Geotextile Tube Maintenance: Best Practices to Extend Lifespan & Avoid Leaks
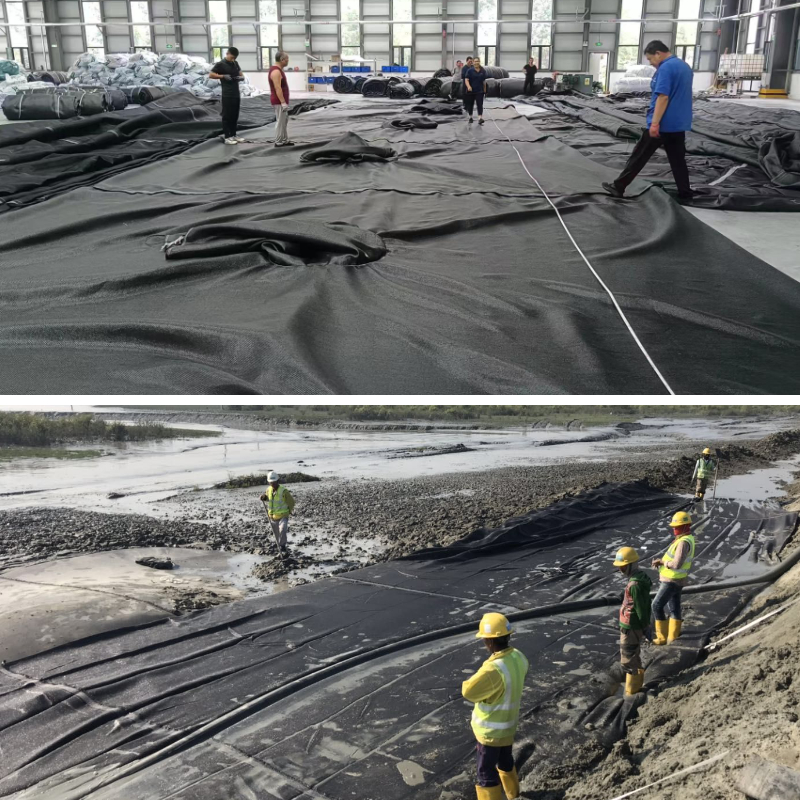
Geotextile tubes—commonly called Geotube or geotextile tube bags—are imperative for coastal protection, erosion control, and wastewater treatment. These durable, permeable material buildings (filled with sand, sediment, or sludge) stand up to harsh conditions, however their durability and leak-free overall performance rely totally on proactive maintenance. Neglecting renovation leads to material degradation, seam failures, or steeply-priced leaks that undermine task goals. Below are actionable renovation satisfactory practices for contractors and web page managers, overlaying inspections, cleaning, repairs, and seasonal care to hold your geotextile tube functioning optimally.
1. Conduct Routine Inspections: Catch Early Signs of Wear
Consistent inspections are the spine of geotextile tube maintenance, as they let you tackle small problems (frayed fabric, free seams) earlier than they improve into main problems. The frequency of tests relies upon on the site’s stress level: high-stress areas (coastal/marine zones) want inspections each 2–3 weeks—especially after storms or excessive tides—since saltwater, wave action, and particles pose regular dangers to geotextile tube bags. Low-stress web sites (wastewater lagoons) can be inspected monthly, as they face much less bodily put on however may additionally have chemical buildup (sludge residue) that degrades cloth over time. New geotextile tube installations (first 6 months) require biweekly exams to make sure filling stays even and seams continue to be invulnerable in the course of the settling phase.
During inspections, center of attention on key areas: cloth situation (look for fraying, punctures, or UV harm like brittleness—Geotube fabric is UV-treated, however extended solar publicity in tropical climates weakens it), seam integrity (check heat-welded, stitched, or glued seams for separation; even small gaps motive sediment leakage), filling uniformity (ensure the tube’s diameter is consistent—variations over 6 inches suggest uneven filling, growing stress points), and leak detection (watch for moist spots, sediment buildup, or pooling water round coastal Geotube structures, or sludge seepage in wastewater applications).
2. Keep Geotextile Tubes Clean: Prevent Fabric Degradation
Dirt, debris, chemical residue, or organic boom (algae, mold) degrades geotextile tube fabric over time, blockading permeability and weakening its structure. Regular cleansing preserves material integrity and ensures the tube works as intended. For coastal/marine Geotube structures, get rid of particles (driftwood, seaweed, plastic) weekly with a rake or handheld tool—avoid sharp objects that puncture geotextile tube bag fabric. Rinse the tube each and every 1–2 months with low-pressure water (garden hose or strain washer on the lowest setting) to get rid of salt crust, which dries out and stiffens fabric, main to cracks.
For wastewater/industrial geotextile tubes, after sludge dewatering, use a high-pressure water jet (compatible with the fabric—check producer guidelines) to clear leftover sludge from indoors and exterior pores; clogged pores decrease permeability and purpose odors. For mildew or algae boom (common in humid climates), easy the geotextile tube with a mild, biodegradable detergent—never use bleach or harsh chemicals, as they destroy down fabric. Always rinse utterly to eliminate cleaning soap residue. Critical tips: keep away from abrasive equipment (wire brushes) that scratch fabric, and have cleansing crews put on soft-soled footwear to forestall punctures on large geotextile tube bags.
3. Repair Damage Promptly: Stop Leaks Before They Worsen
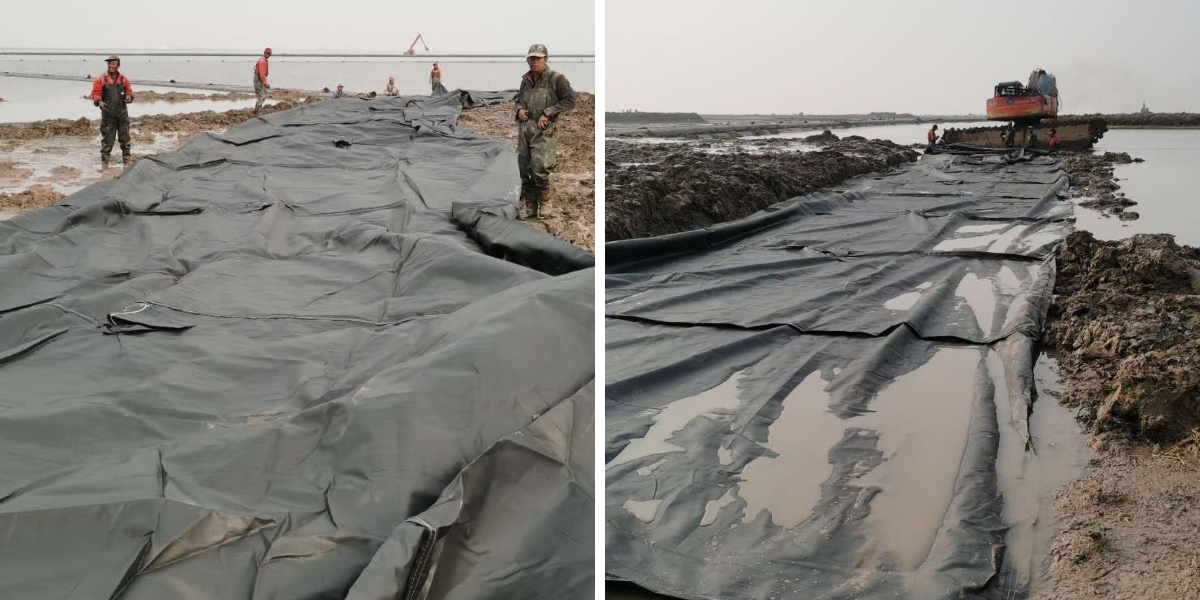
Even with inspections and cleaning, geotextile tube (including Geotube) can get broken via weather, debris, or impact. Quick repairs stop leaks and keep away from luxurious replacements. For small punctures or fraying (under 6 inches), begin by means of cleansing the place with water and slight detergent to eliminate dirt—debris stops restore materials from adhering. Cut a patch from extra geotextile tube fabric (matching weight and permeability) that’s 3–4 inches large than the damage, then practice geotextile-compatible adhesive (polyurethane-based) to the patch and broken area. Press firmly to clean air bubbles, and let therapy 24–48 hours earlier than exposing to water.
For seam separation, trim frayed threads to create a smooth edge—never pull free stitches, as this widens gaps. For heat-welded Geotube seams, use a warmth gun (set to manufacturer-recommended temperature) to re-seal the gap, preserving the gun 2–3 inches from material and rolling the seam whilst heat for a tight bond. For stitched seams, re-stitch with UV-resistant, heavy-duty thread (matching authentic weight) the use of a geotextile stitching computer or massive needle, and add a cloth patch over the seam for greater leak protection. For massive injury (over 6 inches) or structural sagging (from tremendous sediment loss), contact the producer or a professional—these problems require reducing out the broken area and changing it with new geotextile tube bag material, which wants specialized equipment to make certain perfect sealing.
4. Adjust Maintenance for Seasons: Protect Against Weather Extremes
Seasonal climate impacts geotextile tube performance, so tailor your hobbies to tackle precise risks. In summer time (hot, dry climates), inspect Geotube fabric for warmth damage—prolonged excessive temperatures can make plastic-based fabric brittle. Water the surrounding soil (for coastal tubes) to maintain cloth cool, and keep away from scheduling cleansing or repairs for the duration of noon heat. For UV protection, observe a manufacturer-approved UV spray to exposed geotextile tube sections annually.
Winter (cold, freezing zones) requires clearing snow and ice from geotextile tube bags promptly—heavy snow provides weight that traces seams, and freezing water expands in material pores, inflicting cracks. Use a soft-bristled broom to do away with snow; by no means use salt or de-icers, as they corrode fabric. For marine geotextile tubes in icy waters, test for ice abrasion alongside the tube’s base—install transient foam padding if needed.
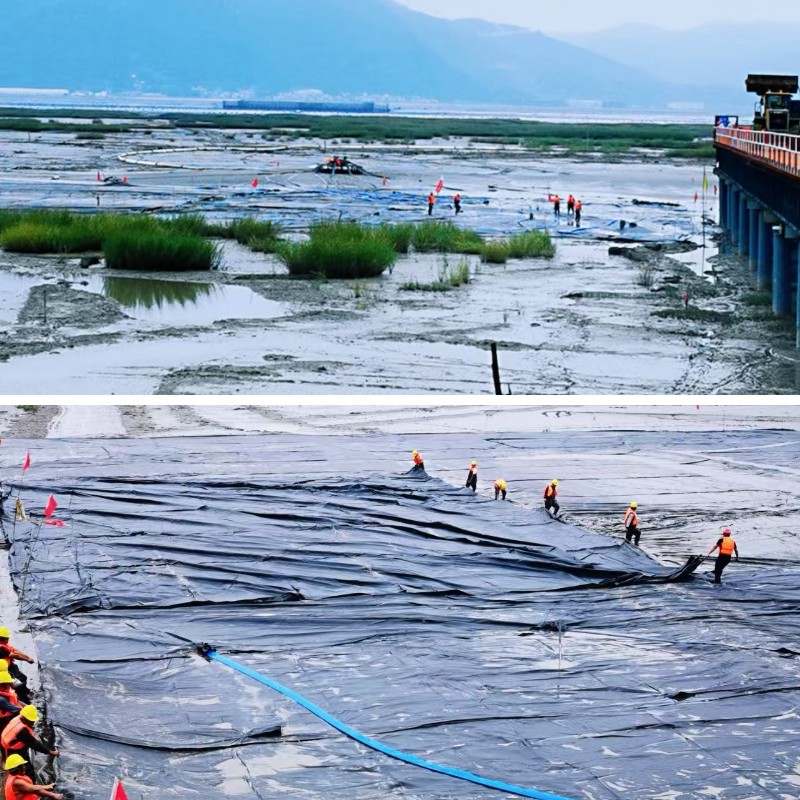
Spring (wet, windy weather) capacity post-storm inspections to take a look at for particles harm or shifted filling. Repair small tears immediately, and add greater anchors to Geotube structures in high-wind areas to forestall movement. For wastewater tubes, expand cleansing frequency to put off rain-driven particles that clogs pores.
Final Tips for Long-Term Geotextile Tube Success
Choose the right geotextile tube for your mission (e.g., heavy-duty Geotube for coastal use, specialized geotextile tube bags for wastewater) to limit preservation needs. Document all upkeep—log inspections, repairs, and cleansing schedules—to song lifespan and pick out ordinary problems (e.g., widely wide-spread seam injury in a high-wave zone). Train groups to handle geotextile tube fabric gently (avoid sharp tools, heavy equipment) and comply with producer pointers for cleansing and repairs.
By following these practices, you’ll lengthen your geotextile tube’s lifespan, hold leak-free performance, and maximize your investment—whether defending coastlines, stabilizing slopes, or treating wastewater, proactive renovation ensures your Geotube or geotextile tube bag delivers dependable consequences for years.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province