Safety Considerations When Working with Concrete Impregnated Fabric
Concrete impregnated fabric—including cement canvas and concrete impregnated canvas—has emerged as a game-changing cloth in construction, imparting flexibility, durability, and speedy set up for tasks ranging from erosion manipulate to transient structures. While this modern fabric streamlines workflows, it additionally introduces special security dangers that demand cautious attention. Neglecting protection protocols when handling, installing, or curing concrete impregnated material can lead to injuries, mission delays, or compromised structural integrity. This information outlines indispensable protection issues to guard workers, make sure compliance, and maximize the overall performance of concrete impregnated cloth systems.
Understanding the Hazards of Concrete Impregnated Fabric
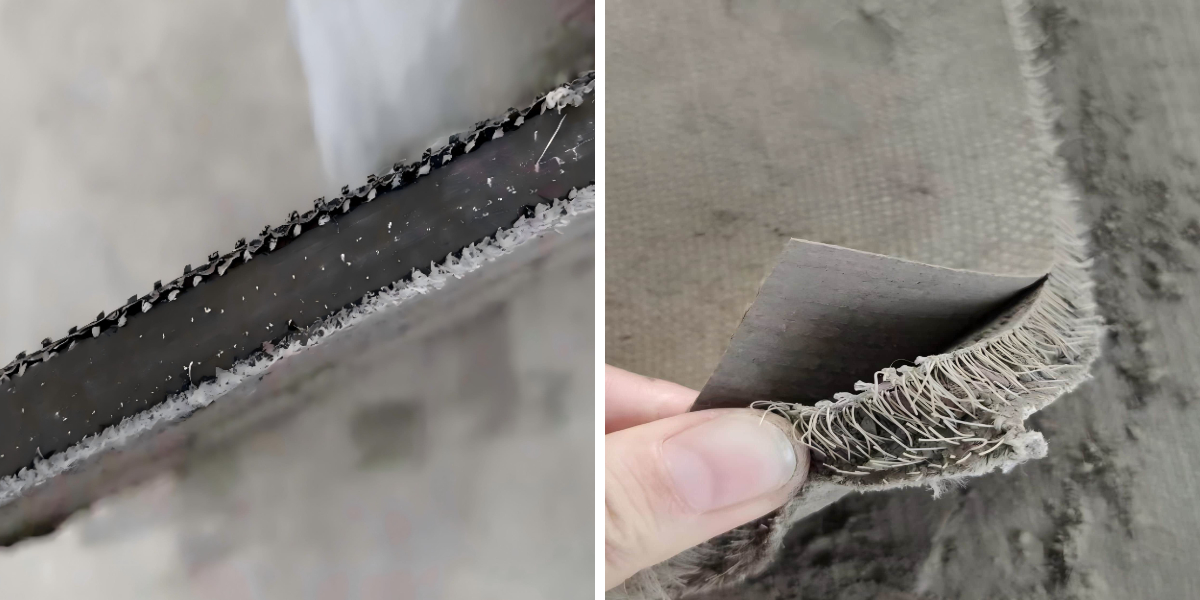
Before diving into protection practices, it’s indispensable to understand the dangers related with concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, and concrete impregnated canvas. The core thing of these substances is a cementitious mixture, which brings inherent hazards: uncured cement includes alkaline compounds that purpose chemical burns, whilst the material substrate (typically polyester or polypropylene) can create airborne fibers at some point of cutting. Additionally, moist concrete impregnated canvas is heavy and unwieldy, posing guide coping with risks, and curing concrete generates warmth that can lead to thermal burns or dehydration in enclosed spaces. Even minor oversights—like failing to put on shielding equipment when mixing cement for concrete impregnated fabric—can end result in long-term pores and skin injury or respiratory issues.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Concrete Impregnated Fabric Work
The first line of protection towards dangers is appropriate private protecting tools (PPE), and its significance can't be overstated when working with concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, or concrete impregnated canvas.
Essential PPE for All Stages
Hand Protection: Chemical-resistant gloves (neoprene or nitrile) forestall direct contact with uncured cement, which can purpose caustic burns or dermatitis. Avoid latex gloves, as they provide minimal safety towards alkaline substances. For reducing concrete impregnated fabric, add cut-resistant gloves to defend in opposition to sharp edges or stray fibers.
Eye and Face Protection: Safety goggles or a full face defend shields the eyes from cement dust, splashes, and flying cloth particles—critical when mixing cement for concrete impregnated canvas or trimming cloth to size.
Skin Protection: Long-sleeved shirts and full-length pants made of heavy, non-absorbent material (e.g., canvas) cowl exposed skin. Avoid cotton clothing, which soaks up moist cement and prolongs contact with the skin.
Respiratory Protection: When slicing or sanding dry concrete impregnated fabric, or mixing cement in poorly ventilated areas, use a particulate respirator (N95 or higher) to filter out airborne cement dirt and cloth fibers, which can irritate the lungs or reason long-term respiratory conditions.
Foot Protection: Steel-toed work boots with slip-resistant soles guard towards falling materials, sharp debris, and moist surfaces—especially when managing heavy rolls of cement canvas or working on uneven job sites.
PPE for Curing Stages
As concrete impregnated canvas cures, it releases warmness and moisture. In enclosed spaces, put on breathable, moisture-wicking underlayers to forestall overheating, and proceed the use of eye safety to keep away from infection from rising steam.
Safe Handling and Storage of Concrete Impregnated Fabric
Improper dealing with and storage of concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, or concrete impregnated canvas can compromise each protection and cloth performance.
Storage Best Practices
Concrete impregnated material and cement canvas ought to be saved in a dry, protected region to stop untimely hydration (contact with moisture that triggers curing). Keep rolls expanded on pallets to keep away from contact with damp floors, and seal any opened packaging tightly to block humidity. Label storage areas truely to keep away from unintended publicity to water, and make certain the area is well-ventilated to limit dirt buildup. Never stack heavy rolls of concrete impregnated canvas too high—instability can lead to falls and injuries.
Safe Handling Techniques
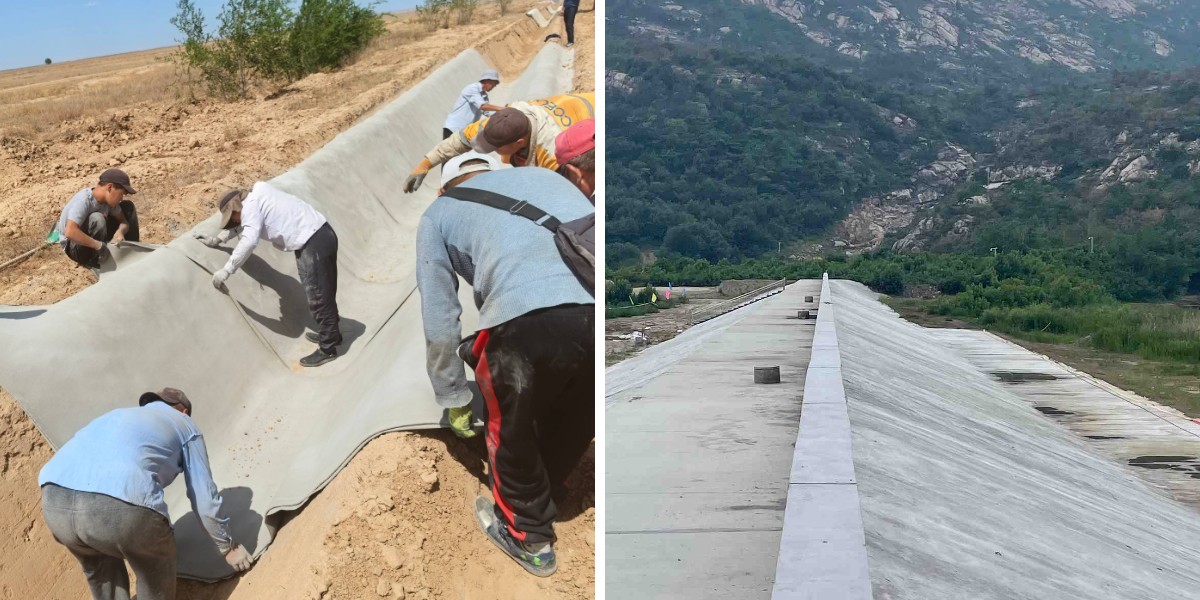
Manual Handling: Wet concrete impregnated cloth is substantially heavier than dry material, so constantly use crew lifting for massive rolls or panels. Bend at the knees, maintain the load shut to the body, and keep away from twisting while lifting to stop traces or returned injuries. For outsized projects, use mechanical aids (e.g., forklifts, hoists) with smooth slings to keep away from tearing the material or destructive the cement core.
Cutting and Shaping: When reducing concrete impregnated material to suit challenge dimensions, use sharp, purpose-built equipment (e.g., utility knives with retractable blades, electric powered shears) to reduce fraying and airborne fibers. Work in a well-ventilated area, and impervious the material to a secure floor to stop slipping for the duration of cutting. Never reduce dry concrete impregnated canvas close to open flames, as the cloth substrate is flammable.
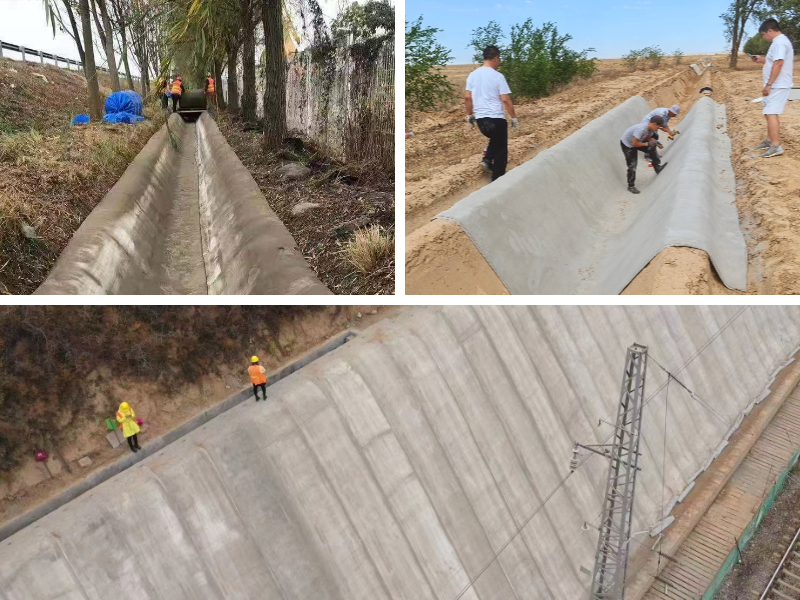
Safe Installation Practices for Concrete Impregnated Fabric
Installation is the high-risk stage for concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, and concrete impregnated canvas, as it entails wetting the material, shaping it, and making sure suited curing—all whilst navigating job website hazards.
Pre-Installation Site Prep
Before putting in concrete impregnated fabric, investigate the work vicinity for hazards: take away sharp rocks, debris, or protruding objects that ought to tear the fabric or reason trips. Mark underground utilities (e.g., pipes, wires) to keep away from unintended injury in the course of placement, and make certain the web site has steady footing for workers. For increased installations (e.g., conserving walls), set up impenetrable scaffolding or fall safety systems—never work from unstable surfaces like ladders for prolonged periods.
Wetting and Curing Safety
Concrete impregnated canvas prompts with water, and wetting ought to be finished cautiously to keep away from splashes or over-saturation. Use low-pressure hoses with spray nozzles to distribute water evenly, and stand upwind to decrease contact with cement-laden water. Avoid over-wetting, as this can weaken the last shape and create slippery surfaces.During curing, reveal temperature levels—concrete impregnated cloth generates warmth as it hardens, and in limited areas (e.g., tunnels, small enclosures), this can lead to warmness exhaustion. Provide sufficient ventilation, time table work all through cooler hours, and grant employees with lots of water to continue to be hydrated. Never stroll on uncured concrete impregnated canvas, as it can shift or collapse, and mark the vicinity with obstacles to stop unintended entry.
Post-Installation Safety
Once concrete impregnated cloth has cured, look at the location for free particles or sharp edges. Trim any frayed cloth with caution, and dispose of waste cloth (e.g., cutoffs, cement dust) in sealed containers to keep away from environmental infection or employee exposure.
Hazard Communication and Worker Training
Even the first-class security protocols fail except suitable coaching and communication. All people dealing with concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, or concrete impregnated canvas ought to get hold of complete education on:
Material dangers (alkaline burns, dirt inhalation, fireplace risks)
Proper PPE determination and use
Safe handling, cutting, and set up techniques
Emergency response (e.g., flushing skin/eyes after cement contact, administering first resource for burns)
Display protection records sheets (SDS) for concrete impregnated material and cement canvas in a seen place on the job site, and preserve pre-shift protection briefings to tackle site-specific dangers (e.g., climate conditions, constrained spaces). For new workers, pair them with skilled group contributors to fortify secure practices.
Emergency Response for Concrete Impregnated Fabric Incidents
Despite precautions, accidents can happen. Prepare for frequent incidents with clear response plans:
Chemical Burns: Flush affected pores and skin with clean, going for walks water for at least 15 minutes, putting off contaminated apparel if necessary. For eye exposure, preserve the eyelid open and flush with water for 20 minutes, then are looking for scientific interest immediately.
Respiratory Irritation: Move the employee to clean air, and if respiration is difficult, administer oxygen (if trained) and name for emergency help.
Heat Exhaustion/Stroke: Relocate the employee to a cool area, get rid of extra clothing, and grant cool water to drink. For extreme instances (confusion, loss of consciousness), name emergency offerings at once.
Slips/Falls: Secure the vicinity to forestall in addition injuries, verify the worker’s condition, and furnish first useful resource for fractures or lacerations.
Conclusion
Concrete impregnated fabric, cement canvas, and concrete impregnated canvas provide unmatched versatility in construction, however their secure use requires vigilance, applicable training, and adherence to protocols. By prioritizing PPE, protected handling, and hazard communication, you defend people from damage and make sure your task gives you the sturdiness and overall performance predicted from this progressive material. Remember: protection is now not an afterthought—it’s the basis of a profitable concrete impregnated material installation.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province