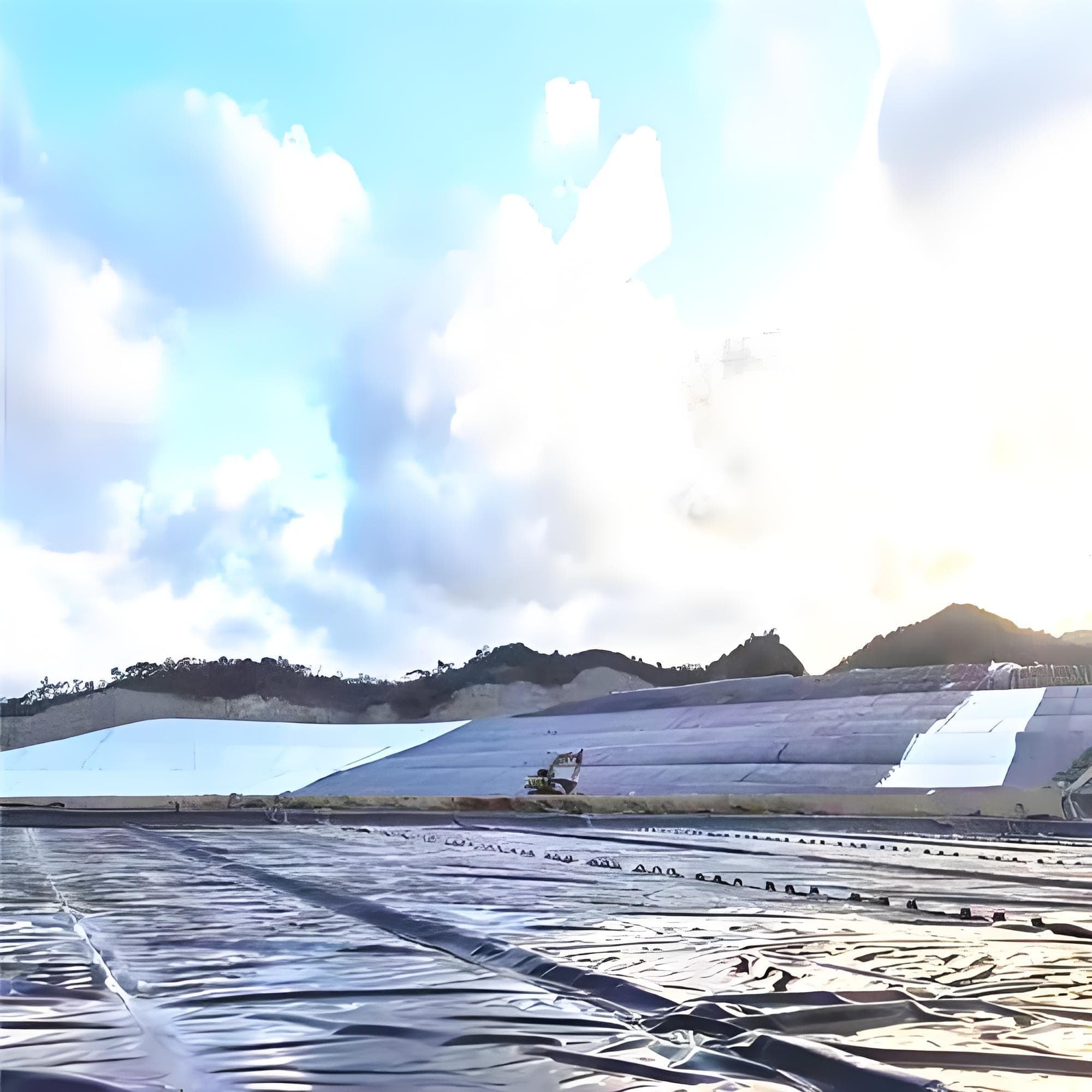
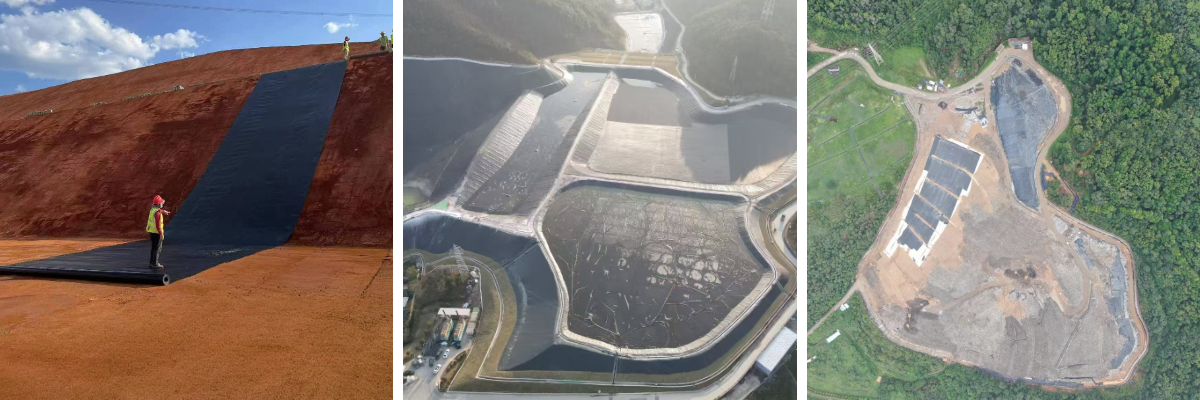
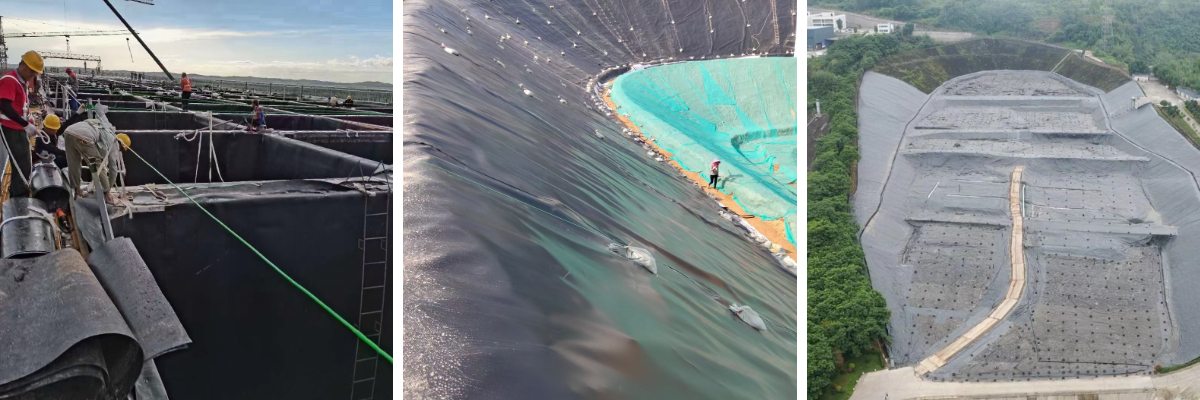
Terpal HDPE Geomembrane
1.High Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to traditional impermeable materials (such as concrete or clay), geomembranes offer faster construction speeds and lower costs.
2.Flexible Construction:
Geomembranes can be cut and spliced according to engineering requirements, making them adaptable to complex terrains.
3.Environmentally Friendly:
Geomembrane materials are non-toxic and harmless, meeting environmental protection standards.
4.Low Maintenance:
With a long service life, geomembranes require minimal maintenance, resulting in low long-term costs.
Product Introduction:
Terpal HDPE Geomembrane is a flexible waterproof barrier material manufactured using high-molecular-weight polymers (such as polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, etc.) as basic raw materials through processes like blow molding, calendering, or casting.
Product Performance
1.Impermeability
The impermeability coefficient of geomembranes can reach below 1×10−13cm/s, effectively preventing the penetration of liquids and gases.
2.Mechanical Properties
Tensile Strength: The tensile strength of HDPE geomembranes can exceed 27MPa.
Elongation at Break: The elongation at break of LDPE and LLDPE geomembranes can exceed 700%, demonstrating strong adaptability to foundation deformation.
3.Chemical Resistance
Geomembranes can resist erosion from various chemical substances, including acids, alkalis, and salts, making them suitable for corrosive environments such as landfills and chemical tanks.
4.Aging Resistance
After the addition of UV stabilizers and antioxidants, the service life of geomembranes can exceed 50 years.
5.Environmental Adaptability
Geomembranes have a wide operating temperature range. HDPE geomembranes can be used long-term in environments ranging from −70∘C to 70∘C.
Product Parameters:
| Metric | ASTM | unit | Test value | Minimum test frequency | ||||||
| test method | 0.75 mm | 1.00 mm | 1.25 mm | 1.50 mm | 2.00 mm | 2.50mm | 3.00 mm | |||
| Minimum average thickness | D5199 | mm | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | Per volume |
| Minimum value (any one of 10) | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | -10% | |||
| minimum density | D 1505/D 792 | g/cm3 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 90,000 kg |
| Minimum average tensile performance (1) | D638 Type IV | |||||||||
| Breakage strength, | N/mm | 20 | 27 | 33 | 40 | 53 | 67 | 80 | 9,000 kg | |
| yield strength | N/mm | 11 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 29 | 37 | 44 | ||
| Strain extension, | % | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | ||
| yield extension | % | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | ||
| Minimum strength of right-angle tear | D 1004 | N | 93 | 125 | 156 | 187 | 249 | 311 | 374 | 20,000 kg |
| Minimum puncture strength | D4833 | N | 240 | 320 | 400 | 480 | 640 | 800 | 960 | 20,000 kg |
| Constant tensile load stress cracking (2) | D5397 | hour | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | Based on GRI GM-10 |
| Carbon black content | D 1603(3) | % | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 9,000 kg |
| Carbon black dispersion | D5596 | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | Note (4) | 20,000 kg | |
| Oxygen induction time (OIT) (5) | 90,000 kg | |||||||||
| (a) Standard OIT | D3895 | minute | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| (b) high-handed OIT | D5885 | minute | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | |
| 85℃ Oven aging (minimum average) (5)(6) | Per formula | |||||||||
| (A) Standard OIT is retained after 90 days | D 5721 | % | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | |
| (B) High voltage OIT is retained for 90 days | D 3895 D5885 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | |
| Ultraviolet resistance (7) | Per formula | |||||||||
| (a) standard OIT | D3895 | Note (8) 50 | ||||||||
| (b) Retention of high pressure OIT after 1600 hours (9) | D5885 | % | ||||||||
Product Applications:
1.Environmental Protection Engineering
Landfills: Geomembranes are used as impermeable liners for the base and slopes to prevent leachate from contaminating groundwater.
Hazardous Waste Treatment Sites: They isolate harmful substances to protect the environment.
2.Water Conservancy Engineering
Reservoirs and Dikes: Geomembranes prevent seepage, improving water resource utilization efficiency.
Canals and Water Channels: They reduce seepage losses during water conveyance.
3.Municipal Engineering
Subways and Tunnels: Geomembranes serve as impermeable linings to prevent groundwater infiltration.
Basements and Roof Gardens: They provide waterproofing and moisture resistance to protect building structures.
4.Agriculture and Aquaculture
Artificial Lakes and Aquaculture Ponds: Geomembranes prevent water seepage, maintaining stable water levels.
Salt Pans and Water Storage Ponds: They enhance the efficiency of water resource storage.
5.Mining and Energy
Tailings Ponds and Heap Leach Pads: Geomembranes prevent wastewater seepage, protecting soil and water bodies.
Oil Storage Tanks and Chemical Plants: They act as impermeable liners to prevent oil and chemical leaks.