Geotextile Permeable
1.High water permeability: It can quickly drain water, avoid waterlogging, and is suitable for drainage scenarios.
2.High tensile strength: It is not easy to break, can withstand a certain load, and is suitable for engineering environments.
3.Good durability: It is resistant to corrosion and ultraviolet rays, and has a long service life.
4.Convenient construction: Lightweight, easy to lay, saving time and labor costs.
5.Good filtering performance: Can block soil particles, ensure smooth water flow and prevent blockage.
Product Introduction:
Geotextile Permeable is a geosynthetic material with water permeability and filtration functions. It is mainly made of synthetic fibers (such as polyester, polypropylene, etc.) through processes such as needle punching, weaving, or hot pressing. Its core characteristics are the combination of "permeability" and "blocking" functions.
Core Features
Water Permeability: The material has a large number of interconnected pores inside, allowing water to penetrate quickly. It is suitable for drainage and water - guiding scenarios.
Filtration: The fiber structure can prevent the loss of particles such as soil and sand, while ensuring smooth water flow and avoiding blockages.
Structure and Material
Material: Commonly used polymer materials such as polyester (PET) and polypropylene (PP) are resistant to chemical corrosion, ultraviolet rays, and have strong durability.
Structure: Mostly needle - punched non - woven fabric or woven fabric, with a high and evenly distributed porosity, taking into account both water permeability and mechanical strength.
Main functions
Drainage and water conduction: Quickly drain the water in the soil, reduce the pore water pressure, and prevent damage caused by waterlogging.
Filtration and isolation: Separate soil layers of different particle sizes, prevent the loss of fine particles, and maintain structural stability.
Reinforcement and protection: Have a certain tensile strength, can enhance the integrity of the soil, and resist external scouring or loads.
Product Parameters:
project | metric | ||||||||||
| Nominal strength/(kN/m) | |||||||||||
| 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |||
| 1 | Longitudinal and transverse tensile strength / (kN/m) ≥ | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 54 | |
| 2 | Maximum elongation at maximum load in longitudinal and transverse directions/% | 30~80 | |||||||||
| 3 | CBR top penetration strength /kN ≥ | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.5 | |
| 4 | Longitudinal and transverse tearing strength /kN | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.25 | |
| 5 | Equivalent aperture O.90(O95)/mm | 0.05~0.30 | |||||||||
| 6 | Vertical permeability coefficient/(cm/s) | K× (10-¹~10-), where K=1.0~9.9 | |||||||||
| 7 | Width deviation rate /% ≥ | -0.5 | |||||||||
| 8 | Unit area mass deviation rate /% ≥ | -5 | |||||||||
| 9 | Thickness deviation rate /% ≥ | -10 | |||||||||
| 10 | Thickness coefficient of variation (CV)/% ≤ | 10 | |||||||||
| 11 | Dynamic perforation | Puncture hole diameter/mm ≤ | 37 | 33 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
| 12 | Longitudinal and transverse fracture strength (grab method)/kN ≥ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
| 13 | Ultraviolet resistance (Xenon arc lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 70 | ||||||||
| 14 | Ultraviolet resistance (fluorescence UV lamp method) | Longitudinal and transverse strength retention rate% ≥ | 80 | ||||||||
Product Applications:
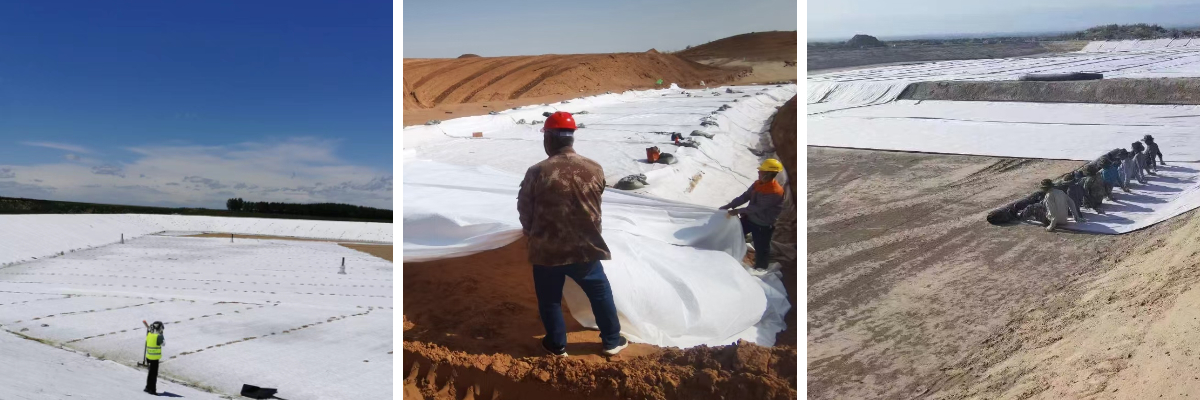
Water Conservancy Projects
Dike and Riverbank Protection: Laid on the surface of dikes or riverbanks, it blocks the scouring of water flow, drains internal water accumulation, and reduces seepage pressure, such as the dike protection in the Yellow River Basin and the Yangtze River channel regulation project.
Reservoir and Channel Seepage Prevention: As a seepage prevention layer, it reduces water seepage, or is used for drainage at the bottom of the reservoir to maintain the stability of the dam body.
River Channel Dredging and Regulation: Laid on the riverbed, it filters the water in the silt, assists in dredging construction, and prevents riverbank collapse at the same time.
Traffic Engineering
Subgrade Drainage and Reinforcement: Laid beneath the subgrade or on the slope, it drains groundwater and rainwater to avoid subgrade settlement; enhances the tensile strength of the soil to prevent road surface cracking.
Tunnel and Culvert Seepage Prevention: Used around tunnel linings or culverts, it filters and guides the seepage water to reduce the risk of structural leakage.
Environmental Engineering
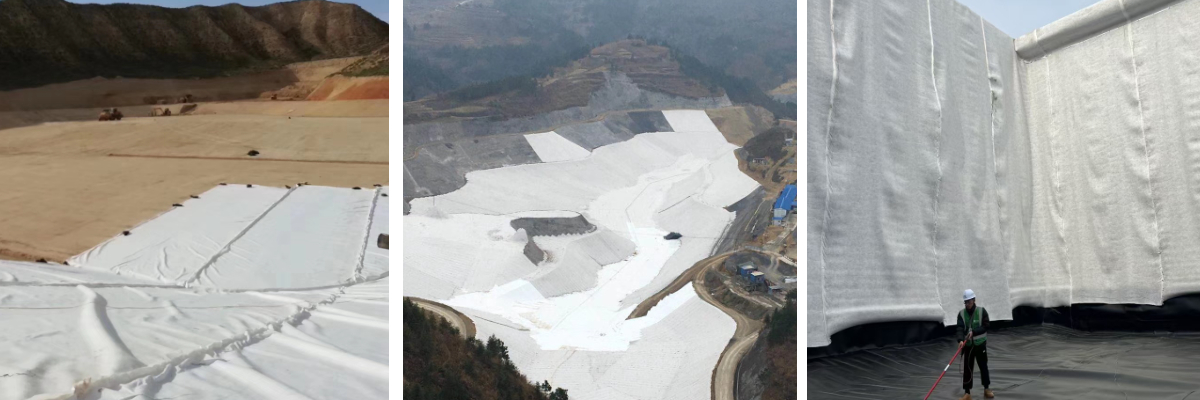
Landfill Seepage Control: Used in conjunction with seepage-proof membranes, it filters impurities in leachate, prevents soil pollution, and simultaneously assists the operation of the drainage system.
Sewage Treatment Tank: As a filter layer, it separates solid particles in sewage, improves treatment efficiency, and reduces equipment blockages.
Municipal Engineering
Urban Drainage System: Used as a filter layer in the stormwater pipeline network to block debris from entering the pipeline, reducing the risk of blockage; or assist in drainage in low - lying areas.
Greening Project: Laid in rooftop gardens and green belts, it drains water while retaining soil nutrients to support plant growth.
Agriculture and Ecological Engineering
Field Drainage and Irrigation: Buried in farmland to drain accumulated water to prevent waterlogging, or maintain soil moisture during droughts and optimize irrigation efficiency.
Slope Greening and Ecological Restoration: Fix vegetation soil, filter rainwater, provide root growth space, and promote slope ecological restoration.
Other Fields
Mining Engineering: Used for mine pit drainage, tailings dam reinforcement, and prevention of disasters such as debris flows.
Aquaculture: Laid at the bottom of fish ponds to adjust the water level, filter silt, and improve the breeding environment.
Through the characteristics of "permeable to water but impermeable to air" and "blocking soil but not water", the permeable geotextile realizes functions such as drainage, filtration, isolation, and reinforcement, balances the relationship between soil and water in various projects, and improves the structural stability and durability.