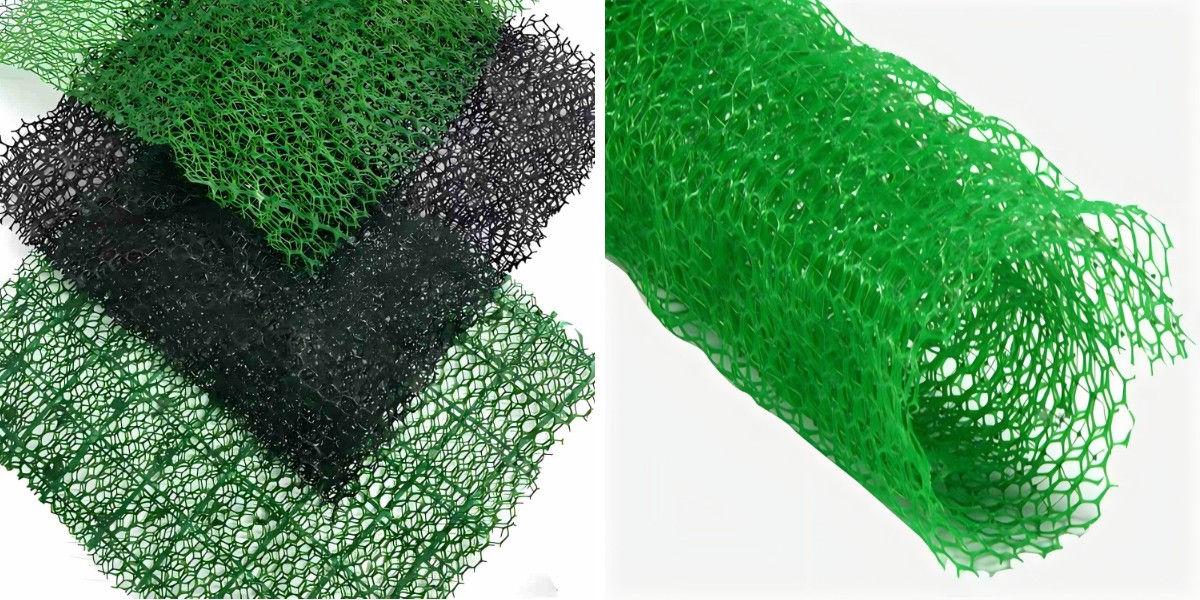
Highway & DOT Projects: Heavy-Duty Specifications for Roadside Slopes
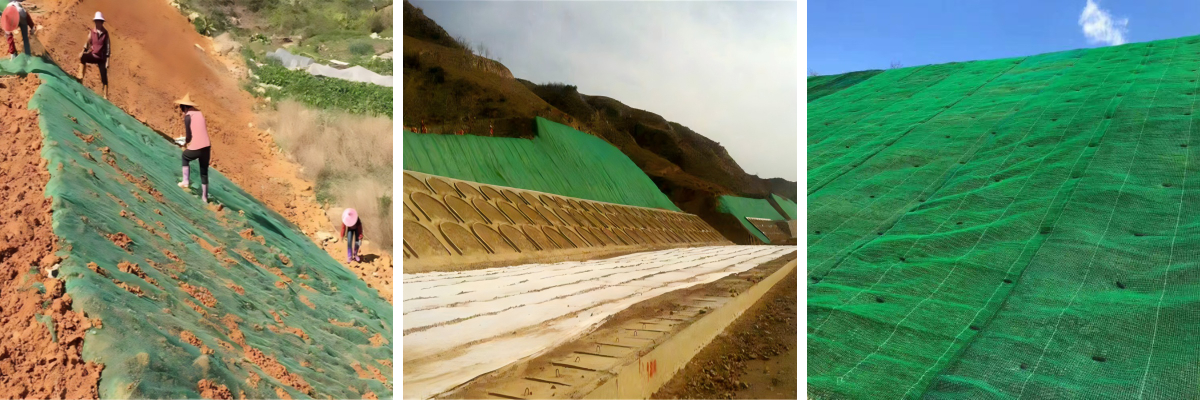
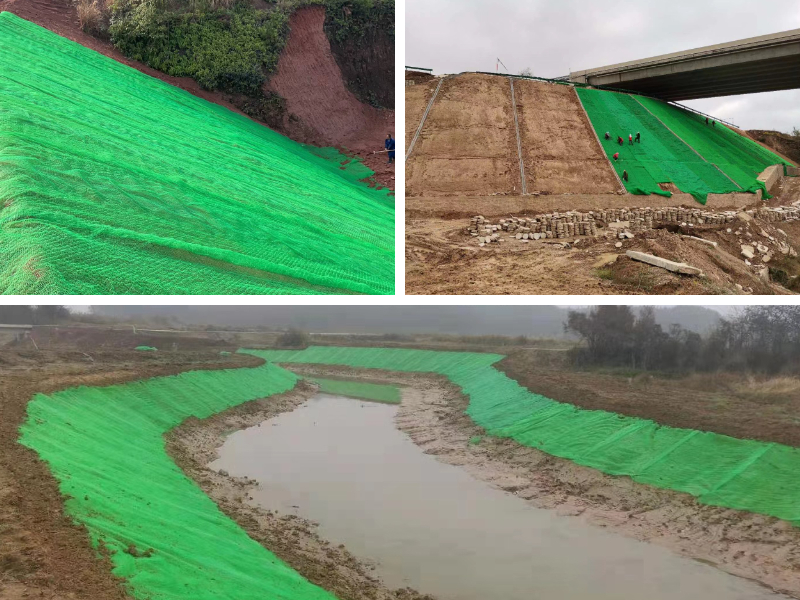
Roadside slopes are fundamental elements of dual carriageway infrastructure, tasked with stopping erosion, stabilizing soil, and making sure driver safety. Department of Transportation (DOT) tasks demand heavy-duty options that can face up to excessive weather, heavy site visitors vibrations, and long-term environmental stress. Traditional slope stabilization methods—such as concrete maintaining partitions or rock riprap—often fall quick in phrases of cost, environmental impact, or adaptability. Enter 3D Vegetation Net Specifications: engineered options that mix structural reinforcement with ecological benefits. By perception Dimensions of 3D Vegetation Net and studying how to Lay 3D vegetation internet correctly, DOTs and contractors can create roadside slopes that meet strict overall performance requirements whilst mixing with the surrounding landscape. This information explores the function of 3D vegetation nets in toll road projects, their heavy-duty specifications, set up quality practices, and why they’re turning into a staple in DOT slope stabilization initiatives.
The Unique Challenges of Highway Roadside Slopes
Highway roadside slopes face a special set of stressors that require strong stabilization:
Traffic-Induced Vibrations: Heavy vehicles and regular visitors generate vibrations that loosen soil, growing erosion risk.Extreme Weather: Intense rainfall, snowmelt, and excessive winds reason floor erosion, gullying, and slope failure.Environmental Regulations: DOTs should comply with strict policies to guard nearby ecosystems, limiting the use of harsh, non-vegetative stabilization methods.Maintenance Constraints: Roadside slopes are challenging to get admission to for repairs, so options have to be low-maintenance and long-lasting.
These challenges require a stability of strength, flexibility, and ecological compatibility—qualities that 3D Vegetation Net Specifications are designed to deliver.
3D Vegetation Net Specifications: Meeting DOT Heavy-Duty Standards
3D Vegetation Net Specifications are engineered to exceed DOT necessities for toll road slope stabilization. These artificial or herbal fiber nets function a 3-dimensional shape that traps soil, helps vegetation growth, and reinforces slope integrity. Key heavy-duty specs include:
1. Material Durability
DOT-approved 3D vegetation nets are made from high-strength substances like polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), or coir (coconut fiber) handled with UV inhibitors. PP/PE nets withstand UV degradation, chemical publicity (e.g., de-icing salts), and organic breakdown, making sure a lifespan of 10–20 years. Coir nets, whilst biodegradable, are dealt with to remaining 3–5 years—long adequate for vegetation to set up and take over slope stabilization.
2. Tensile Strength
Heavy-duty 3D vegetation nets boast excessive tensile power (both longitudinal and transverse) to face up to slope movement and erosion forces. DOT specs commonly require a minimal tensile power of [X] kN/m, making sure the internet doesn’t tear below stress from water runoff or soil settlement.
3. Porosity and Water Permeability
To forestall waterlogging (a primary motive of slope failure), 3D Vegetation Net Specifications consist of excessive porosity. The net’s open shape permits water to infiltrate the soil whilst trapping sediment, decreasing floor runoff and erosion. This permeability aligns with DOT stormwater administration guidelines, defending close by waterways from sedimentation.
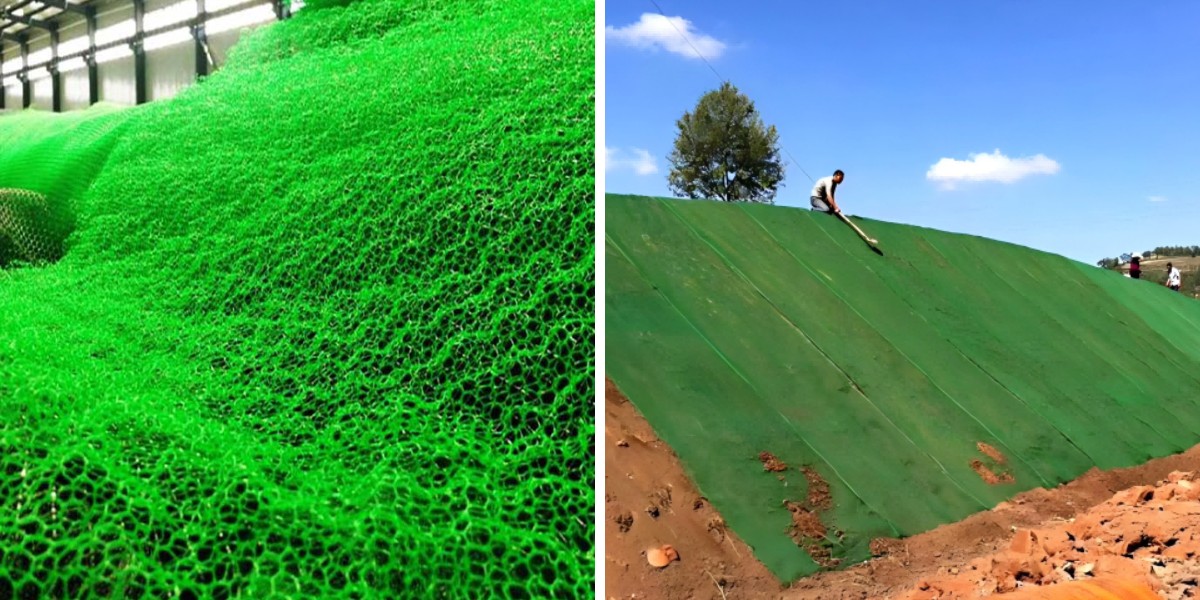
Dimensions of 3D Vegetation Net: Tailoring to Highway Slopes
Dimensions of 3D Vegetation Net fluctuate based totally on slope steepness, soil type, and DOT assignment requirements. Choosing the proper dimensions ensures choicest performance:
1. Roll Size and Coverage
3D vegetation nets are reachable in rolls of widespread widths (2–4 meters) and lengths (50–100 meters), making them convenient to transport and deploy on dual carriageway sites. The insurance location per roll is calculated to reduce seams, as overlapping sections can create vulnerable points. For steep slopes (≥3:1), wider rolls are favored to minimize the quantity of horizontal seams, which are greater inclined to erosion.
2. Thickness and Height
The net’s thickness (or height) tiers from 5–15 cm. Thicker nets (10–15 cm) are used for steep, unstable slopes, as they supply increased soil confinement and vegetation support. Thinner nets (5–8 cm) work nicely on mild slopes or as a secondary reinforcement layer. DOTs regularly specify thickness primarily based on slope gradient: steeper slopes require taller nets to forestall soil displacement.
3. Mesh Size
Mesh dimension (the distance between internet fibers) usually levels from 10–20 mm. Smaller mesh sizes (10–15 mm) are perfect for fine-grained soils, as they entice smaller sediment particles. Larger mesh sizes (15–20 mm) go well with coarse-grained soils, permitting for higher water infiltration whilst nevertheless supplying reinforcement. Dimensions of 3D Vegetation Net are frequently personalized to in shape the soil texture of the motorway task site.
How to Lay 3D Vegetation Net: DOT-Compliant Installation
Proper set up is integral to maximizing the effectiveness of 3D vegetation nets. DOTs require strict adherence to set up protocols to make certain slope stability:
1. Site Preparation
Before putting in the net, put together the slope by using clearing debris, rocks, and vegetation. Grade the slope to create a uniform surface, and restore any present erosion gullies with compacted soil. For unstable soils, add a layer of topsoil or compost to enhance vegetation growth. Ensure the slope has suitable drainage (e.g., French drains) to stop water buildup.
2. Unroll and Position the Net
To Lay 3D vegetation net, begin at the pinnacle of the slope and unroll the internet downward, making sure it lies flat towards the soil. Avoid stretching the net, as anxiety can purpose tearing for the duration of set up or after vegetation growth. For multi-roll installations, overlap adjoining nets via 30–50 cm (more for steep slopes) to create a non-stop barrier. Secure the overlap with UV-resistant staples or pins to stop separation.
3. Anchor the Net
Anchor the internet the usage of biodegradable or steel staples (depending on DOT specifications) positioned each and every 30–50 cm alongside the edges and seams. For steep slopes, use longer anchors (20–30 cm) to penetrate deeper into the soil, stopping the internet from shifting. At the pinnacle of the slope, bury the internet aspect in a 30–40 cm deep anchor trench stuffed with compacted soil—this prevents water from seeping below the internet and inflicting erosion.
4. Seed and Mulch
After putting in the net, broadcast native grass or wildflower seeds over the slope. The 3D shape traps the seeds, stopping them from washing away. Cover the seeds with a skinny layer of straw or timber mulch to preserve moisture and speed up germination. DOTs regularly specify native vegetation to aid neighborhood ecosystems and minimize protection needs.
Benefits of 3D Vegetation Nets for DOT Highway Projects
3D vegetation nets provide a vary of blessings that make them perfect for dual carriageway and DOT slope stabilization:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to concrete partitions or rock riprap, 3D vegetation nets are drastically greater affordable. They require much less labor and gear to install, and their low-maintenance format reduces long-term costs. DOTs document financial savings of 30–50% when the usage of 3D vegetation nets rather of normal methods.
2. Environmental Compliance
3D Vegetation Net Specifications prioritize ecological compatibility. The nets guide vegetation growth, which improves air quality, reduces warmness island effects, and gives habitat for wildlife. This aligns with DOT environmental mandates to reduce the affect of toll road tasks on nearby ecosystems.
3. Long-Term Stability
Once vegetation establishes, the root machine works with the internet to create a natural, self-sustaining slope stabilization system. The roots bind the soil, whilst the internet presents structural reinforcement—ensuring long-term steadiness even in harsh conditions. DOTs have documented slopes stabilized with 3D vegetation nets that have withstood predominant storms besides erosion.
Conclusion: 3D Vegetation Nets—The DOT’s Choice for Roadside Slopes
3D Vegetation Net Specifications, paired with perfect Dimensions of 3D Vegetation Net and right set up strategies to Lay 3D vegetation net, are revolutionizing dual carriageway slope stabilization. These heavy-duty options meet DOT overall performance requirements whilst providing fee savings, environmental benefits, and long-term durability.
For DOTs and contractors tasked with constructing and preserving safe, resilient highways, 3D vegetation nets are extra than simply a stabilization method—they’re an funding in sustainable infrastructure. By selecting the proper specifications, tailoring dimensions to venture needs, and following set up pleasant practices, you can create roadside slopes that guard drivers, help ecosystems, and stand the take a look at of time. As toll road initiatives proceed to prioritize security and sustainability, 3D vegetation nets will stay a integral device in the DOT toolkit.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province