Customizing 3D Vegetation Nets: How Specifications Impact Project Outcomes
In the realm of contemporary civil engineering and environmental restoration, 3D vegetation nets have emerged as a versatile answer for erosion control, slope stabilization, and inexperienced infrastructure development. Unlike standard flat nets, these 3-dimensional constructions supply a strong framework for vegetation increase whilst reinforcing soil integrity. However, their effectiveness hinges on ideal customization—specifically, tailoring 3D vegetation internet specs to in shape mission requirements. This article explores how key specs impact effects in purposes ranging from landslide prevention to city greening, highlighting the function of lay landslide safety vegetation internet techniques, inexperienced infrastructure vegetation internet designs, and optimized 3D vegetation internet specifications.
Understanding 3D Vegetation Net Basics: Beyond One-Size-Fits-All
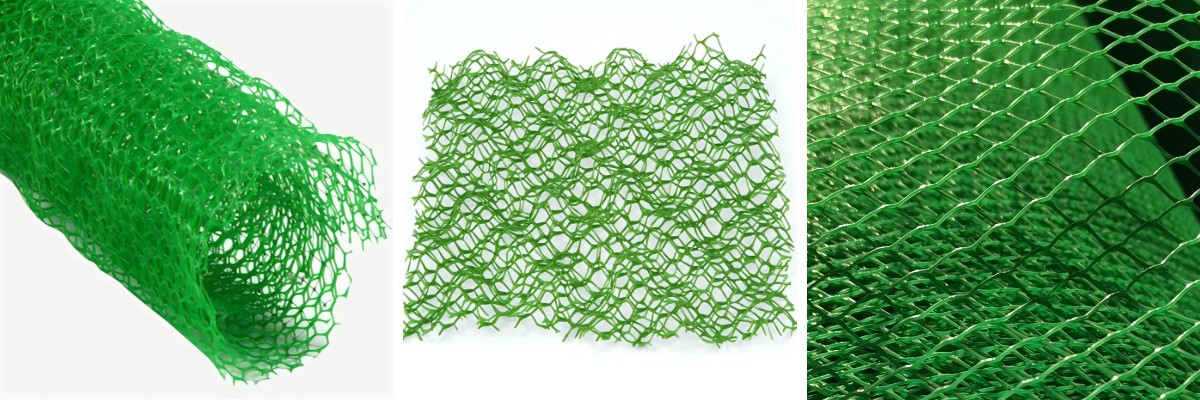
3D vegetation nets are engineered from substances like polypropylene, coir, or biodegradable polymers, proposing a raised, mesh-like shape that traps soil, retains moisture, and helps root growth. Their 3D diagram distinguishes them from flat nets by using growing micro-environments that speed up plant establishment. However, no single internet works for each and every project. 3D vegetation internet specifications—including thickness, mesh size, fabric type, and UV resistance—must align with web site conditions, climate, and venture goals.
For example, a steep slope susceptible to landslides needs a distinct internet specification than a rooftop backyard in an city inexperienced infrastructure project. Ignoring these nuances can lead to untimely degradation, terrible vegetation growth, or even assignment failure. Customization ensures the internet acts as each a bodily barrier and a organic catalyst, bridging engineering wants with ecological functionality.
Key 3D Vegetation Net Specifications and Their Project Impacts
1. Material Selection: Durability vs. Biodegradability
The preference of fabric is foundational to 3D vegetation internet performance. Polypropylene nets provide excessive tensile power and UV resistance, making them best for long-term tasks like lay landslide safety vegetation internet on dual carriageway embankments. Their lifespan of 5–10 years ensures steadiness till vegetation roots wholly anchor the soil.
In contrast, coir or biodegradable nets are desired for inexperienced infrastructure vegetation internet applications, such as rain gardens or riparian restoration. These substances ruin down naturally over 2–3 years, removing waste and permitting vegetation to take over as the fundamental stabilizer. For tasks in touchy ecosystems, biodegradable selections decrease environmental have an impact on whilst assembly non permanent stabilization needs.
2. Thickness and Density: Balancing Strength and Growth
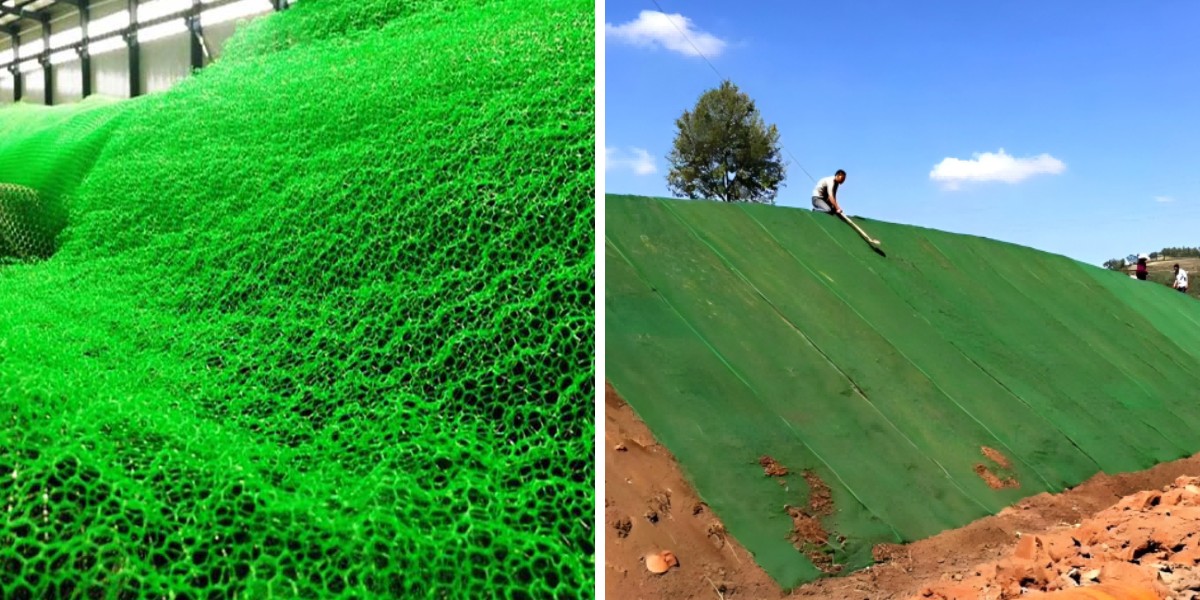
3D vegetation internet thickness (typically 10mm–50mm) and mesh density at once have an effect on soil retention and plant growth. Thicker nets with smaller mesh sizes (10mm x 10mm) excel in lay landslide safety vegetation internet on steep slopes (30°+). They entice greater soil particles, face up to erosion from heavy rainfall, and stop shallow slides by means of distributing weight evenly.
For inexperienced infrastructure initiatives like inexperienced roofs or vertical gardens, thinner nets (10mm–20mm) with large meshes (20mm x 20mm) are optimal. These permit roots to penetrate deeper into the developing medium whilst decreasing cloth weight—critical for structural load administration on buildings.
3. UV Resistance: Adapting to Climate Conditions
UV radiation can degrade artificial nets over time, specially in sunny regions. 3D vegetation internet specs should consist of UV stabilizers for tasks in arid or high-altitude areas. For example, a internet used in desolate tract slope stabilization need to stand up to 500+ hours of UV publicity except brittling.
In shaded environments, such as forested landslide zones, UV resistance is much less critical, permitting for price financial savings on non-stabilized materials. Mismatched UV specs can lead to internet breakdown earlier than vegetation matures, undoing stabilization efforts.
Application-Specific Customization: Case Studies
1. Landslide Protection: Precision in Slope Stabilization
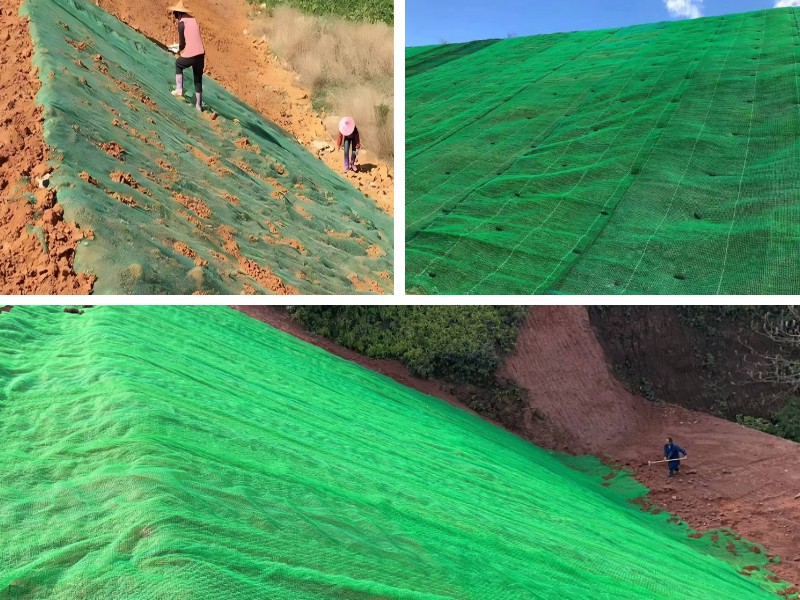
lay landslide safety vegetation internet requires meticulous specification tuning. On a 45° slope in a tropical area inclined to monsoons, engineers chosen a 30mm-thick polypropylene internet with a 15mm x 15mm mesh. The net’s excessive tensile electricity (20kN/m) resisted soil motion all through heavy rains, whilst its 3D shape retained seeds and compost. UV stabilizers ensured sturdiness in excessive sunlight, and the net’s porous graph allowed extra water drainage—preventing soil saturation, a frequent set off for landslides.
Within 12 months, vegetation insurance reached 80%, with roots interwoven via the internet to structure a bolstered soil matrix. This customization decreased landslide threat via 70% in contrast to conventional nets.
2. Green Infrastructure: Merging Function and Aesthetics
Urban inexperienced infrastructure depends on green infrastructure vegetation internet designs that stability performance with visible appeal. For a rooftop backyard in a town center, engineers selected a 15mm-thick coir internet with a 25mm x 25mm mesh. The biodegradable cloth aligned with the project’s sustainability goals, whilst the large mesh allowed numerous plant species (grasses, sedums) to thrive.
The net’s light-weight graph (150g/m²) minimized roof load, and its herbal brown coloration blended with vegetation. Over 18 months, the internet decomposed, leaving a self-sustaining ecosystem that decreased constructing cooling prices via 20%—demonstrating how tailor-made specs beautify each ecological and financial outcomes.
Common Pitfalls of Poorly Specified 3D Vegetation Nets
Choosing the incorrect 3D vegetation internet specs can lead to pricey failures:
Oversized Mesh in Erosion Zones: A internet with 50mm x 50mm mesh used on a sandy slope failed to entice soil, ensuing in 30% erosion inside six months.
Non-Biodegradable Nets in Wetlands: Polypropylene nets left in a wetland restoration task inhibited native plant growth, requiring costly removal.
Inadequate UV Resistance in Deserts: A popular internet except stabilizers degraded in 18 months, exposing a motorway slope to renewed landslide risk.
These examples underscore the significance of aligning specs with website conditions, climate, and challenge timelines.
Conclusion: Customization Drives Success in 3D Vegetation Net Projects
3D vegetation nets are effective tools, however their success relies upon on 3D vegetation internet specs tailor-made to challenge needs. Whether lay landslide safety vegetation internet on a rugged slope or integrating a inexperienced infrastructure vegetation internet into an city landscape, cloth type, thickness, mesh size, and UV resistance should be cautiously calibrated.
By prioritizing customization, engineers and venture managers make sure these nets supply long-term stability, guide wholesome vegetation growth, and align with environmental goals. In an generation the place sustainability and resilience are paramount, optimized 3D vegetation nets show that precision in specification leads to terrific assignment outcomes.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province