Understanding Concrete Impregnated Fabric Material Compositions: Fibers, Polymers, and Cement
Concrete impregnated cloth has revolutionized construction, repair, and emergency response through merging the electricity of concrete with the flexibility of textiles. But its great overall performance isn’t simply a product of combining two materials—it’s the end result of cautiously engineered compositions of fibers, polymers, and cement. Each aspect performs a indispensable position in defining the fabric’s durability, flexibility, and usability. This information dives deep into the fabric make-up of concrete impregnated fabric, exploring how fibers grant reinforcement, polymers beautify durability, and cement promises structural strength. We’ll additionally join these factors to real-world purposes of concrete fabric material and the historic evolution of cloth and concrete combinations. By perception these compositions, you’ll obtain perception into why this fabric outperforms common concrete in unique eventualities and how to pick out the proper variant for your project.
The Foundation: Fibers as the Reinforcement Backbone
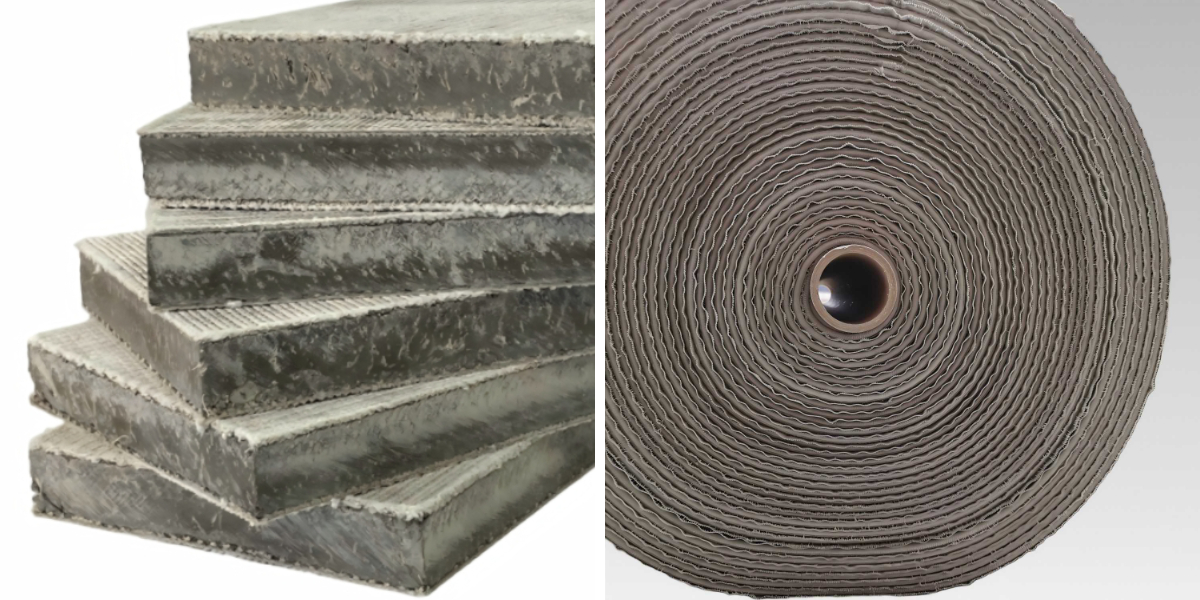
At the core of concrete impregnated material is a fibrous matrix that acts as each a service for the cement combine and a reinforcement layer. Unlike the brittle nature of simple concrete, fibers add tensile strength—enabling the cloth to face up to stretching and cracking. The kind of fiber used without delay affects the fabric’s flexibility, durability, and cost.
Common fiber substances encompass polypropylene, polyester, and on occasion glass fibers. Polypropylene is lightweight, resistant to moisture and chemical degradation, and affordable—making it a famous preference for general-purpose concrete fabric fabric. Polyester gives greater tensile power and UV resistance, making it perfect for outside or long-term purposes like slope stabilization. Glass fibers, even though much less common, supply fantastic electricity however require cautious managing to keep away from brittleness.
The fiber structure—whether woven, non-woven, or knitted—also matters. Woven fibers create a tight, uniform matrix that distributes stress evenly, whilst non-woven fibers structure a porous mat that traps cement particles extra effectively. This fibrous spine bridges the hole between the tension of cement and the adaptability of textiles, a key enchancment over early cloth and concrete experiments that relied on herbal fibers susceptible to rot.
The Binding Agent: Polymers for Durability and Flexibility
Polymers are the unsung heroes of concrete impregnated fabric, bettering the whole thing from workability to long-term performance. These artificial components are built-in into the cement combine or lined onto the fibers to tackle concrete’s inherent limitations—brittleness, sluggish curing, and susceptibility to environmental damage.
One quintessential function of polymers is enhancing adhesion between fibers and cement. Without polymers, the cement combine would possibly crack or separate from the fibers when the cloth is bent or stretched. Acrylic or styrene-butadiene polymers create a bendy bond, making sure the composite cloth acts as a single unit. Polymers additionally decrease water demand in the cement mix, rushing up curing time—a game-changer for emergency repairs the place speedy hardening is essential.
Additionally, polymers beautify sturdiness by using including resistance to UV radiation, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical exposure. For concrete fabric material used in coastal areas or industrial sites, polymer coatings guard in opposition to saltwater corrosion or harsh chemicals, extending the material’s lifespan some distance past what regular cloth and concrete ought to achieve.
The Structural Core: Cement for Strength and Rigidity
Cement is the issue that offers concrete impregnated cloth its structural strength. Typically, Portland cement (or modified variations like rapid-setting cement) is used, as it hardens rapidly when activated with water and types a dense, inflexible mass. The cement combine is cautiously formulated to stability power and workability—too a good deal cement can make the material brittle, whilst too little reduces structural integrity.
Rapid-setting cement is a frequent preference for concrete impregnated material due to the fact it permits the fabric to harden in hours alternatively than days. This is indispensable for purposes like emergency pipe repairs or catastrophe safe haven construction, the place downtime ought to be minimized. The cement is evenly dispensed inside the fibrous matrix, making sure that when activated, each section of the material hardens uniformly—creating a consistent, load-bearing structure.
Unlike normal concrete, which requires aggregates (sand, gravel) to attain full strength, concrete fabric cloth frequently makes use of a cement-only or light-weight combination mix. This continues the cloth bendy earlier than activation and reduces weight, making it less complicated to transport and install. The fibrous matrix replaces the function of aggregates in distributing stress, ensuing in a fabric that’s each sturdy and adaptable.
How Components Work Together: The Synergy of Concrete Impregnated Fabric
The magic of concrete impregnated material lies in the synergy between fibers, polymers, and cement. Fibers grant tensile energy and flexibility, polymers enhance adhesion and durability, and cement grants compressive power and rigidity. Together, they create a composite fabric that outperforms its man or woman parts.
For example, when concrete fabric cloth is draped over a curved floor (like a broken culvert), the fibrous matrix lets in it to conform to the structure besides tearing. When activated with water, the cement hardens, developing a inflexible shell—while the fibers stop cracking through absorbing tensile stress. Polymers make sure the cement and fibers stay bonded, even as the shape expands or contracts with temperature changes. This synergy is a large development over early cloth and concrete combinations, which regularly failed due to negative adhesion and fiber degradation.
Tailoring Compositions for Specific Applications
Not all concrete impregnated material is the same—manufacturers tailor the composition to suit unique challenge needs. Here’s how elements are adjusted for frequent applications:
Emergency Repairs
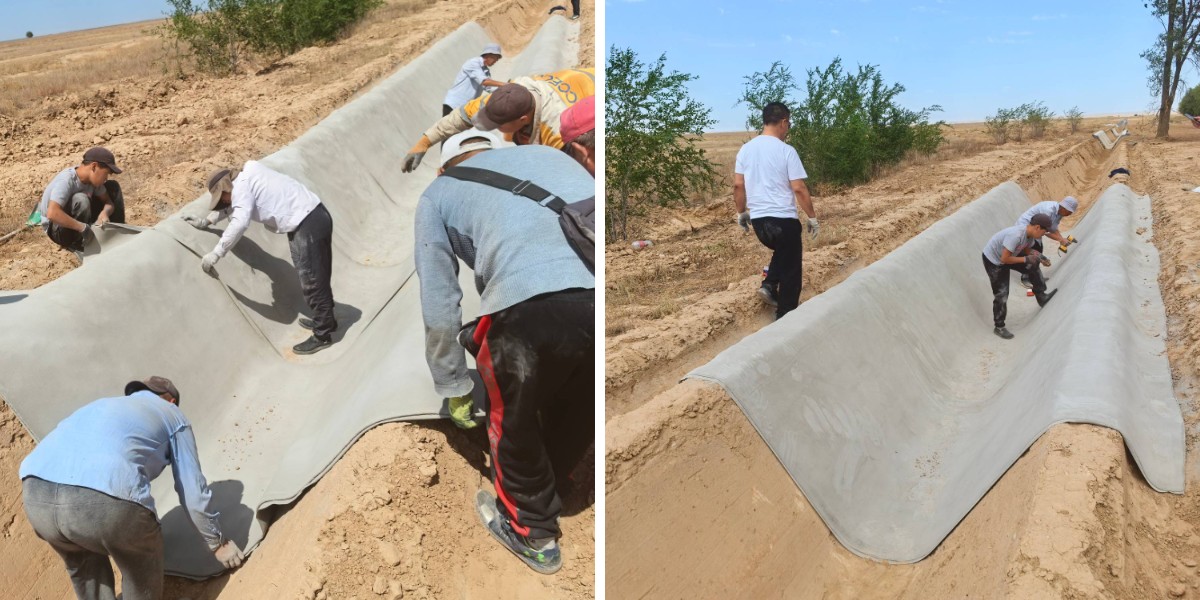
For speedy fixes (e.g., potholes, pipe leaks), concrete material material makes use of rapid-setting cement and polypropylene fibers. The polymer combine is optimized for quick curing, permitting the restore to be done in hours. The light-weight composition makes it convenient for employees to lift and deploy barring heavy equipment.
Outdoor Slope Stabilization
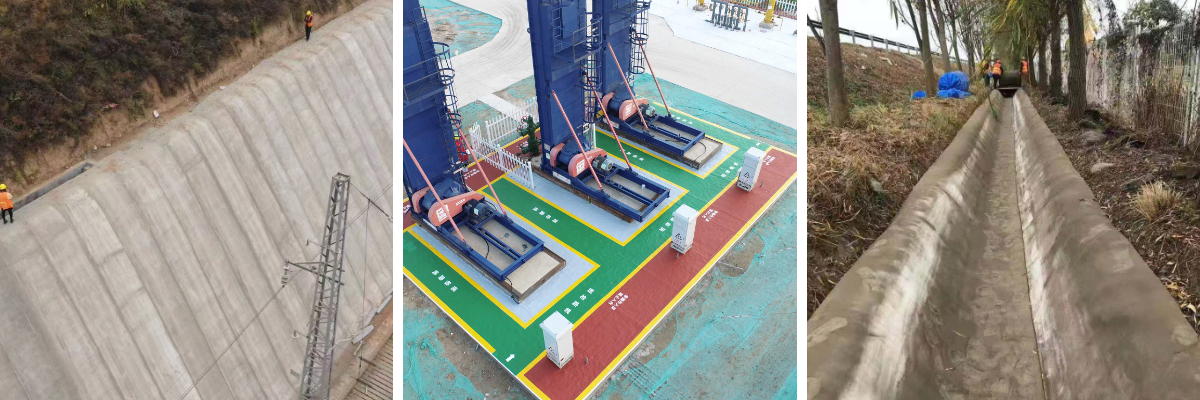
Slope stabilization requires UV resistance and long-term durability. These fabric use polyester fibers, UV-stabilized polymers, and slow-setting cement (to enable time for installation). The fibrous matrix is woven tightly to lure soil and vegetation, growing a stable, erosion-resistant surface.
Industrial Chemical Containment
For chemical tanks or industrial drainage ditches, concrete impregnated cloth elements chemical-resistant polymers (like epoxy) and glass fibers. The cement combine is modified to withstand acids and alkalis, making sure the material doesn’t degrade when uncovered to harsh substances.
From cloth and concrete to Modern Marvel: The Evolution of Composition
The trip from cloth and concrete to today’s concrete impregnated material is a story of fabric innovation. Early 19th-century experiments used herbal canvas and simple cement, however the aggregate was once inclined to rot, cracking, and negative adhesion. The shift to artificial fibers (polypropylene, polyester) solved the rot problem, whilst polymers addressed adhesion and durability. Modern cement formulations, which includes rapid-setting and chemical-resistant variants, accelerated the material’s applications.
This evolution wasn’t simply about replacing materials—it used to be about grasp how every issue contributes to performance. By optimizing the stability of fibers, polymers, and cement, producers created a cloth that retains the first-class houses of concrete and textiles, filling a hole in development that usual techniques couldn’t.
Conclusion: Composition Defines Performance
The overall performance of concrete impregnated material is immediately tied to its fabric composition. Fibers grant the reinforcement wished for flexibility, polymers beautify sturdiness and adhesion, and cement offers the structural electricity that makes it a attainable choice to normal concrete. Whether you’re the use of concrete material cloth for an emergency restore or a long-term development project, grasp these aspects helps you choose the proper product for the job.
From the early days of cloth and concrete to today’s superior composites, the center of attention on fabric science has modified this science into a versatile, dependable solution. As producers proceed to refine compositions—incorporating recycled fibers or eco-friendly polymers—concrete impregnated cloth will solely come to be greater sustainable and effective, solidifying its region in the future of construction.
Contact Us
Company Name: Shandong Chuangwei New Materials Co., LTD
Contact Person :Jaden Sylvan
Contact Number :+86 19305485668
WhatsApp:+86 19305485668
Enterprise Email: cggeosynthetics@gmail.com
Enterprise Address: Entrepreneurship Park, Dayue District, Tai 'an City,
Shandong Province